Most people tend to think of the sports supplement industry as being very new. And while commercial supplements have only really been around for the last 40-50 years, athletes from all sports have been using performance-enhancing substances for hundreds if not thousands of years.
Examples include:
Bog myrtle – a plant with energizing properties reportedly taken by Viking warriors before battle; it’s the original pre-workout!
Animal organs – athletes in ancient Rome and Greece consumed raw and dried, powdered animal glands and organs in the hope of increasing their bravery, strength, and endurance. The heart and testes were especially popular – the heart for courage and testes for power.
Coco leaves – used by hunters and warriors in South America to increase bravery and endurance. Cocaine is made from coco leaves.
Caffeine – while many people take the energizing effects of caffeine for granted, until as recently as 2004, it was on the International Olympic Committee’s list of banned substances, and more than a couple of cups of coffee could result in disqualification (1).
Most supplements are suitable for men and women, but there are several that are especially useful for males. In this article, we reveal the ten best supplements for men who lift for boosting health, fitness, performance, and virility.
Important Supplements for Lifting
Right from the outset, it’s important to understand that you don’t HAVE to take supplements. If you eat a well-balanced diet, there is every chance that you’re getting all the nutrients you need to survive and thrive.
That said, some supplements and nutrients may enhance your health or performance, especially if you have a nutritional deficiency.
Remember, though, that no supplement will make up for an otherwise poor diet, ineffective workout program, or chronic sleep deprivation. The best way to think of supplements is as effort multipliers; the harder YOU work, the greater THEIR effect will be.
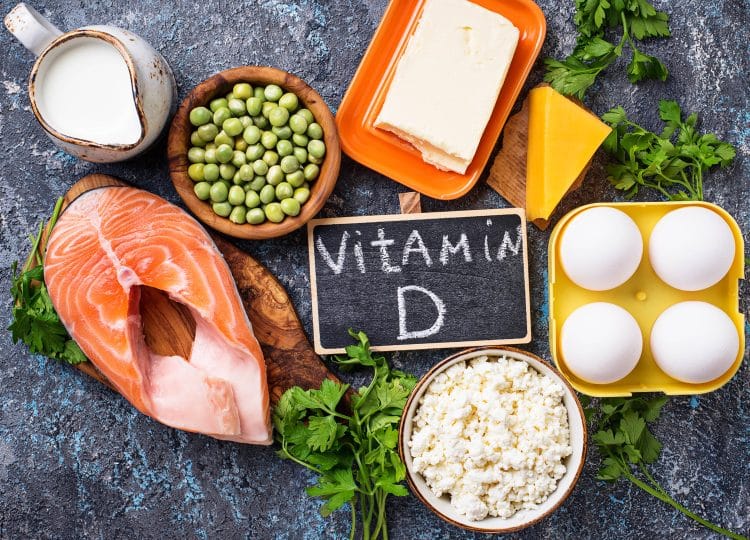
1. Vitamin D
Your body produces vitamin D when you expose your skin to the sun. But, unless you are a beach lifeguard or otherwise work outdoors, most men don’t get enough sun exposure and are likely to be vitamin D deficient.
Vitamin D is critical for testosterone production, which is why it’s such an important nutrient for men. The so-called sunshine vitamin also plays a role in heart and bone health, making it even more critical for older fellows.
How much to take: The RDA (recommended daily allowance) for men is 600 IU per day. However, research suggests that a higher intake of 1500 to 2000 IU per day would be more appropriate and beneficial (2).
2. Magnesium
Magnesium is a mineral that is crucial for overall male wellness, playing an essential part in protein synthesis, glucose control, nerve function, and regulating the circadian (sleep/wake) rhythm. It also plays a role in anabolic hormone production.
Magnesium is present in many foods, including spinach, brown rice, milk, beef, carrots, and apples, but even then, deficiencies are common, with as many as 50% of the male population being low in this vital mineral. Deficiencies in exercisers as especially prevalent, as intense workouts deplete stores of this essential mineral.
Related: Best Magnesium Supplements
3. Zinc
If you want to be strong, muscular, and virile, zinc is arguably the most important mineral. When zinc levels are low, your testosterone levels tend to fall too, and you will be less sensitive to the effects of insulin, which could lead to fat gain (4). Zinc is also critical for immunity. You lose zinc through sweating, making it even more critical for male exercisers.
Related: Best Zinc Supplements
Get all the magnesium and zinc you need in one convenient dose with ZMA. Read more about ZMA here.
4. CoQ10
Co-enzyme Q10 (CoQ10 for short) is a pseudovitamin, which means it’s essential for life, but your body makes some on its own. That said, consuming supplemental CoQ10 helps feed your mitochondria, which are the cells that produce energy. In addition, CoQ10 may also reduce arterial plaque, lowering your risk of coronary heart disease (7).
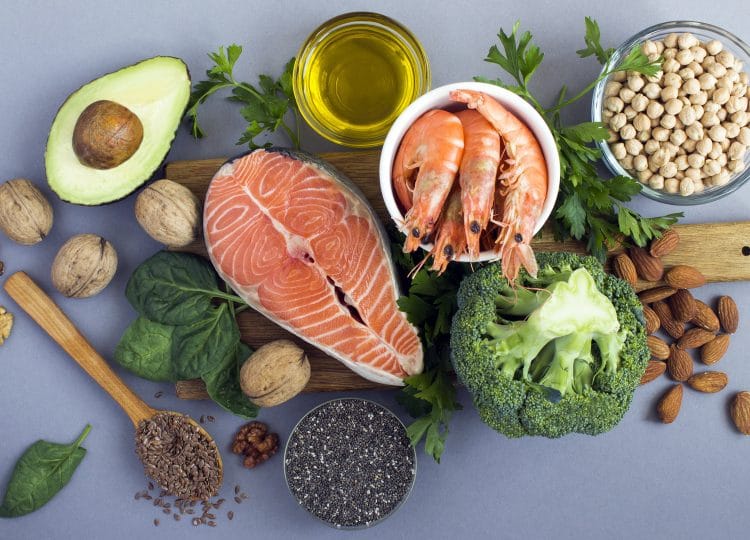
5. Omega 3 Fatty Acids
Omega 3s are polyunsaturated fatty acids with several significant benefits for men. Foremostly, taking omega 3s may reduce your risk of suffering cardiovascular disease, which is more common in men than women. They may also lower your risk of developing dementia, Parkinson’s, and Alzheimer’s diseases.
Also, omega 3s are anti-inflammatory, so they’re good for things like joint health and enhancing recovery after exercise (5).
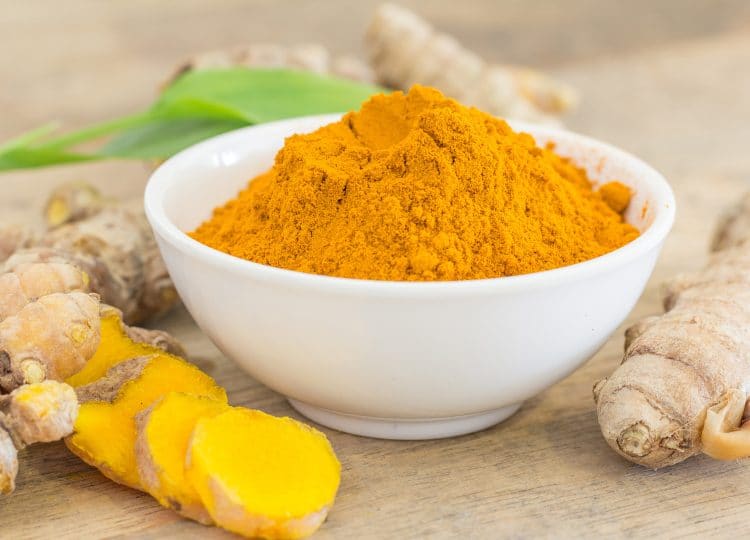
6. Curcumin
Curcumin is a potent antioxidant found in the spice turmeric. It can help lower inflammation, speed up healing, and combat free radicals, which are disruptive molecules that damage cells and even your DNA. Most importantly for men, curcumin can help lower estrogen levels, which leads to an increase in testosterone by default (6).
How much to take: There is no RDA for curcumin, but most men should take between 1500-2000 mg per day alongside 15-20 mg of piperine to maximize absorption.
Related: Best Curcumin Supplement
7. Psyllium Husk Powder
A lot of men fail to consume the recommended 35 grams of fiber per day, which increases the risk of intestinal and bowel diseases such as diverticulitis, irritable bowel syndrome, and colorectal cancer.
Psyllium husk powder is an easy way to add fiber to your diet without having to resort to eating more fruit, vegetables, or whole grains. In addition, consuming psyllium husk powder before meals will help lower your blood glucose, making it easier to get and stay lean, as well as reducing cholesterol and triglyceride levels, cutting your risk of heart disease (8).
8. Aspirin
Men are more prone to coronary heart disease than women. Taking aspirin helps prevent unwanted blood clots and improves blood flow, lowering the risk of myocardial infarction and stroke. It’s also a recognized treatment for erectile dysfunction, which is often caused by circulatory problems (9 & 10).
Aspirin is not safe for everyone, so speak to your doctors before adding this drug to your daily supplement stack.
9. Resveratrol
Resveratrol is a plant compound with powerful antioxidative benefits. Good sources include red wine, grapes, red berries, and peanuts. However, even those these foods contain resveratrol, it’s easier to get what you need in supplement form.
Most people associate resveratrol with better cardiovascular health, but it has many more potential uses, including (11):
- Lower blood pressure
- Healthier blood lipid profile
- A healthier brain
- Improved insulin sensitivity
- Less joint pain
- Slower tumor growth
- Lower estrogen levels
- A longer, healthier life
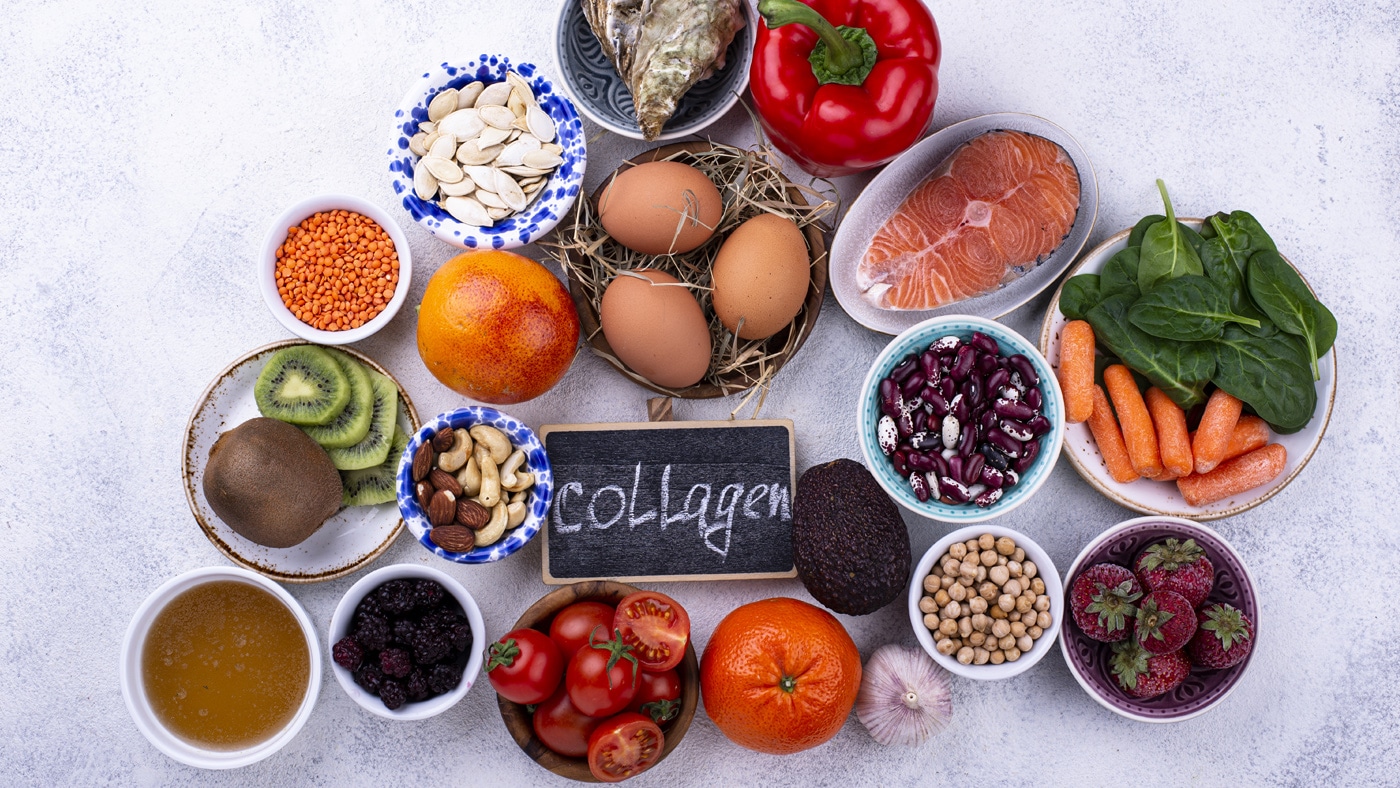
10. Collagen
If you lift weights, you are probably already taking a protein supplement, such as whey. But intense training can take a lot out of your body, potentially damaging your tendons, ligaments, and joints, which is where collagen comes in.
Collagen is the most abundant protein in your body, and it’s an integral part of things like connective tissue and hyaline cartilage. Taking a collagen supplement may help strengthen your joints, reduce joint pain, and even slow down the effects of aging on your skin. And, like all types of protein, collagen will also enhance recovery after exercise (12).
There are several types of collagen – 28 in fact. But the best type of collagen for lifters is type II, which is derived from chicken carcasses. You can get collagen by making chicken bone broth, but it’s easier to just use a type II collagen supplement.
Wrapping Up
You don’t need to take all these supplements. In fact, you don’t need to take any of them if you don’t want to. However, if you have any nutritional deficiencies or are unhappy with your training energy or progress, something on this list may help.
Review each supplement and take note of its benefits and effects. Then, simply match the supplement to your needs. For example, if you work indoors and rarely see the sun, vitamin D is a good option that should have some significant benefits.
Conversely, if your joints are banged up, omega 3s and collagen could be just what you need to ease any aches or stiffness. Need extra energy? CoQ10 will help fire up your mitochondrial furnaces.
Most natural supplements are safe to use, but make sure you also read up on any potential downsides or interactions before using. While aspirin can be very beneficial, especially for older men, it can cause problems for people with blood clotting disorders, stomach ulcers, or kidney disease.
The chances of unwanted side effects are small, but you should always do your due diligence to avoid unnecessary problems and risks.
References:
1. PubMed: Urine Caffeine Concentration in Doping Control Samples from 2004 to 2015 (source)
2. PubMed: Evaluation, Treatment, And Prevention of Vitamin D Deficiency: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline (source)
3. National Institute of Health: Magnesium Fact Sheet for Health Professionals (source)
4. PubMed: Zinc Status and Serum Testosterone Levels of Healthy Adults (source)
5. PubMed: Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids: Benefits and Endpoints in Sport (source)
6. PubMed: Curcumin: A Phytochemical Modulator of Estrogens and Androgens in Tumors of The Reproductive System (source)
7. PubMed: Clinical Evidence for Q10 Coenzyme Supplementation in Heart Failure: From Energetics to Functional Improvement (source)
8. Cambridge University Press: The Effect of a Fiber Supplement Compared to A Healthy Diet on Body Composition, Lipids, Glucose, Insulin and Other Metabolic Syndrome Risk Factors in Overweight and Obese Individuals (source)
9. PubMed: The Role of Aspirin in the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease (source)
10. PubMed: Efficacy of Aspirin for Vasculogenic Erectile Dysfunction in Men: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Control Trials (source)
11. PubMed: Health Effects of Resveratrol: Results from Human Intervention Trials (source)
12. PubMed: The Effects of Collagen Peptides on Muscle Damage, Inflammation and Bone Turnover Following Exercise: A Randomized, Controlled Trial (source)
Tip: If you're signed in to Google, tap Follow.