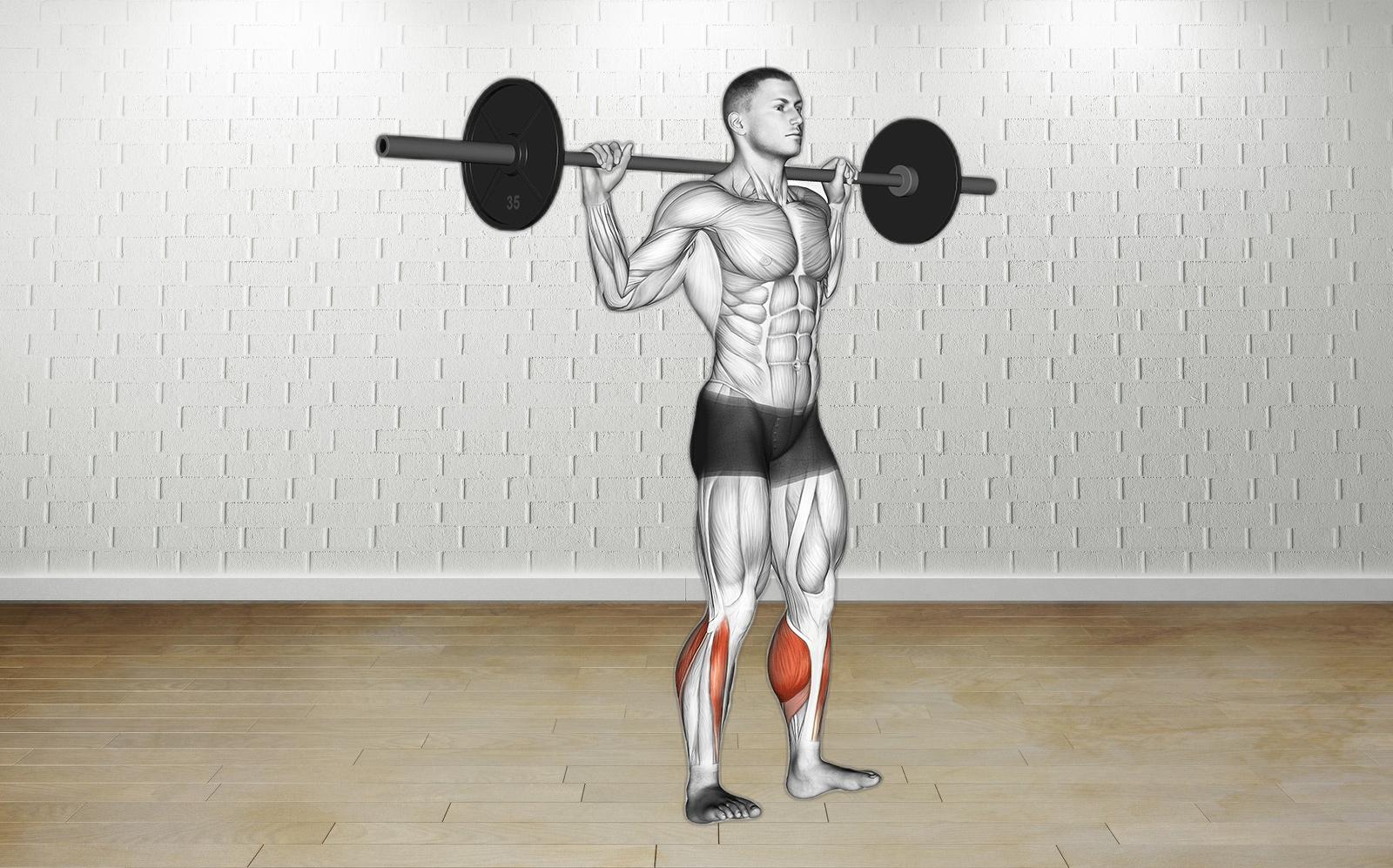
The Barbell Standing Rocking Calf Raise is a proven exercise to build strong, defined calves—vital for everyday activities like walking, running, and climbing. Strong calves not only enhance athletic performance and stability but also play a key role in injury prevention. Aesthetically, well-developed calves add a pleasing dimension to your legs, making them a must-have for fitness enthusiasts.
This dynamic movement targets the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles, fostering muscle growth, endurance, and power. For best results, include this exercise in your workout two to three times a week, allowing proper recovery between sessions. If you feel excessive soreness, incorporate an additional rest day to prevent overtraining.
Safety is paramount. Maintain proper posture by keeping your core engaged throughout the exercise. If the barbell feels too heavy, opt for body weight or resistance bands as effective alternatives. Perform slow, controlled movements and hold your heels just above the ground to keep your calves fully engaged. Start with a shoulder-width stance, position the barbell securely across your upper back, and rise onto the balls of your feet for maximum benefit. Consistency and focus are the foundation of achieving sculpted calves, so begin your journey today!
How to Perform the Barbell Rocking Standing Calf Raise
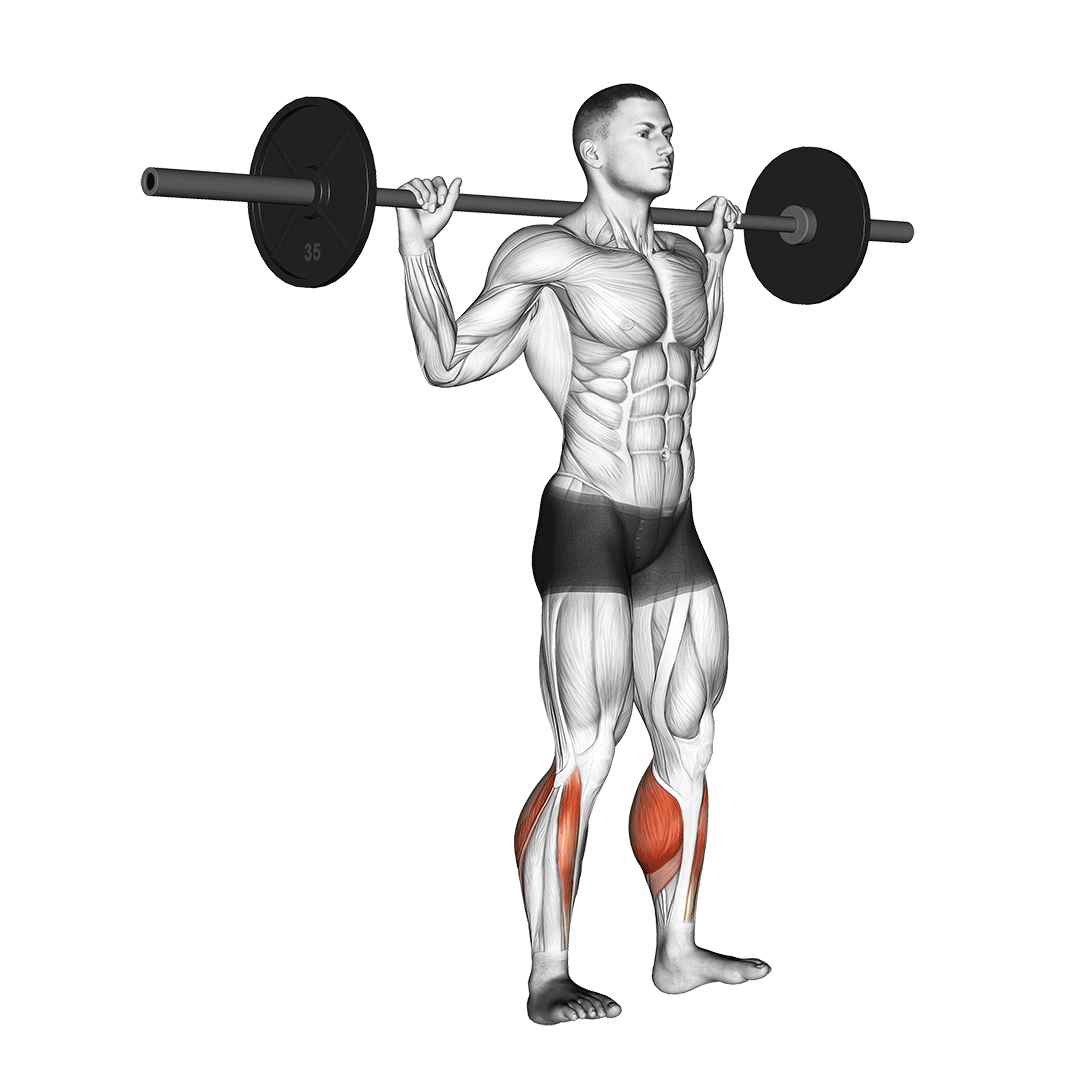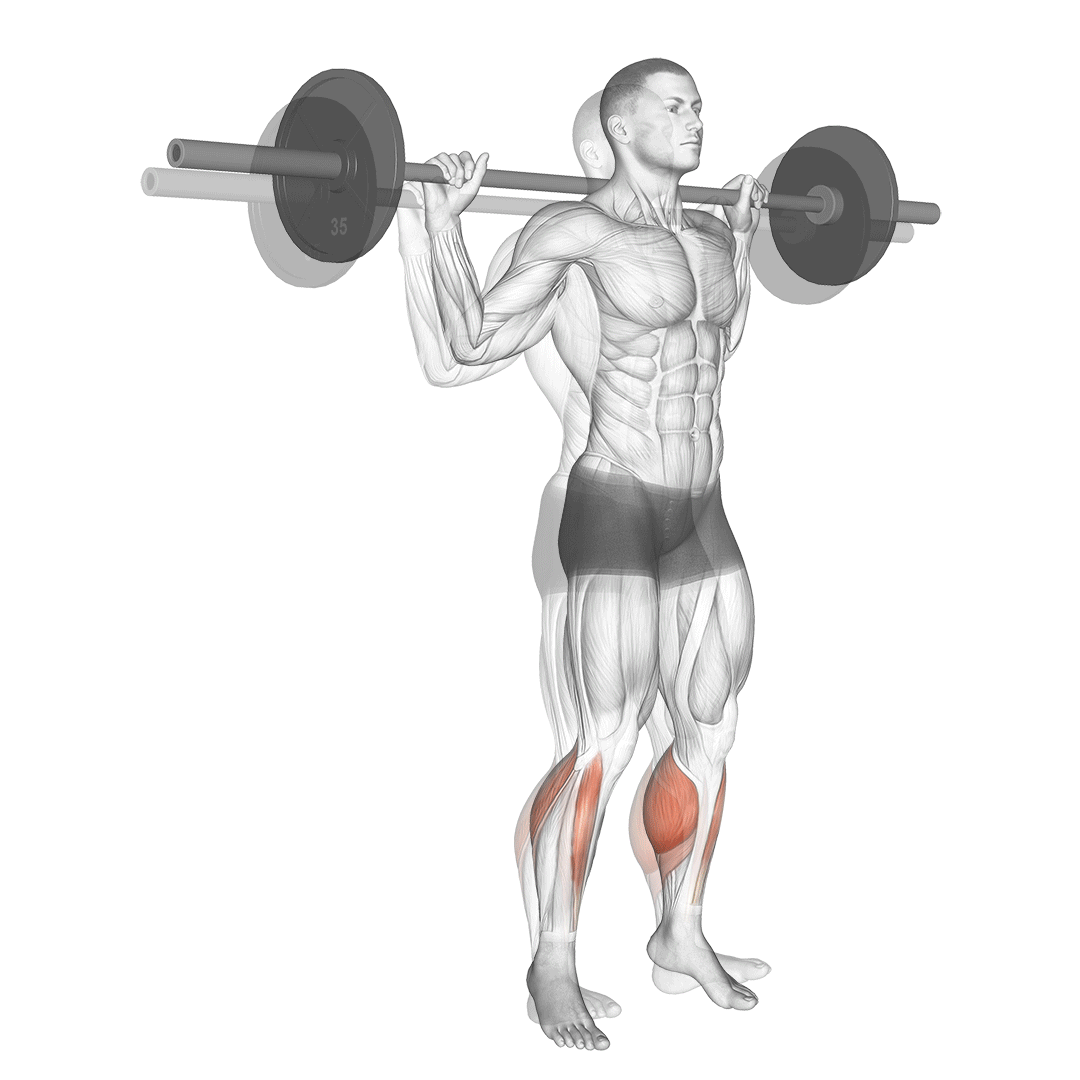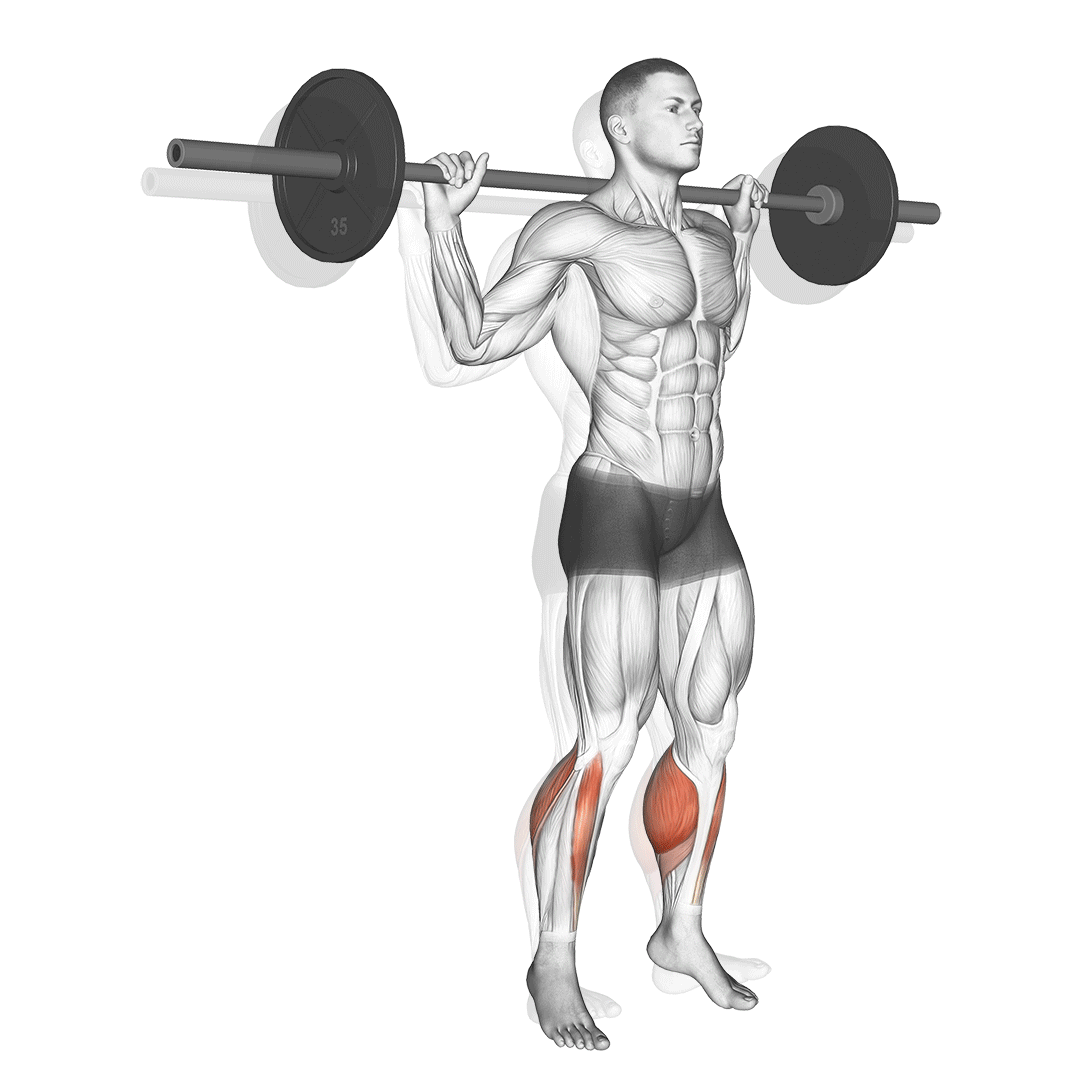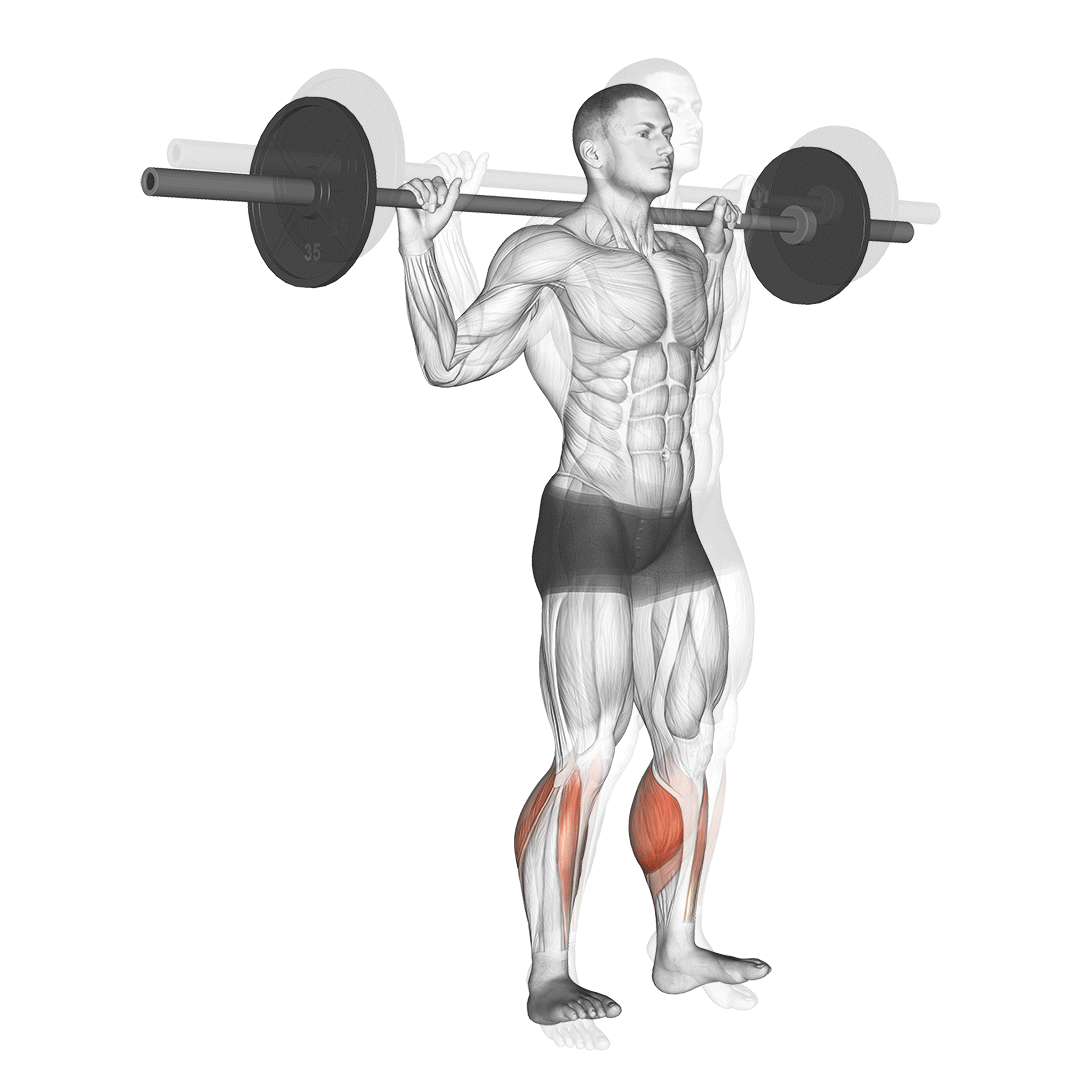
- Stand upright with feet shoulder-width apart. Rest the barbell across your upper back, gripping it firmly with both hands. Engage your core.
- Lift your heels off the ground, rising onto the balls of your feet.
- Pause briefly at the top to maximize calf contraction.
- Lower your heels slowly, stopping just before they touch the ground to maintain tension.
- Repeat for the desired number of repetitions with controlled, steady motions.
Pro tip: Inhale as you lift your heels and exhale as you lower them for optimal control and engagement.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Improper Foot Position: Ensure feet are shoulder-width apart for balance and optimal muscle activation.
- Rushing Through Movements: Fast, jerky motions compromise effectiveness and increase injury risk. Focus on slow, deliberate lifts.
- Shortened Range of Motion: Avoid limiting engagement by not lowering your heels fully. Keep tension throughout the motion.
- Overarching the Back: Engage your core to maintain a neutral spine and avoid strain.
- Excessive Weight: Begin with manageable weights to prioritize form over load, gradually increasing as strength improves.
Key Benefits
- Enhanced Calf Strength: Strengthen the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles for improved lower-body performance.
- Improved Balance and Stability: Training on the balls of your feet reinforces ankle stability and reduces the risk of falls.
- Functional Movement Gains: Mimic real-life movements like walking and running for better athletic and everyday functionality.
- Postural Improvements: Core engagement during the exercise supports better spinal alignment and reduces back discomfort.
- Plyometric Power Boost: Strengthened calves enhance explosive movements like sprinting and jumping, essential for athletic performance.
Exercise Variations
Alternative Exercises
Safety Precautions
Prioritize safety by standing with feet shoulder-width apart and distributing weight evenly. Use a secure, overhand grip on the barbell, ensuring it rests on your upper back rather than your neck. Begin with an appropriate weight for your fitness level, focusing on perfecting your form before increasing the load.
Perform each movement with control, avoiding any bouncing or momentum to maintain muscle engagement and minimize injury risk. Ensure your training space is hazard-free to support safe and focused execution. Consistent mindfulness and proper technique are critical to making this exercise both effective and safe.
Tip: If you're signed in to Google, tap Follow.









