Frequency is far more important in endurance training. If you are training for a marathon taking even 3 days off without running will set you back in your training. Typically this kind of training consists of shorter distances during the week and one long distance at the weekend. Due to the high frequency of training younger people with more muscle mass are more susceptible to injury. These injuries are typically to tendons and muscles. Older people with less muscle mass won’t have the same load on muscles and joints. Another note: road running does not course arthritis; you would need to be training at super marathon distances to cause any degenerative changes.
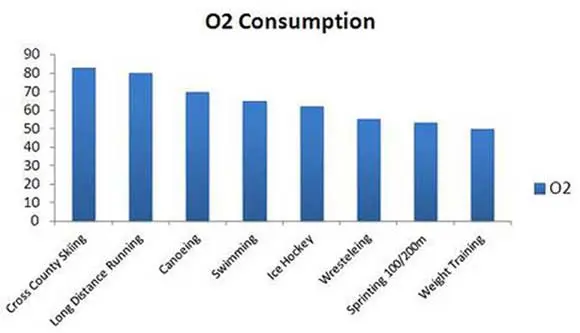
Overview of sports with the highest O2 demand:
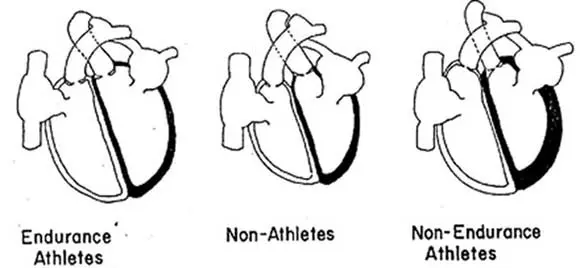
Cardiovascular Changes:
You use oxygen to make more efficient energy:
When we exercise we use oxygen to make energy more efficiently. Without oxygen, the body is very inefficient at creating energy over long periods. Endurance training improves our bodies’ ability to get oxygen from our lungs, through our cardiovascular systems and into our muscles.
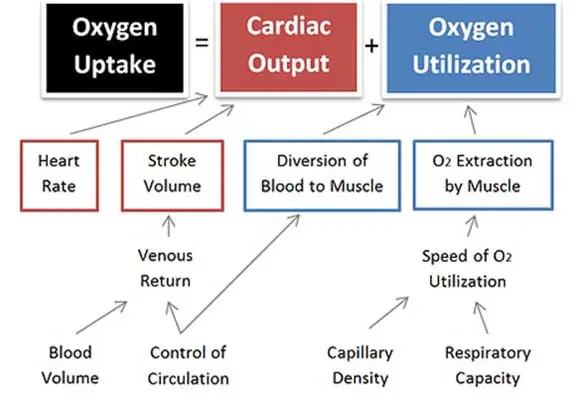
Oxygen Uptake = cardiovascular performance
Cardiac Output = the hearts efficiency/performance
Oxygen Utilization = efficient use of O2 by muscles
Oxygen Uptake
An increase in Cardiac Output and/or and improvement in Oxygen Utilization will result in improved Oxygen Uptake and improved performance. While the uptake of oxygen is the term people would mostly associate with the cardiovascular system it is, in fact, the removal of carbon dioxide that is probably more important.
Your heart changes shape:
Changes in your heart include an increase in size/volume of your left atrium. This allows your heart to pump blood around your body more efficiently. There is a reduction in resting heart rate and an increase in the force of the pump and the amount of blood your heart can pump per beat along with reduced blood pressure.
Fun fact:
Interestingly some of the top guys who write on rice do a lot of endurance training. They may swim for up to 6 hours a day. As a result, their resting heart rate is very low. This allows them to have a very steady hand. They will listen to their heartbeat and make incisions in between beats when their body is at its most calm.
Endurance and Cycling
Epo is the drug that has been brought to the world’s attention via the “Tour de France”. Epo is a drug that tells basically tells your body to produce more red blood cells. These red blood cells are what carry oxygen and carbon dioxide around your body. The more you have the more effective the system. This can also be done via high altitude training. In this case your body is in an oxygen-deprived environment, therefore, is produces more red blood cells to compensate. Benefits can last for up to 4 months as that’s a red blood cells lifespan.
Smoking:
Lung performance is a huge part of this equation. Smoking is definitely to be avoided if you want to maximize Oxygen Uptake.
How to measure endurance:
Cardiovascular performance is typically measured by VO2 max. You are connected to a breathing apparatus and put on a treadmill. Then you run until you collapse and find out what your VO2 max is.
Note:
One thing that is important to note is that your lungs don’t get any bigger and the oxygen transport to and from your lungs don’t change. They are genetically controlled. What does change is your ability to inflate and deflate your lungs? This comes with muscular adaptations in your inhalation and exhalation muscle.
Musculoskeletal changes
Your muscles also go through a number of adaptations to improve the utilization of the oxygen and removal of carbon dioxide.
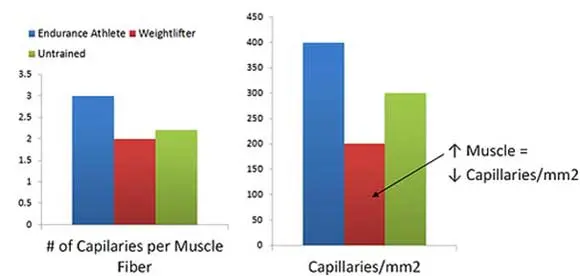
Increased capillaries supply:
Capillaries are the tiny blood vessels that deliver O2 and remove CO2 to/from your muscles. If you have more capillaries you can deliver O2 and remove CO2 more efficiently. This is done via hormonal release and also mechanical pressure.
It’s like delivering a parcel, if there is a road directly to the house it’s easy, but if the house is in the middle of a field it’s not so easy.
Oxidative capacity/Mitochondrial changes: Mitochondria are the power plants of your muscles. They convert anaerobic energy into aerobic energy which is 15 times more efficient. It uses O2 along with fat and carbs in this process. The larger and the more mitochondria you have the more energy you can convert. Also with training the mitochondria move closer to capillaries where they can pick up the O2 faster thus making the process more efficient.
Glycogen stores increase:
Glycogen- fancy name for Carbs
Glycogen is stored in both the liver and muscles. With endurance training, there will be an increase in glycogen (and fat) storage in muscles. Carb cycling is something that endurance athletes, such as marathon runners, do to increase their glycogen stores and thus energy. The majority of energy used during an endurance event is carbs, this is why an endurance athlete has a high carb diet. Marathon runners will typically have a carb supplement (gel) every 40 mins of a race/training. This is because the free glycogen in their blood will be depleted and they need to replenish it for more energy.
Fat Utilization:
Endurance training switches the body from burning carbs to burning fats more often and sooner. This is a metabolic change. It is far more efficient over longer period as we have far more fat energy stored in our body. Coffee also has the same effect which is why it is a number one for increasing endurance. The moral of the story here is the sooner you can switch to burning fat the more carbs you will spare and the longer you will be able to run. The switch between the two is commonly known as “the wall”.
Blood Glucose = carbs in blood
Blood FFA = fat in blood
Glycogen = carb stores in liver and muscles
Triglycerides = fat stores in adipose (fat) tissue
Fiber Type Changes:
Your fiber type expressions will migrate closer to Type 1 muscle fibers over time. This is a main reason what a powerlifter would find it extremely difficult to become an ironman or vice versa.
Hypertrophy of Type I muscle fibers.
Type I or slow oxidative muscle fibers are small and slow but have a huge amount of endurance. You most likely won’t notice the increase which typically maxes out at 2 months.
Take home message.
• Endurance training is all about frequency. The effects of a single session are minimal but the accumulation of training hours results in adaptation.
• Taking a week off is not recommended as it will significantly set you back if you’re preparing for an event.
• Adaptations take place in both your cardiovascular system and musculoskeletal system.
• Type I fiber hypertrophy will not yield any major muscle bulk as these are small fibers. This hypertrophy will max out at about 2 months.
• Other musculoskeletal and cardiovascular adaptations will continue to improve over years of training.
• Cessation of training results in significant loss of gains.
Tip: If you're signed in to Google, tap Follow.