Fasting has been an age-old practice across several cultures. While some may observe fasting for religious purposes, others practice it for weight loss and its associated benefits.
Regardless of the purpose, fasting has a range of health benefits. One such advantage that many swear by is its positive impact on inflammation.
Inflammation, especially the chronic form, can hamper the body’s functioning, which in turn could have a rippling effect on your health.
Calculate Your 5:2 Fast Day Calories
Get your personalized calorie targets for fast days and normal days on the 5:2 intermittent fasting diet.
Calculate My 5:2 Plan →Having been a health practitioner for almost a decade, I have had many people ask me about minimizing inflammation through fasting.
Fasting has anti-inflammatory benefits, but we must optimize them with proper fasting techniques. In this article, I will explain the association between fasting and inflammation and how to minimize it in your body.
Whether you are on a weight loss journey or want to try fasting to deal with inflammation, this guide has something for you.
What is Fasting?
Before diving into the impact of fasting, let’s understand what fasting means and how it can impact your body.
Fasting involves abstaining from food for a certain period.
Fasting can be done in different forms. There are various kinds of fasting, ranging from completely abstaining from food for a set period to consuming only low-calorie liquids during the fasting window.
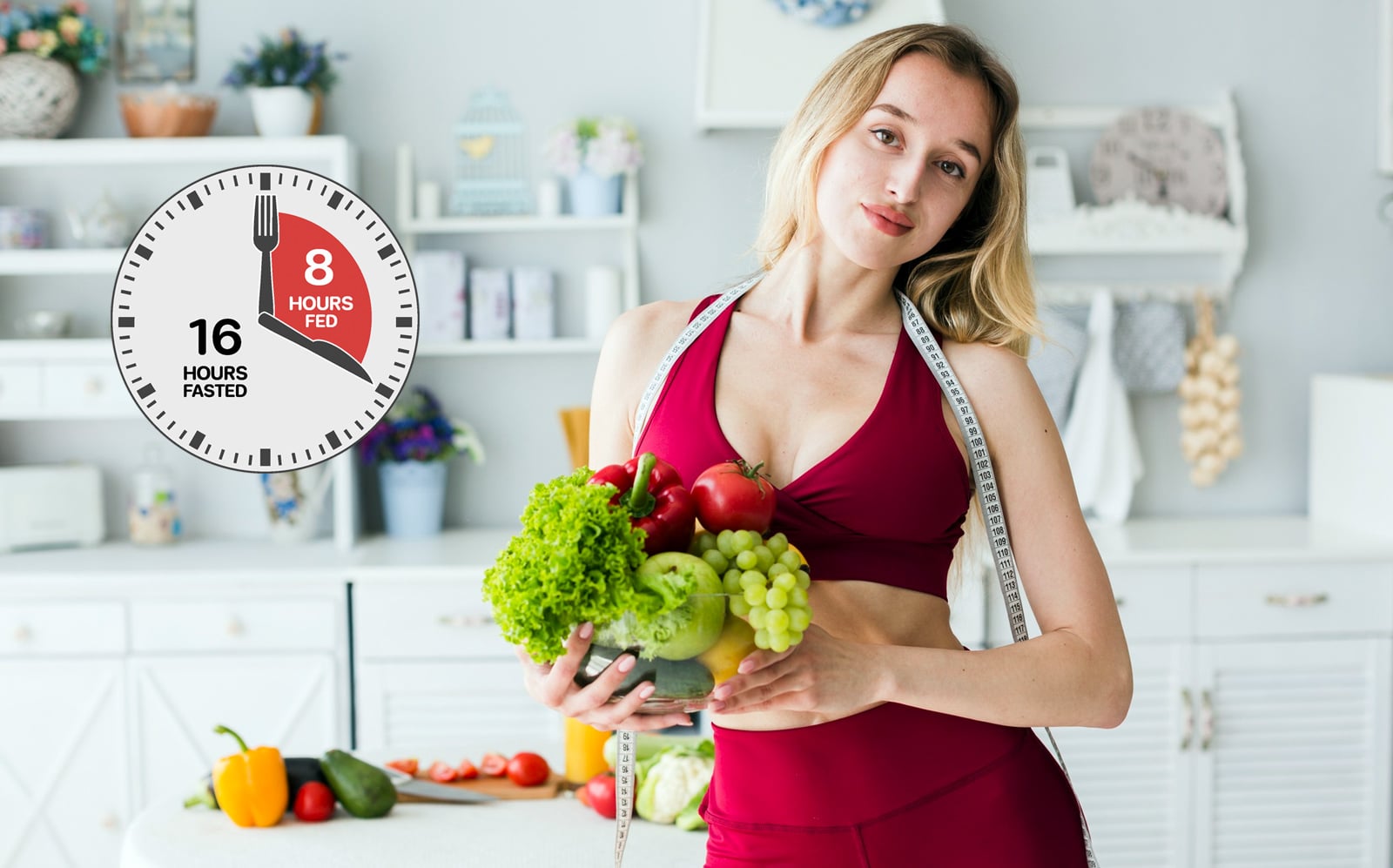
While there are several fasting regimens, intermittent fasting (IF) has caught the attention of thousands of health enthusiasts around the globe. It has emerged as one of the most popular types of diet due to its flexible approach and lack of prescribed diets.
Intermittent fasting involves alternating between periods of voluntary fasting and eating. You could choose between daily time-restricted fasting or weekly intermittent fasting based on your lifestyle and preferences. Some popular IF plans include 16:8, 12:12, Alternate Day Fasting, and 5:2.
Research shows intermittent fasting can boost overall health and help prevent various health issues like inflammation. (1)
Let’s first learn more about inflammation and how it affects our body through fasting mechanisms.
What is Inflammation?
Research indicates that inflammation occurs as a result of your body’s defensive response to an irritant or harmful stimuli. Through this process, the body’s immune system identifies threats from foreign elements and tries to eliminate them by triggering the healing process. (2)
Inflammation can be either chronic or acute. While chronic inflammation is long-term, acute inflammation can begin rapidly and turn severe in a shorter period.
Causes of Inflammation
Well, as inflammation is a physiological response that naturally occurs as an effort to heal the body, you cannot consider inflammation as completely bad. However, red flags or symptoms associated with inflammation should be immediately addressed. Here’s why.
Persisting inflammation can cause chronic health conditions. Inflammation has been associated with several lifestyle diseases, such as metabolic syndrome, heart diseases, obesity, type 2 diabetes, many neurodegenerative disorders, and certain cancers.
Common causes of inflammation:
- Germs/pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, or fungi
- Exposure to chemicals or high radiation
- External injuries to the body
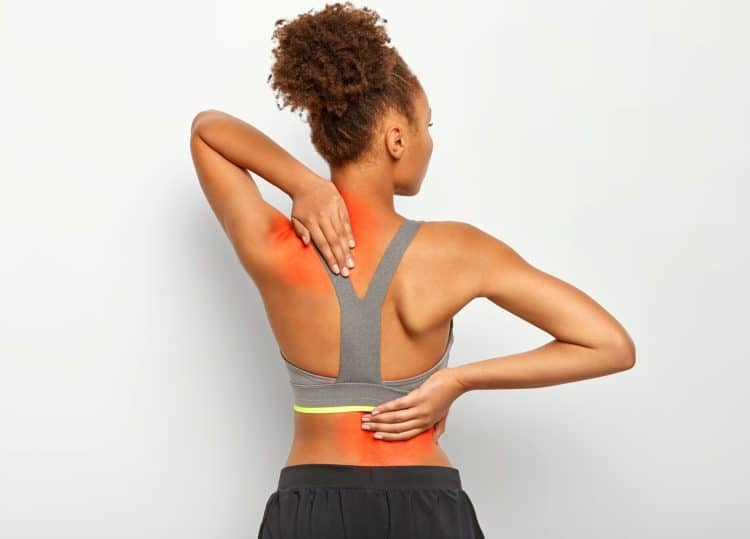
When triggered, your body is likely to show symptoms of acute inflammation. These could include swelling, pain, excessive heat generation, redness, or body dysfunction. For instance, it could become difficult to move an inflamed joint. While inflammation can cause different symptoms, inflammation may occur asymptomatically.
What Happens When The Body Experiences Inflammation?
When inflammation occurs, immune cells release inflammatory mediators, including hormones like histamine and bradykinin. Such hormones, when released, cause dilation of the small blood vessels, enabling increased blood flow to the injured tissues. Hence, you may experience redness or a heated sensation around the inflamed areas.
As blood flow to the injured area increases, it carries immune cells to the damaged tissues, initiating healing.
As a protective function, your brain receives pain signals from hormones that trigger the nerves. Hence, you become aware of the affected area and try to protect the trouble area.
The increased influx of immune cells to the injured tissue leads to swelling in the affected area. The swelling usually reduces when the fluid moves out of the wounded tissue. You may also experience a rush of fluid release from mucous membranes when inflamed, as it can aid in flushing out the toxins from your body. (3)
Why Must Inflammation Be Checked?
Prolonged inflammation can be problematic. Suppressing the inflammatory response is essential to stop inflammation from advancing from the acute to the chronic stage. This can also prevent any additional damage to your tissues.
If tissue injury is not resolved, it can result in chronic inflammation, potentially leading to various health conditions such as psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), or ulcerative colitis. These ailments last a lifetime and affect your everyday life. Hence, prolonged inflammation can be problematic.
When the body is continuously experiencing chronic inflammation, it can cause a spike in the stress hormone cortisol. A poor diet, stress, highly refined food products or sugars, chemical-infused food products, and excessive smoking or drinking are among some factors that can cause long-term inflammation.
You must check your exposure to the elements that contribute to chronic inflammation, as they can increase the generation of free radicals, causing oxidative stress. Free radicals and oxidative stress can put your body at an increased risk of damage to cell membranes, telomeres, and other cell components.
Finding ways to reduce inflammation is important, and here’s how fasting can come to the rescue:
How Fasting Affects Inflammation?
Now that you know the potential causes of inflammation, let’s look at the possible impact of fasting on inflammation.
Your diet plays a crucial role in the problems associated with inflammation.
Here are some key benefits of fasting on inflammation:
Fasting Helps Lower Inflammation by Reducing Oxidative Stress
According to a study, fasting methods such as intermittent fasting can modify brain activity to maximize its function and energy metabolism. In the process, the body generates ketones that can reduce body fat and enhance the insulin sensitivity of cells and muscles, thus reducing oxidative stress and inflammation throughout the body and brain. (4)
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and other antioxidants prevents inflammation. You can include a healthy diet in your eating periods to enable the body to fight free radicals and prevent oxidative damage that may trigger chronic inflammation.
Fasting Improves Autoimmune Response
A study indicates how dietary restriction can decrease the number of monocytes circulating in the body. Monocytes are a type of leukocytes present in the blood and tissues that work as immune cells to prevent infection or treat injuries.
It concluded that intermittent fasting is an effective practice to reduce chronic inflammation without damaging the function of the immune system. (5)
Fasting Helps Combat Age-Related Inflammatory Issues
Another study draws attention to the correlation between aging and inflammation to unravel how fasting can help overcome increasing inflammatory problems with age. The study shows that aging can cause functional decline, increasing the body’s disease vulnerability. Unsettled chronic inflammation is often the underlying cause. (6)
The same study discusses how fasting has proven to have a positive anti-aging benefit in mice and can protect the body against age-related ailments. The findings also reveal how slight calorie restriction can reduce inflammatory gene expression.
Moreover, fasting can help you achieve weight loss goals, enabling your body to control inflammation. Excess body fat, especially around the waist (visceral fat), is not good. Hence, to counter it, the body launches an inflammatory response. This inflammation increases as you keep gaining weight.
Uncontrolled weight gain can lead to obesity, which is an inflammatory condition and can trigger other chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome, heart disease, and other ailments associated with inflammation. Fasting, especially intermittent fasting, can help lose excess body weight and decrease inflammation.
FAQs
1. How can diet help combat inflammation?
Taking care of your diet can reduce chronic inflammation. For instance, a diet rich in fruits and vegetables can fuel your body with antioxidants that help minimize cell damage. When you eat less processed and refined food products, you also tend to block your inflammatory responses. Thus, incorporating a healthy diet is beneficial for combating inflammation.
2. How can fasting heal my body from inflammation?
Limiting your food intake and restricting calories prevents overfeeding. It can be beneficial on a cellular level, allowing your body the time to heal from the harm caused by inflammation. Intermittent fasting can reduce oxidative stress and inflammation by influencing the gut microbiota.
3. How does inflammation become chronic, and can it harm my body?
Inflammation can become chronic when your immune system is compromised. It can be caused by the presence of toxins in the body or due to obesity. When the body undergoes such an immune attack for an extended period that may last for weeks, months, or several years, inflammation turns chronic.
Ongoing inflammation can damage your cells and tissues, causing long-term harm, sometimes even without you noticing it. It can also be the triggering factor behind diseases such as obesity, strokes, cancer, heart disease, rheumatoid arthritis, and obstructive pulmonary disease.
4. What must I consider when considering intermittent fasting to reduce inflammation?
If you are new to fasting, you can start with shorter fasting periods and gradually extend the time. Also, ensure you drink plenty of fluids, especially when fasting for multiple days. Consult your doctor if you have any pre-existing health conditions or are on any form of medication.
It is best to avoid heavy meals and consider breaking fasts gently with easily digestible food. You should always combine fasting with regular exercise and a healthy lifestyle that balances your mental and physical health.
Conclusion
Inflammation can take a toll on your health. However, balanced dietary choices and calorie restriction can help minimize the internal damage caused by inflammation.
Fasting can be highly effective in controlling inflammation as it can create protective mechanisms for a stronger immune response. However, if it is your first time fasting, consider consulting a medical professional to guide you through the process.
It is best to begin with shorter fasting periods to see how your body responds. Consulting a doctor can also help determine other underlying health conditions causing inflammation.
References
Fitness Volt is committed to providing our readers with science-based information. We use only credible and peer-reviewed sources to support the information we share in our articles.
- Aly, S.M. (2014) Role of intermittent fasting on improving health and reducing diseases, International journal of health sciences. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4257368/ (Accessed: 13 December 2023).
- Pahwa, R. (2023, August 7). Chronic Inflammation. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf.
- What is an inflammation? (2018, February 22). InformedHealth.org – NCBI Bookshelf.
- Aly, S.M. (2014) Role of intermittent fasting on improving health and reducing diseases, International journal of health sciences. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4257368/ (Accessed: 13 December 2023).
- Jordan, S. et al. (2019) Dietary intake regulates the circulating inflammatory monocyte pool, Cell. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7357241/ (Accessed: 13 December 2023).
- Zhou, R.-H. et al. (2021) The influence of fasting and caloric restriction on inflammation levels in humans: A protocol for systematic review and Meta Analysis, Medicine. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8052001 (Accessed: 13 December 2023).
Article Updates Timeline:
Our editorial team experts constantly update the articles with new information & research, ensuring you always have access to the latest and most reliable information.
January 6, 2024
Written By
Dr. Rashmi Byakodi
Edited By
Vidur Saini
Fact Checked By
Dr. Malik
Tip: If you're signed in to Google, tap Follow.