All About Calf Muscles
The calf muscles consist of three compartments. The anterior, lateral and posterior compartment.
The anterior compartment consists of the tibialis anterior, extensor digitorum longus, fibularis tertius, and the extensor halluces. The tibialis anterior is a superficial muscle of anterior leg, it laterally parallels the sharp anterior margin of tibia. It originates at the lateral condyle, and upper two-thirds of tibia. Insertion is by tendon into inferior surface of medial cuneiform, and first metatarsal bone, the prime mover of dorsiflexion. Extensor digotorum longus is a unipennate muscle on the anterolateral surface of leg, lateral to tibialis anterior muscle. It originates at lateral condyle of tibia, proximal three-fourths of fibula, and inserts at the middle and distal phalanges of toes two – five via extensor expansion. It’s the prime mover of toe extension. The fibularis tertius small muscle usually continuous and fused with distal part of extensor digitorum longus. It originates at the distal anterior surface of fibula and interosseous membranes, and inserts on dorsum of fifth metatarsal, dorsiflexes and inverts foot. The extensor hllucis is deep to extensor digitorum longus and tibialis anterior. It originates at the anteromedial fibula shaft and interoseues membrane. The tendon inserts on distal phalanx of great toe. This muscle extends the great toe.
All of the muscle contained within the anterior compartment dorsiflex the foot and toes, they also help to turn the foot inward. The lateral compartment consists of the fibularis longus, and fibularis brevis. These muscles assist in plantarflexion as well as moving the pulling the foot outward. Fibularis longus is a superficial lateral muscle that overlies fibia. It originates at the head, and upper portion of lateral side of fibula. Insertion is by a long tendon that curves under the foot to the first metatarsal, and medial cuneiform. It plantarflexes and inverts the foot. The fibularis brevisis a smaller muscle deep to fibularis longus enclosed in a common sheath. It originates at distal fibula shaft insertion by a tendon running behind the lateral malleolus to insert on proximal end of fifth metatarsal. It both plantar flexes, and inverts foot.
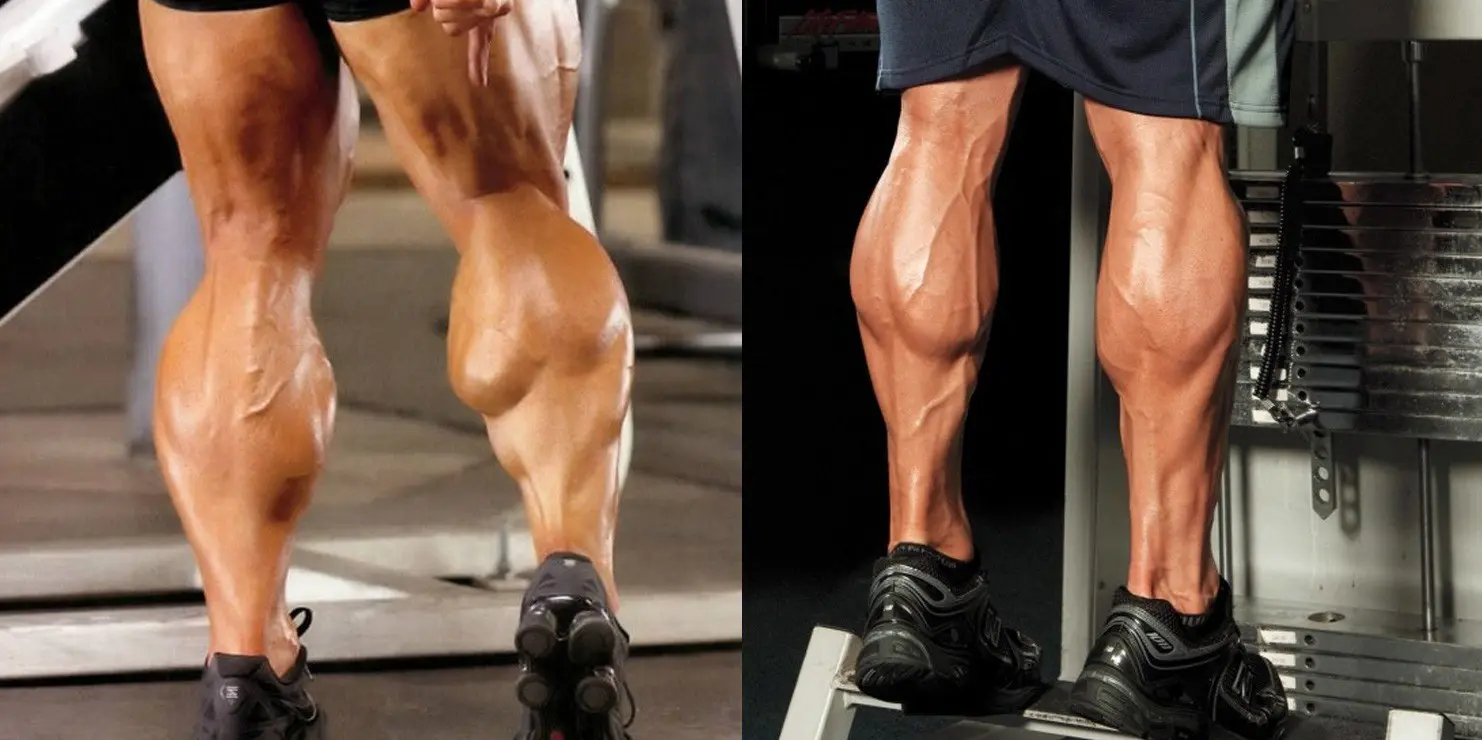
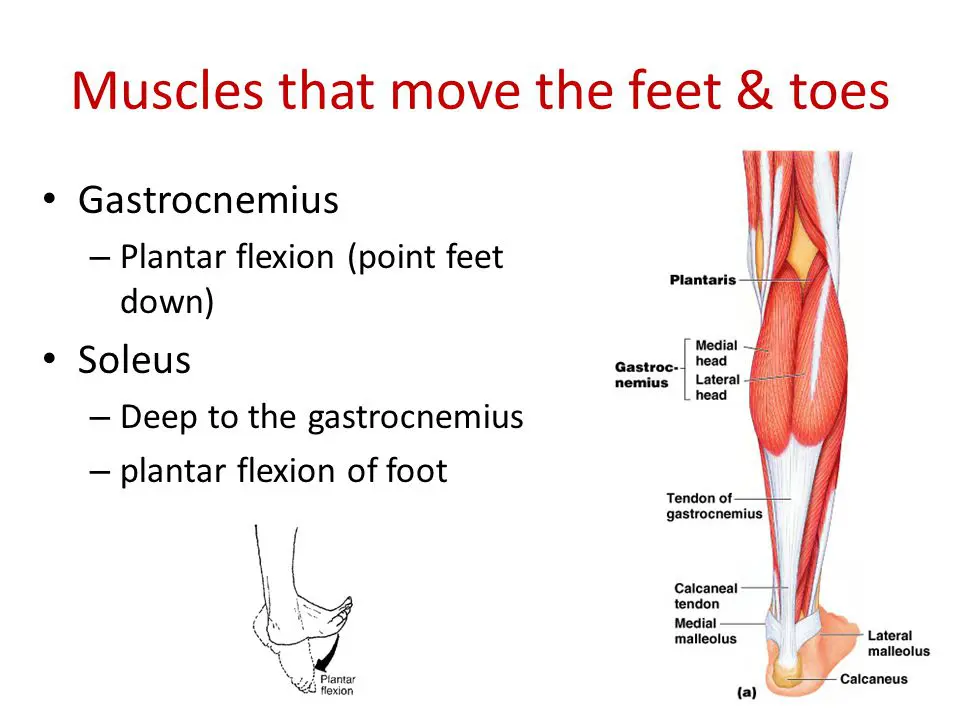
In terms of training, the muscles we tend to look to are the ones contained within the posterior compartment or the ‘Triceps Surae’ which consists of the gastrocnemius, and the soleus. The gastrocnemius is the most superficial muscle of the pair, with two prominent bellies that form the proximal curve of the calf. It originates from two heads from the medial and lateral condyles of femur, and inserts on the posterior calcaneous via calcaneal tendon. It plantar flexes the foot when the knee is extended, and can also flex the knee when the foot is dorsiflexed. The soleus is a broad flat muscle deep to gastrocnemius on the posterior surface of the calf. It originates from superior tibia-fibula, and interosseus membrane inserts on posterior calcaneus via calcaneal tendon. It plantar flexes the foot, and is an important locomotor and postural muscle during walking and running.
Happy Lifting!
Tip: If you're signed in to Google, tap Follow.