Irrespective of how hard you train, you cannot build muscle until you’re consuming a balanced, protein-rich diet. Protein is the building block of muscle. Similarly, amino acids are the building blocks of protein, making them the foundation of muscle.
Amino acids play vital roles in your body, from transporting nutrients to repairing and rebuilding bigger and stronger muscle tissues.
There are two main types of amino acids — essential amino acids (EAAs) and branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs).
In this article, I’ll take you over the different types of amino acids and explain how each of them contributes to muscle growth. We’ll also uncover how you can ensure you get enough amino acids to maximize hypertrophy. This will be the most detailed guide on amino acids you’ve ever read; I promise. That said, we have a lot to unpack, so sit tight and read on.
Understanding Essential Amino Acids (EAAs)
Let’s begin with essential amino acids (EAAs). They have ‘essential’ in their name as your body cannot produce them on its own, and you must get them through food or supplements.
EAAs are non-negotiable when it comes to building muscle mass.
Ask a regular gym-goer the most important food source for building muscles, and they’ll probably say whey protein. However, only a few understand how whey protein functions to support muscle and strength gains.
Whey protein is a complete protein, meaning it has all nine essential amino acids. After you consume whey protein, it is broken down into amino acids that are then delivered to the muscles to kickstart muscle protein synthesis and subsequent recovery.
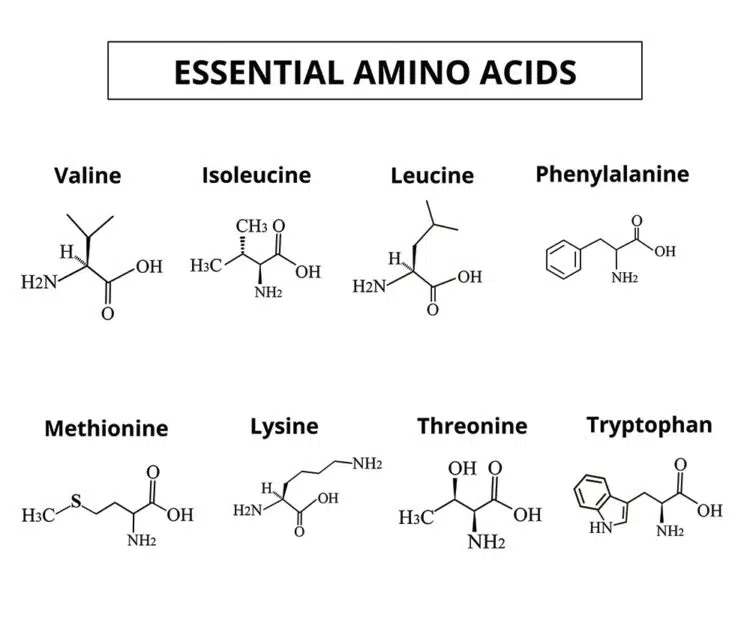
9 EAAs & Their Roles
There are nine EAAs, each with its own unique superpower. Here is a lowdown on each:
- Histidine: Produces red and white blood cells, which are essential for oxygen transport and immune function. These also play a critical role in optimal workout recovery.
- Isoleucine: Facilitates muscle metabolism and energy regulation, which can support your performance during intense training sessions.
- Leucine: This is the most important EAA for muscle protein synthesis. It activates mTOR, which signals to your brain that it is time to grow.
- Lysine: It helps with calcium absorption and bone health, helping build a solid foundation for your muscles to grow bigger and stronger.
- Methionine: Involved in various metabolic processes, including tissue growth and repair. It is also a powerful antioxidant, helping flush out metabolites after intense training.
- Phenylalanine: A precursor to tyrosine, an amino acid that is crucial for producing neurotransmitters like dopamine and norepinephrine.
- Threonine: Vital for immune function and maintaining protein balance in the body. Threonine also contributes to collagen production, helping with healthy joints and connective tissue.
- Tryptophan: A precursor to serotonin, a neurotransmitter that influences mood, sleep, and recovery. Sleep is when the muscles grow bigger and stronger, so you shouldn’t overlook it.
- Valine: This is very similar to isoleucine in that it plays a crucial role in muscle metabolism, energy production, and tissue repair.
Most Important Amino Acid For Hypertrophy
So, which amino acid is the most important for building muscle mass?
Experts consider leucine the most effective amino acid for muscle growth as it’s a key part of muscle protein synthesis.
Leucine can be found in dairy, meat, eggs, and plant-based sources like soybeans, quinoa, lentils, and chickpeas.
A study published in the Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition concluded that whey protein supplements with a 40 percent leucine composition stimulated muscle protein synthesis approximately 50 percent more than the lower leucine profile despite containing the same amount of total EAAs. (1)
Limiting Amino Acids
Now that you know leucine is the main amino acid you need to maximize muscle growth, you might be thinking about how you can increase your leucine intake.
Leucine can be consumed in isolation as a dietary supplement, typically in powder or capsule form.
However, gulping down all the leucine you can find might not be the most effective approach.
Why is that, you ask?
You should be familiar with a concept called limiting amino acids.
Amino acids work synergistically, meaning they must be taken together for optimal function. If your body doesn’t have enough of even one EAA, it will limit muscle protein synthesis, even if you’re loading on the other amino acids.
Consuming a complete protein source is the best way to ensure optimal essential amino acid utilization for muscle protein synthesis.
While leucine triggers protein synthesis, you need other amino acids for the actual muscle-building process.
So, you must prioritize consuming leucine from a complete protein source or supplement to ensure a balanced amino acid profile and optimal growth.
Branched-Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs): The Muscle Growth Trio
Branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) are the other types of amino acids. They got their name as their molecular structure resembles a branch with multiple arms. This shape gives them special properties, allowing them to be metabolized differently than other amino acids.
3 Types of BCAAs
In contrast to the nine essential amino acids, there are just three BCAAs. What else? This trio is also a part of the EAAs. However, I’ll use this section as an opportunity to dig deeper into them and explain the intricacies of these three:
Leucine
As explained above, leucine is the most important amino acid for promoting muscle gain. Some of the most critical functions of leucine include boosting muscle protein synthesis, inhibiting protein degradation, glucose oxidation, controlling blood sugar, improving immune function, lowering chronic inflammation, and balancing appetite and satiety. (2)
Isoleucine
Think of isoleucine as the energy manager of the body, as it plays a vital role in regulating glucose metabolism and energy production. Your body needs a constant supply of energy during intense workouts, and isoleucine steps in to ensure your body is using glucose efficiently, helping you maintain your performance for longer. (3)
Isoleucine also plays several other crucial roles in the body, including hemoglobin production, blood sugar regulation, promoting immunity, healing wounds, and detoxification of nitrogenous waste.
Valine
You could consider valine as the muscle’s maintenance crew. It shares several functions with isoleucine, supporting muscle repair and growth and energy production. Valine also improves mitochondrial function and lowers oxidative stress. Research shows that valine supplementation can boost growth and reproductive performance in animals. It can also promote gut microbiota and immune functions. (4)
Amino Acids in the Diet: Food Sources
You now understand the importance of amino acids. Let’s now talk about how you can consume them to meet your daily targets and maximize your gains. These are the most popular animal and vegan amino acid sources:
- Animal Sources: Meat, poultry, fish, eggs, and dairy
- Plant Sources: Legumes, nuts, seeds, soy products, and quinoa
Remember, the exact amount of EAA or BCAAs you need will vary depending on factors like your age, gender, fitness level, diet, and training objectives.
Plus, you must consume a balanced, protein-rich diet to ensure you are getting all the essential amino acids. Eating too much of one thing and cutting out the others will lead to substandard results.
Meal Planning Tips For Optimal Amino Acid Consumption
Planning your meals in advance can help you get the best bang for your buck. Here is how to do it:
Combine Grains and Legumes
If you are not already doing it, you’re missing out on the most convenient way to ensure a complete protein profile. Pair rice and beans and quinoa and lentils for a lip-smacking meal while getting all the nine essential amino acids.
Vary Your Protein Sources
Eating chicken daily can get boring really quickly. Instead, mix it up with fish, eggs, beans, and other high-quality protein sources. I also recommend trying new recipes every few days to keep your diet exciting.
Spread Your Protein Intake Throughout the Day
Many make the mistake of limiting high-protein foods to particular meals, let’s say lunch or dinner. However, consuming protein in every meal ensures you have enough amino acids throughout the day for optimal muscle recovery and growth.
Considerations for Vegans and Vegetarians
Irrespective of what others say, meeting the daily protein intake target required for hypertrophy is more challenging for vegans and vegetarians compared to non-vegetarians. However, it is completely possible. It just takes a bit more planning. Here’s what you must do:
- Focus on variety: Eat a wide range of legumes, nuts, seeds, soy products, and whole grains.
- Combine complementary proteins: In line with what is explained above, pair grains with legumes, nuts with seeds, and so on.
- Use vegan protein powder: A plant-based protein supplement can be a great way to plug the gap in your daily protein intake.
Amino Acid Supplementation: What to Know
BCAA and EAA supplements can enhance muscle protein synthesis, reduce muscle soreness and fatigue, improve exercise performance, and aid in muscle recovery after intense training sessions.
Furthermore, you should prioritize a whey protein shake after a training session as it contains all nine essential amino acids, which can support muscle recovery and growth.
Intra-Workout Supplementation
Many lifters prefer sipping on an intra-workout drink. These formulas are excellent for giving you a mid-workout kick, which can help you sustain your training performance. However, which one should you pick — EAAs or BCAAs?
Objectively speaking, EAAs are a better intra-workout supp than BCAAs. There are two main reasons for this:
Complete Amino Acid Profile Makes Them Superior For Muscle Protein Synthesis
Since EAA contains all nine amino acids, including the three BCAAs, they are better at promoting muscle protein synthesis. While BCAAs are important for muscle growth, they might not be as effective when taken in isolation.
Improved Recovery and Reduced Muscle Soreness
The nine EAAs boost recovery from exercise and limit muscle soreness by delivering all the nutrients needed for muscle tissue repair.
However, you must remember that supplements are not magic pills (or powders). Combine them with a balanced diet and a structured training program to make the most of them.
Conclusion
Understanding how BCAAs and EAAs work can help you make informed decisions about your nutrition and maximize your results. Remember, you shouldn’t be overly reliant on one type of amino acid in your diet.
Consume a wide variety of high-quality protein sources, mix and match your food sources, and spread your protein intake throughout the day for optimal muscle gains. Finally, you must also ensure a balanced training and recovery plan to achieve the desired results.
If you have any questions about amino acids, post them in the comments below, and I’ll be happy to help!
References:
- Ferrando AA, Wolfe RR, Hirsch KR, Church DD, Kviatkovsky SA, Roberts MD, Stout JR, Gonzalez DE, Sowinski RJ, Kreider RB, Kerksick CM, Burd NA, Pasiakos SM, Ormsbee MJ, Arent SM, Arciero PJ, Campbell BI, VanDusseldorp TA, Jager R, Willoughby DS, Kalman DS, Antonio J. International Society of Sports Nutrition Position Stand: Effects of essential amino acid supplementation on exercise and performance. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2023 Dec;20(1):2263409. doi: 10.1080/15502783.2023.2263409. Epub 2023 Oct 6. PMID: 37800468; PMCID: PMC10561576.
- Duan, Y., Li, F., Li, Y., Tang, Y., Kong, X., Feng, Z., Anthony, T. G., Watford, M., Hou, Y., Wu, G., & Yin, Y. (2016). The role of leucine and its metabolites in protein and energy metabolism. Amino acids, 48(1), 41–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-015-2067-1
- Gu, C., Mao, X., Chen, D., Yu, B., & Yang, Q. (2019). Isoleucine Plays an Important Role for Maintaining Immune Function. Current protein & peptide science, 20(7), 644–651. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389203720666190305163135
- Sharma S, Zhang X, Azhar G, Patyal P, Verma A, Kc G, Wei JY. Valine improves mitochondrial function and protects against oxidative stress. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2024 Jan 24;88(2):168-176. doi: 10.1093/bbb/zbad169. PMID: 38093456; PMCID: PMC10807754.
Tip: If you're signed in to Google, tap Follow.