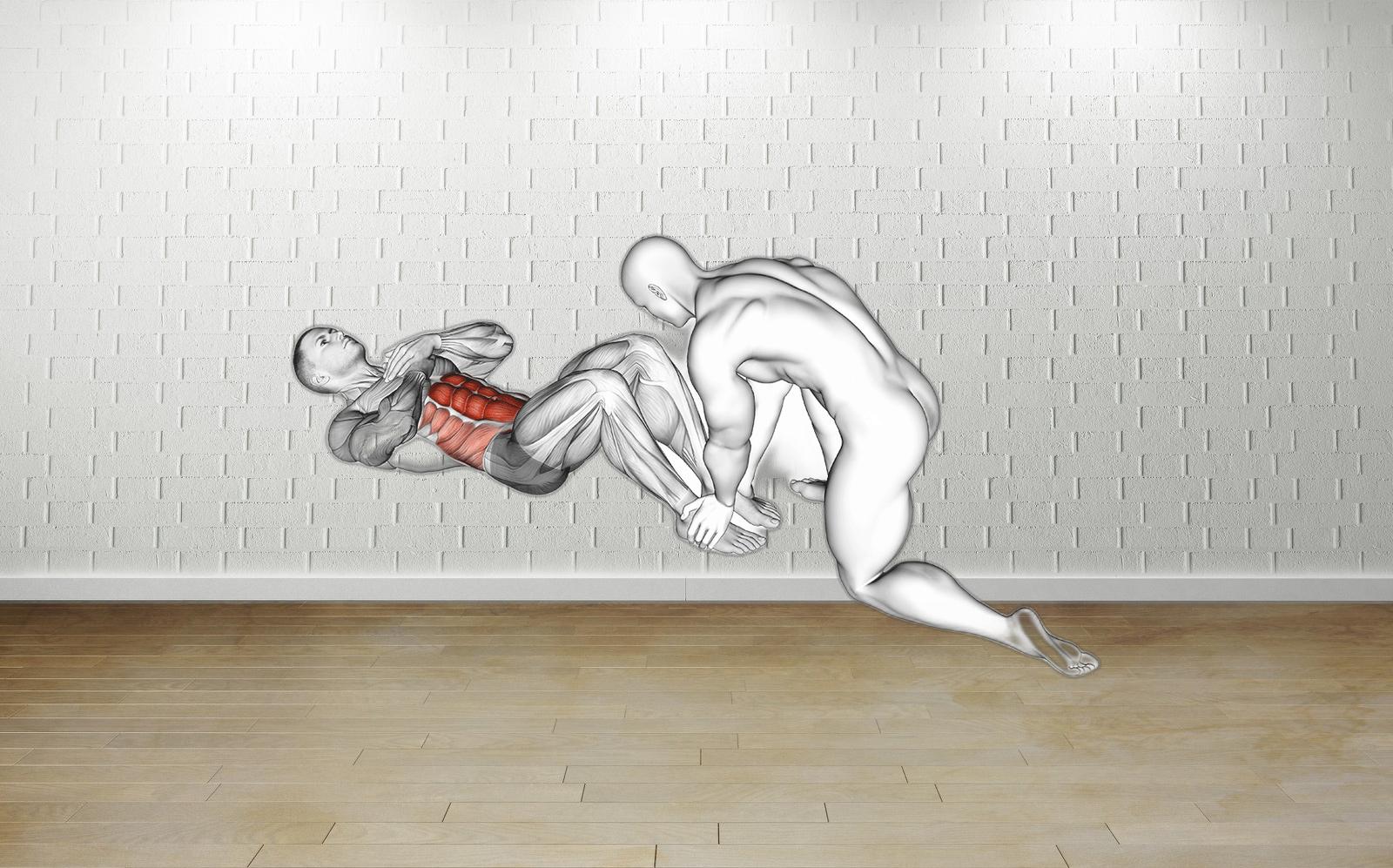
The Assisted Sit-Up is an effective exercise for strengthening abdominal muscles and enhancing core stability, which is vital for overall health and fitness. This versatile movement can be easily integrated into any workout routine, making it suitable for both beginners and more experienced fitness enthusiasts. Utilizing an exercise ball or a partner’s support provides an added layer of assistance, promoting proper form and control during the exercise.
This exercise primarily targets the rectus abdominis, while also engaging the obliques and other core muscles that are crucial for improving posture and supporting a variety of movements. To maximize results, aim to incorporate Assisted Sit-Ups into your routine two to three times per week. It is important to maintain a straight back and avoid pulling on your head or neck, ensuring safety and effectiveness. By adjusting the level of support or range of motion, individuals at different fitness levels can benefit from this foundational exercise.
Whether at home or in the gym, the Assisted Sit-Up is adaptable to your environment and needs, helping you build stronger abs and enhance your fitness journey.
How to Do a Assisted Sit-Up
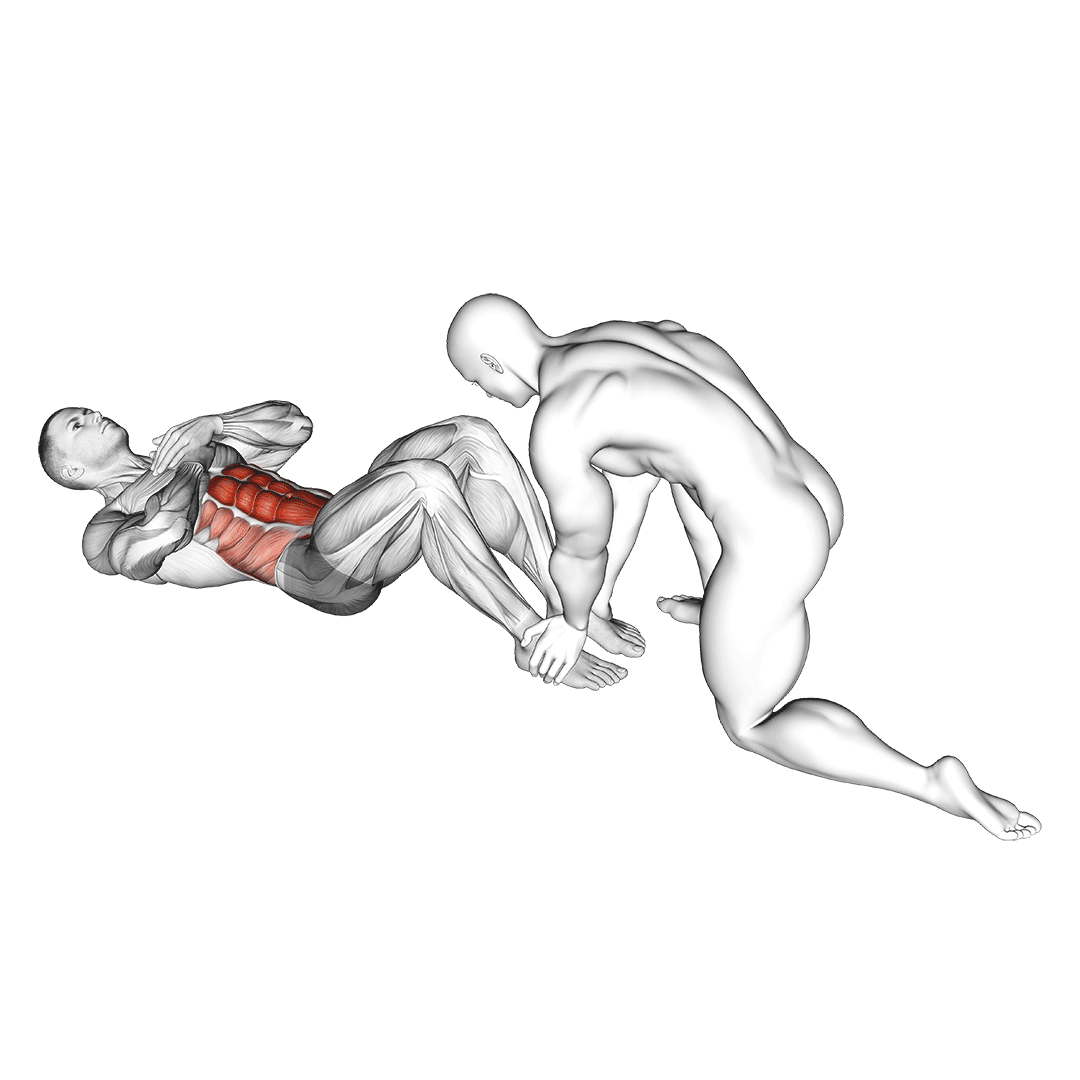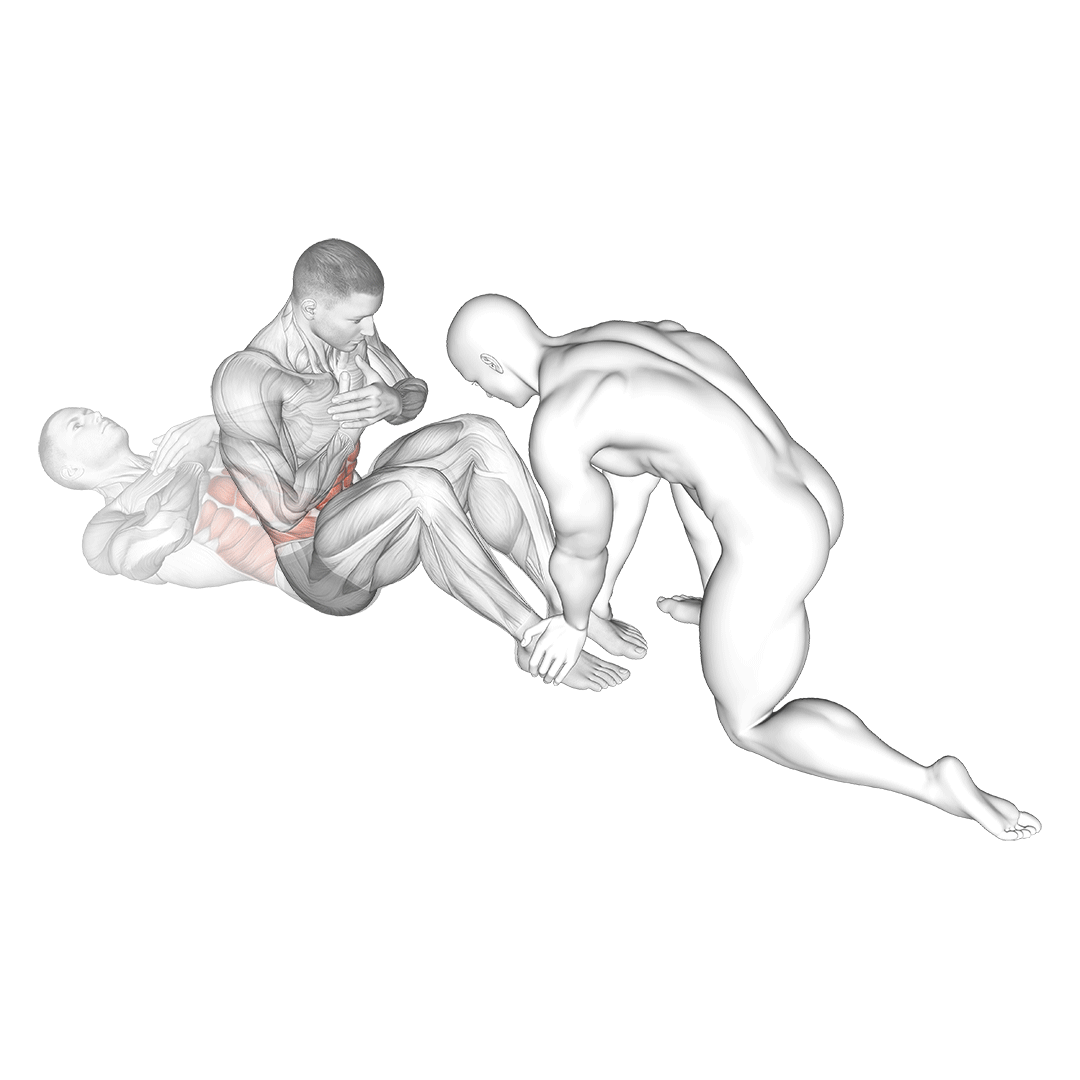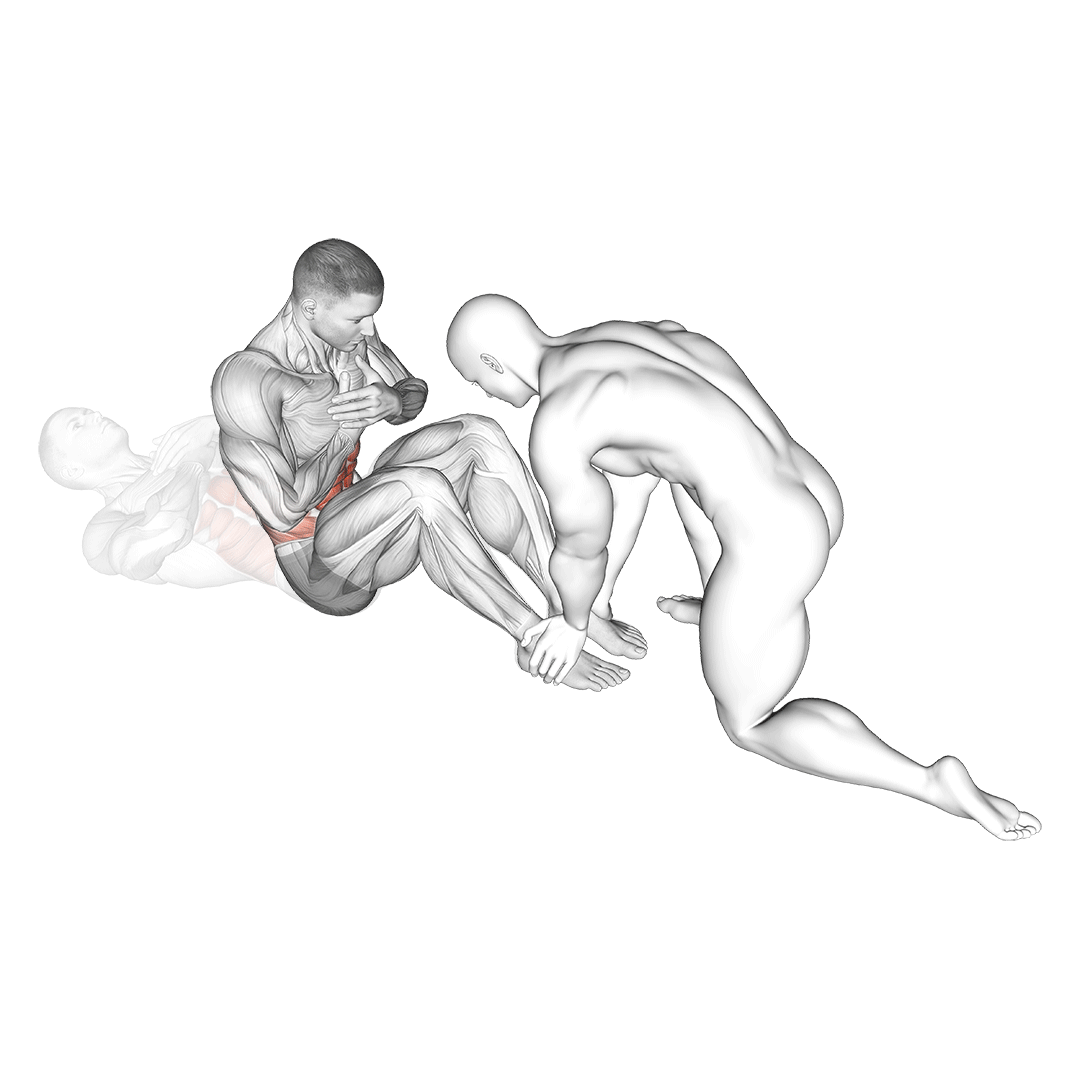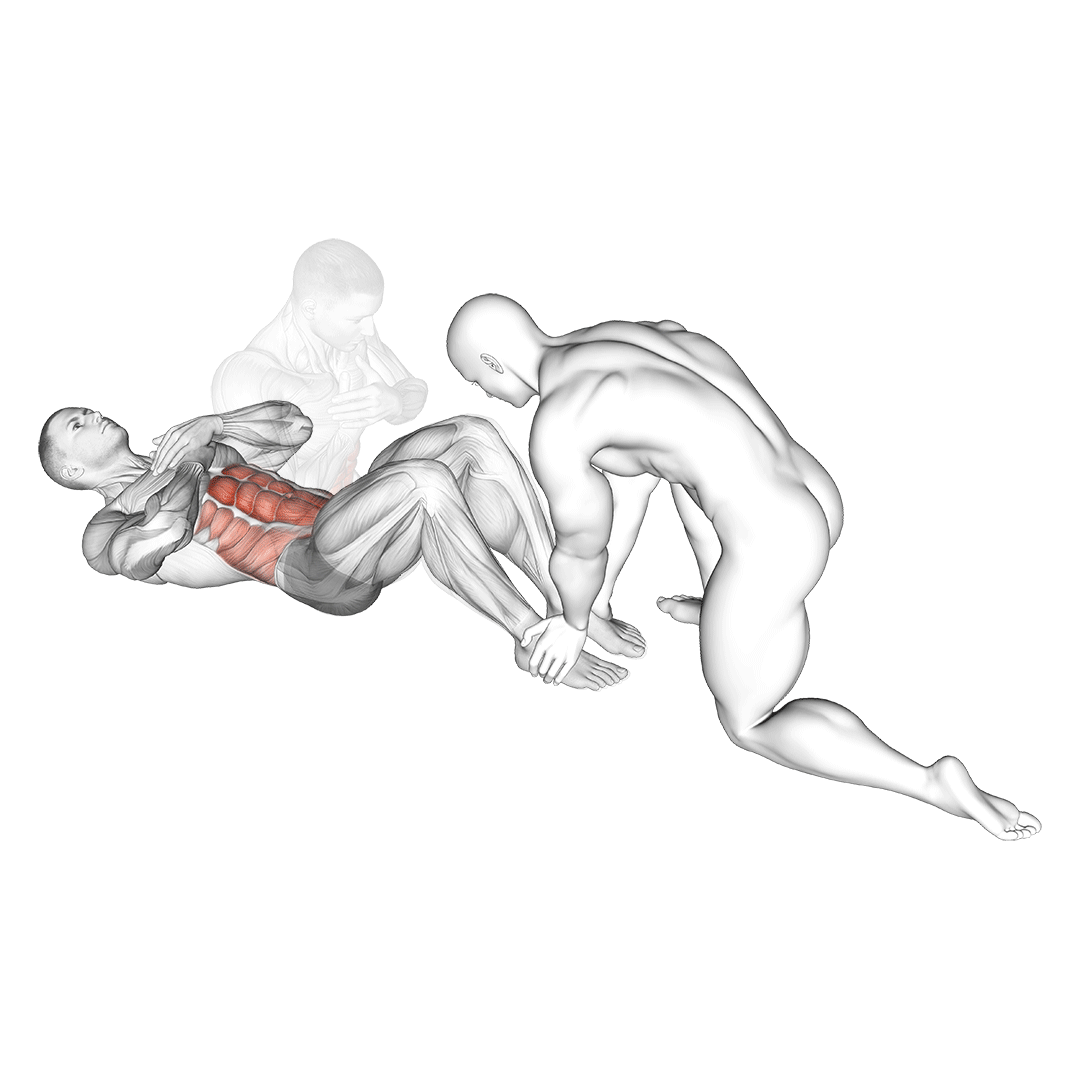
Begin by lying on your back on a mat with your knees bent and feet flat on the floor. Use an exercise ball or a partner to provide support behind your shoulders.
- Engage your core and place your hands behind your head, elbows out to the sides.
- With the support, gently lean back to the starting position, keeping your back straight.
- Inhale deeply and, as you exhale, use your abs to lift your torso towards your knees.
- Pause at the top of the movement for a moment, then slowly lower your body back down.
- Repeat for the desired number of repetitions, maintaining control throughout the movement.
Remember to exhale as you rise and inhale as you lower your body to maximize efficiency and support your core engagement.</p
Common Mistakes
- Not Engaging the Core: Failing to tighten your abdominal muscles before starting can lead to ineffective sit-ups. Always start by consciously engaging your core muscles to stabilize your body during the movement.
- Using Momentum: Relying on momentum rather than controlled movement can reduce the effectiveness of the exercise. Focus on using your abdominal muscles to lift your torso instead of swinging your body forward.
- Incorrect Head and Neck Position: Lifting your head or pulling on your neck can lead to strain. Keep your head aligned with your spine and gently support it with your hands without yanking.
- Insufficient Range of Motion: Only raising your torso slightly may prevent you from fully engaging the abs. Aim to lift your torso until it is approximately perpendicular to the floor for maximum engagement.
- Lack of Control During Lowering: Letting your body drop too quickly can cause injuries and reduce effectiveness. Focus on a slow and controlled descent to strengthen your core effectively.
Benefits of Mastering the Assisted Sit-Up for Stronger Abs
- Enhanced Core Strength: The assisted sit-up effectively targets the rectus abdominis and obliques, leading to improved core stability and strength. This foundational strength supports overall fitness and performance in various activities.
- Improved Posture: Engaging the core muscles during the assisted sit-up assists in developing better spinal alignment and posture. A strong core reduces the risk of slouching and associated musculoskeletal issues.
- Lower Back Support: By utilizing an exercise ball or partner for support during the movement, the assisted sit-up minimizes strain on the lower back. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with previous back injuries or those new to strength training.
- Increased Flexibility: The controlled movement of the sit-up promotes flexibility in the hip flexors and lower back. Regular practice can lead to an increased range of motion that enhances daily functional activities.
- Enhanced Breathing Technique: The emphasis on coordinated breathing during the exercise—exhaling during the lift and inhaling while returning to the starting position—helps develop better lung capacity and breathing efficiency, which are crucial in endurance activities.
Exercise Variations
Alternative Exercises
Safety Precautions
Before you begin the assisted sit-up, it’s crucial to make sure your body is properly warmed up. A few minutes of light cardiovascular activity, such as walking or dynamic stretches, can prepare your muscles and joints for the workout. This helps reduce the risk of injury and ensures that your body is ready to perform movements effectively.
During the exercise, maintain proper form to prevent strain on your back and neck. Keep your feet flat on the floor and ensure that your knees are bent at a comfortable angle. As you lift your torso, engage your core muscles fully and avoid pulling on your head or neck with your hands. Instead, let your abdominal muscles do the work to lift your body. This will help you achieve better results and minimize discomfort.
If you are using an exercise ball or a partner for support, ensure that they are stable and secure. The ball should be appropriately sized for your height, and if you use a partner, they should provide gentle and consistent support throughout the movement. If you feel any pain or discomfort during the exercise, stop immediately and reassess your form or take a break. Listening to your body is vital for avoiding injuries and ensuring a safe workout experience.
Interested in measuring your progress? Check out our strength standards for Sit Ups.
Tip: If you're signed in to Google, tap Follow.