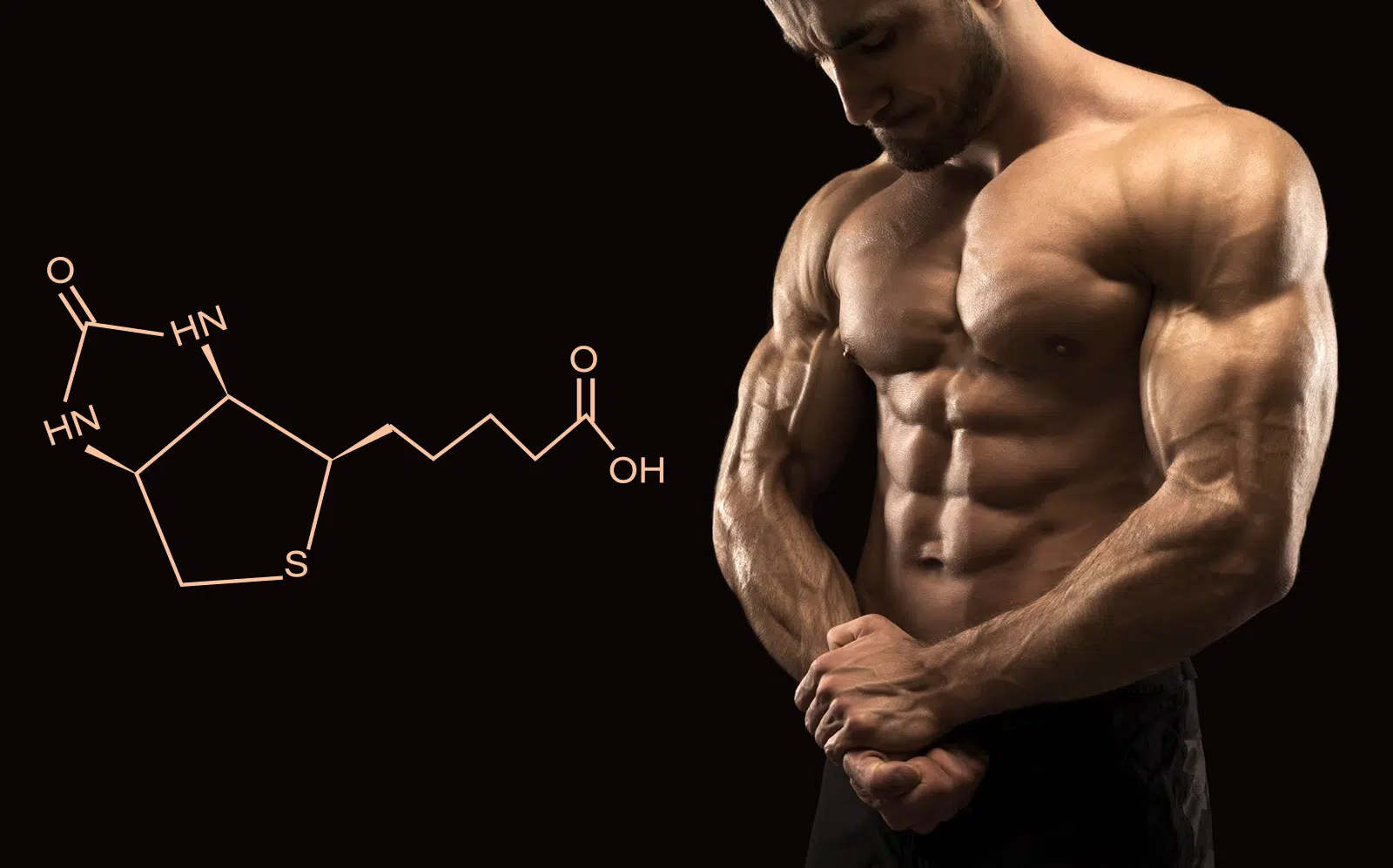
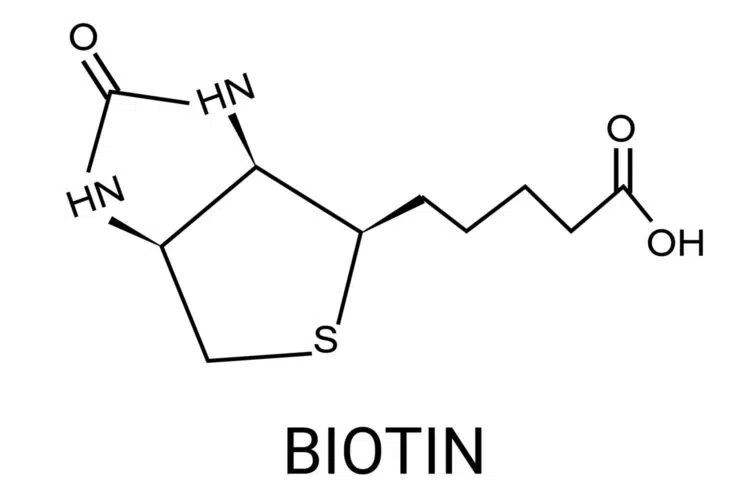
Sticking to basic diet, training, and recovery principles can help kickstart your transformation journey. However, if you want to hit all your fitness and performance goals, you must get all the minute details right.
For instance, most bodybuilding enthusiasts know they must meet their daily macronutrient (proteins, carbs, and fats) goals and follow a structured training program to build muscle and strength. But ask them about the importance of micronutrients and how they are prioritizing them, and they look like a deer caught in headlights.
While some vitamins, such as vitamins C, D, B12, and K, have gained popularity in recent years, several other crucial vitamins are still flying under the radar that could be holding back your fitness progress.
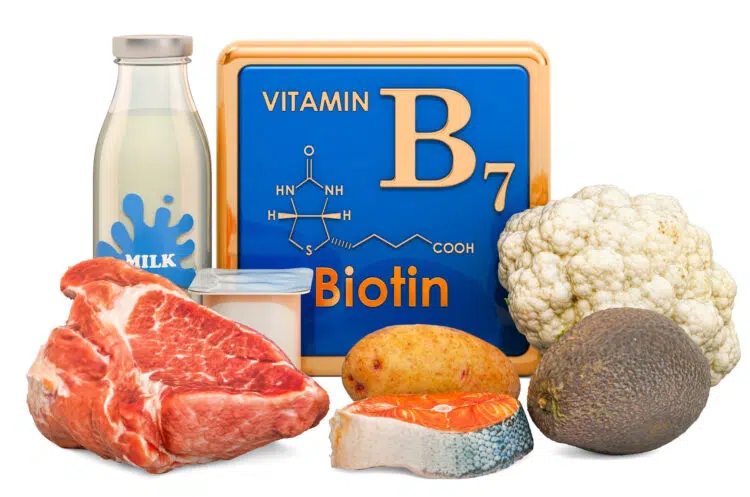
In this article, I want to draw your attention to biotin (vitamin B7), including its uses, benefits, deficiency symptoms, and how it can improve your overall progress.
Biotin and Metabolism: Fueling Your Workouts
Biotin, also known as vitamin B7 or H, is essential for breaking down the food you consume into energy to be used throughout the day. It helps break down carbs into glucose to be used as fuel by the body. It uses fats and protein to ensure optimal raw material availability for muscle building and maintaining overall health and well-being.
A scientific review published in the Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease concluded that biotin deficiency can lead to impaired energy metabolism and potential implications for muscle growth and fat loss due to its impact on macronutrient synthesis. (1)
Biotin and Exercise Performance
Let’s now get to the fun stuff and discuss how this vitamin can boost training performance:
Higher Energy Levels
Eating an adequate amount of biotin ensures your body efficiently converts food into energy, giving you the stamina to push harder in the gym. It can be a game-changer whether you are a bodybuilder, powerlifter, Olympic weightlifter, or a hobbyist exerciser.
Not eating enough biotin can negatively affect your work capacity, making it challenging to sustain moderate-intensity workouts.
Reduced Fatigue
An early onset of fatigue can hamper your training performance and results. Biotin can help support energy production and ensure you have enough gas in the tank to last through a grueling workout.
People who are consistently dealing with sluggishness and fatigue should monitor their biotin intake as it could be a contributing factor.
Improved Recovery
A high-volume workout can deplete your energy levels and increase the occurrence of delayed-onset muscle soreness (DOMS). Eating enough protein refills the glycogen stores, potentially speeding up recovery and limiting muscle soreness.
Biotin and Fat Loss: Shedding Unwanted Pounds
I am not a fan of fat-burning supplements, as they are usually a ‘quick fix.’ Most people regain the lost weight shortly after stopping using the supp. Biotin, on the other hand, is a holistic compound that improves overall health and well-being.
Vitamin B7 helps convert the food you eat, especially carbs and dietary fats, into energy. This metabolic boost can help optimize fat loss by prioritizing burning stored body fat as fuel instead of storing excess calories as fat.
Furthermore, biotin can help activate enzymes involved in fatty acid breakdown. These enzymes break down fat molecules into smaller units, releasing energy that your body can use for daily functioning. If this isn’t a cheat code for fat loss, what is?
Biotin and Blood Sugar Control
Stable blood sugar levels are vital for weight management and optimal overall health. A recent systematic review and meta-analysis showed that biotin can reduce fasting blood glucose, total cholesterol, and triglyceride levels in individuals with type 2 diabetes. (2)
It does so by boosting insulin production, a hormone responsible for transporting glucose from your bloodstream into your cells for energy.
Not sure how it works? Here is a quick explainer:
Your body releases insulin to bring blood sugar levels back down after a meal. But, chronically high blood sugar and insulin levels can result in insulin resistance, which can make your body store excess glucose as fat.
Biotin can help prevent these spikes and promote a healthier metabolic environment.
Biotin and Muscle Growth: Building a Stronger You
Lifting weights breaks muscle tissues. Your muscles grow back bigger and stronger while you are resting. However, you must ensure optimal nutrient intake to maximize muscle protein synthesis and growth.
Biotin can boost this progress as it activates the enzymes crucial for protein synthesis. It can also lower the discomfort associated with DOMS and promote faster recovery. By doing this, biotin helps your body bounce back quicker, lowering recovery times.
Biotin plays a key role in cellular energy metabolism, including adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production (3). For the uninitiated, biotin is the body’s primary source of energy during short, intense activities, and it’s the only fuel for muscle contraction.
Biotin can help replenish ATP levels between sets, allowing you to push yourself to the limit in each set.
If you’re wondering, supplemental creatine also plays a key role in muscle energy metabolism. It does so by helping to resynthesize adenosine triphosphate (ATP) from adenosine diphosphate (ADP). This helps improve exercise performance and recovery and boost muscle strength and lean mass (4). Balancing your biotin and creatine intake can help you unlock maximum gains.
The often recommended daily intake of biotin is between 30 and 100 micrograms (mcg) for adolescents and adults. Also, biotin is a water-soluble compound. Any extra biotin that you consume will simply pass through urine.
Biotin Supplements and Muscle Growth
Before you add a biotin supplement to your stack, you should understand that biotin is not a magic pill that will help you transform your body overnight. While it can improve metabolism, speed up recovery, and help burn more fat, it cannot replace a goal-oriented diet with balanced macronutrients.
Also, there is no direct scientific evidence to prove that standalone biotin supplements can enhance muscle growth and recovery. You must think of biotin as a catalyst and not the main ingredient in your diet.
While most people can handle biotin supplements, some might experience mild side effects like nausea and digestive discomfort. Discontinue the supplements if you face similar issues and consult your health care provider for alternatives.
Biotin-Rich Foods: Powering Your Fitness with Nutrition
Unlike most other vitamins, biotin is present in several foods. Include the following foods into your daily diet to prevent vitamin H deficiency:
Animal Sources:
The following animal-based food sources contain a healthy amount of biotin:
- Egg Yolks
- Organ Meats
- Salmon
- Beef
- Chicken
- Pork
- Milk
- Cheese
- Yogurt
- Butter

Plant-Based Sources:
Biotin is abundant in several vegan sources, including:
- Nuts and Seeds
- Sweet Potatoes
- Brocolli
- Avocados
- Banana
- Sunflower seeds
- Nuts (almonds, walnuts, etc.)
- Sweet potato
- Mushroom
- Legumes (beans and lentils)
Diet Tips For Eating Biotin-Rich Foods
Use the following tips to ensure compliance and best results:
Variety is Key
Redundancy is among the biggest reasons why most people give up their diets before reaching their fitness objectives. I have listed 20 food sources in the section above. You should mix up your diet to keep your diet exciting and ensure you’re getting a wide range of nutrients.
Meal Prep
Hunting for food when you are starving increases the probability that you will opt for highly processed foods that will throw you off your diet. Instead, you should prep your meals in advance. This will ensure you always have something to eat throughout the day and avoid poor dietary choices.
I highly recommend using a calorie-counting app like MyFitnessPal to plan your meals. Apps like these allow you to monitor your micronutrient intake along with the macronutrients. This will ensure you consume your daily recommended amount of biotin.
Snack on Biotin
One of the best things about biotin is that it isn’t too difficult to consume an adequate amount daily since most healthy foods contain it. I always keep biotin-rich snacks like nuts and seeds at hand to curb my cravings or keep me entertained when I’m bored. You should consider doing the same.
Understanding Biotin: The Basics
Sports nutrition companies have done an excellent job of educating people about the importance of some vitamins via TV commercials. Vitamin D helps build strong bones, vitamin C is for a robust immune system, and vitamin K is essential for blood clotting. However, there are 13 essential vitamins that the human body needs to function properly.
Biotin is a B complex vitamin found in foods like eggs, milk, and bananas and helps convert food into energy. Its deficiency can cause symptoms like thinning of the hair and a rash on the face. Biotin is especially important for fitness enthusiasts as it plays a crucial role in breaking down macros like fats, carbohydrates, and proteins, ensuring optimal bioavailability. (5)
Biotin acts as a coenzyme, meaning it teams up with other enzymes to ensure they function optimally. This forgotten vitamin not only boosts metabolism but also helps maximize muscle building and fat loss.
Biotin can also help improve your skin, hair, and eye health. A biotin deficiency is more common than most people think and is the reason behind chronic fatigue and a lack of muscle tissue growth and fat loss progress.
Conclusion
Biotin is often overshadowed by its flashier vitamin counterparts. However, you shouldn’t make the mistake of overlooking it.
Biotin helps boost the metabolism and ensures your body is converting food into energy optimally. So, whether you’re aiming to build muscle or shed excess body fat, you must be conscious about your biotin intake.
But remember, body transformation is a marathon and not a sprint. It requires dedication, consistency, and patience to get the best results.
If you have any questions about biotin, post them in the comments section below, and I’ll be happy to help!
References:
- Pacheco-Alvarez, D., Solórzano-Vargas, R. S., & Del Río, A. L. (2002). Biotin in metabolism and its relationship to human disease. Archives of medical research, 33(5), 439–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0188-4409(02)00399-5
- Saleem F, Soos MP. Biotin Deficiency. [Updated 2023 Feb 20]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547751/
- León-Del-Río A. (2019). Biotin in metabolism, gene expression, and human disease. Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease, 42(4), 647–654. https://doi.org/10.1002/jimd.12073
- Persky, A. M., & Rawson, E. S. (2007). Safety of creatine supplementation. Sub-cellular biochemistry, 46, 275–289. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-6486-9_14
- Muthuraman N, Vijayselvi R, Sudhakar P Y, Christudoss P, Abraham P. Assessment of serum biotin levels and its association with blood glucose in gestational diabetes mellitus. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol X. 2023;17:100181. Published 2023 Feb 17. doi:10.1016/j.eurox.2023.100181
Tip: If you're signed in to Google, tap Follow.