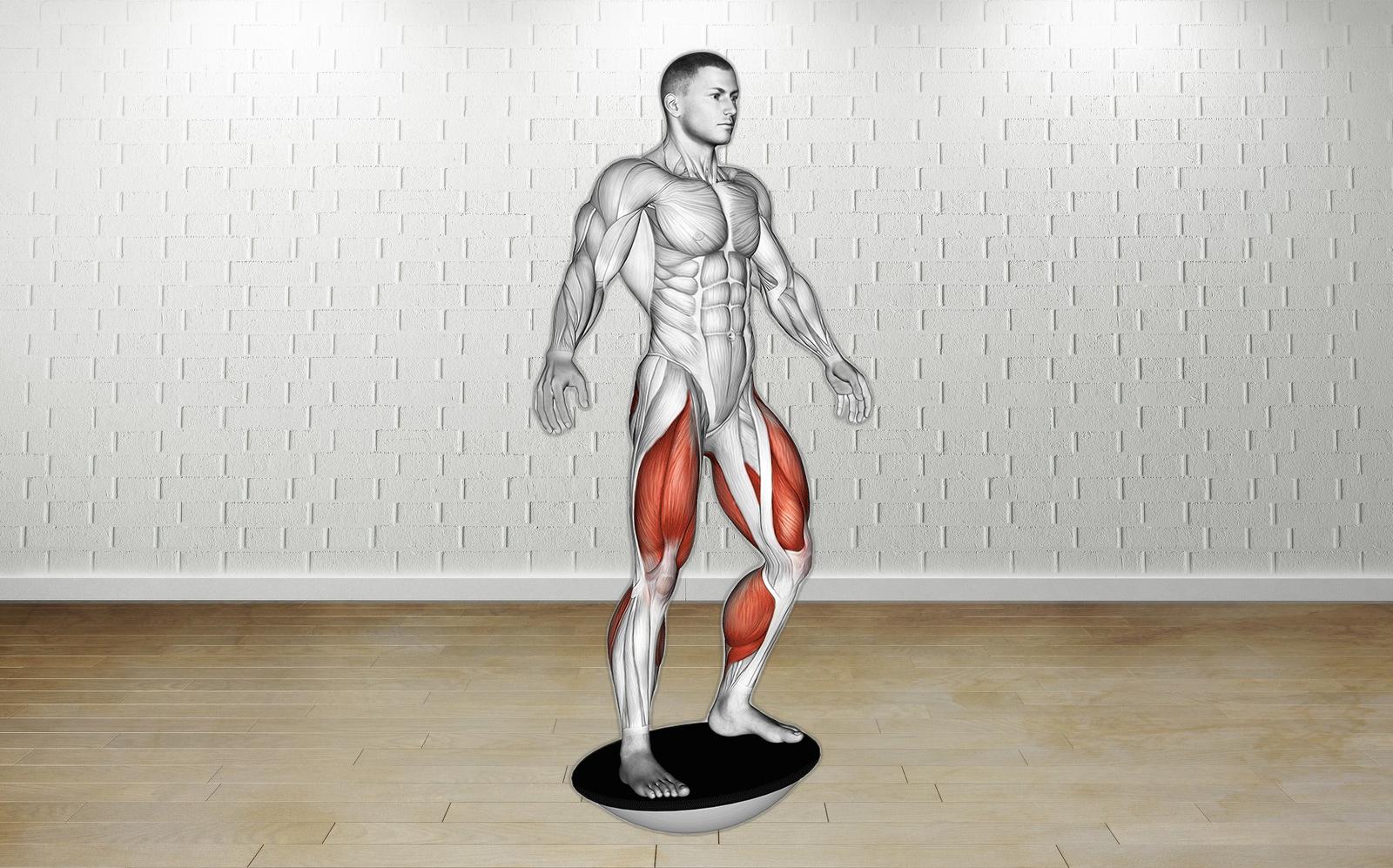
Elevate your fitness regimen with balance board workouts that specifically target your quadriceps while improving overall balance and stability. Whether you’re a teen athlete looking to boost sports performance or a senior aiming to maintain mobility, these workouts offer a fun and challenging way to enhance your fitness at any level.
Why Balance Board Workouts for Quads?
Balance board exercises engage your core muscles and place a strong emphasis on quadriceps strength—crucial for knee extension, walking, and squatting. Performing squats on a balance board forces your body to work harder to maintain stability, effectively activating auxiliary muscles and enhancing core strength.
How to Perform Balance Board Squats
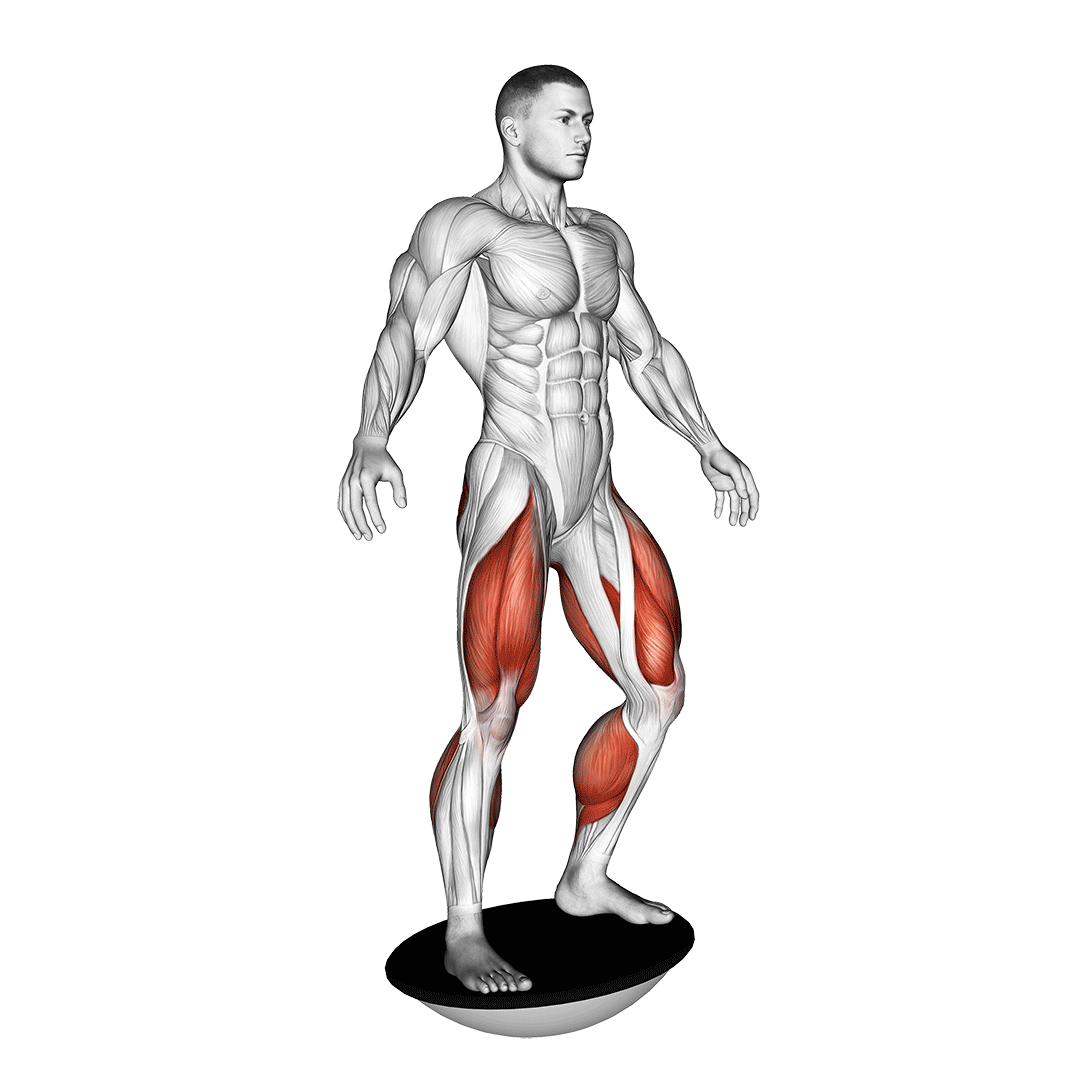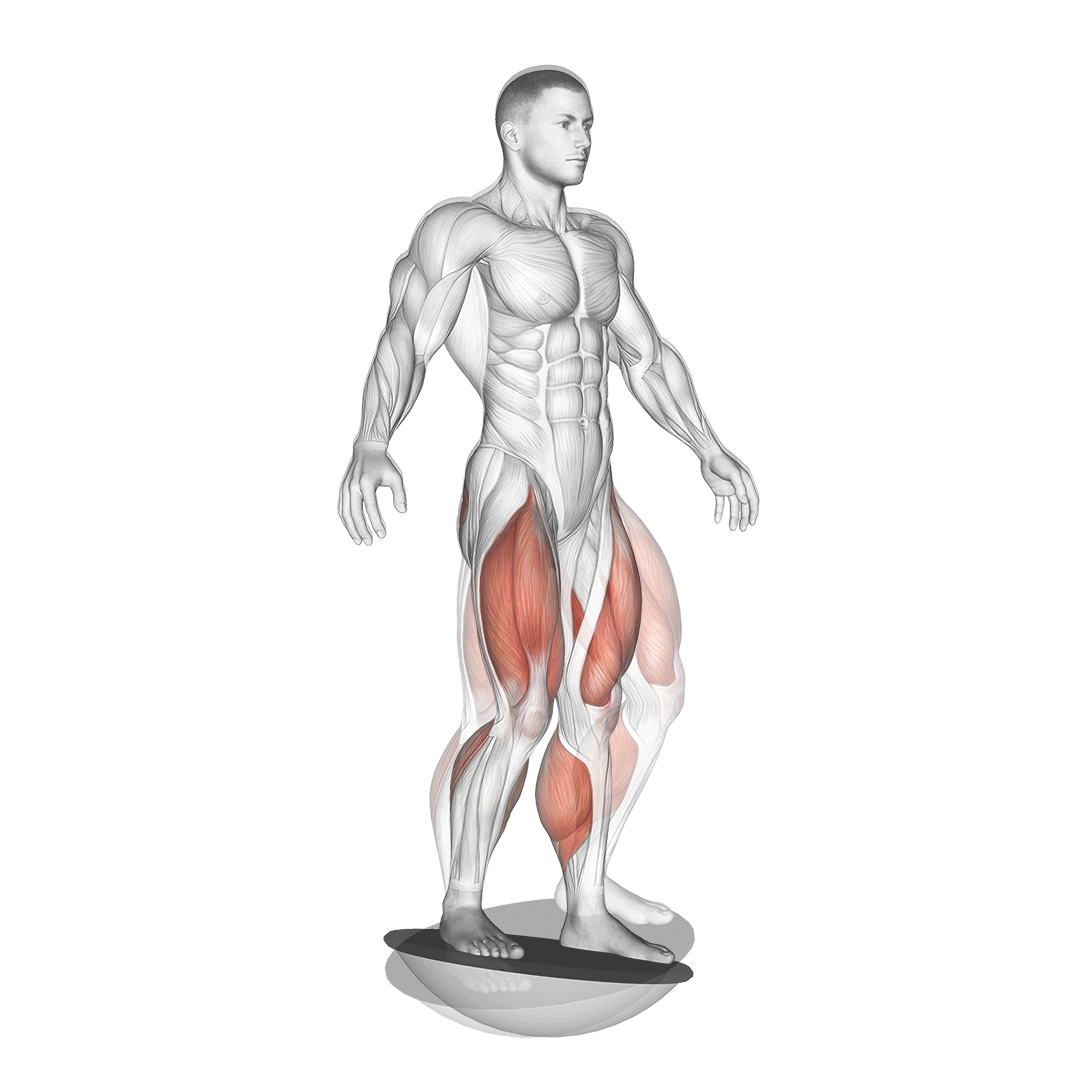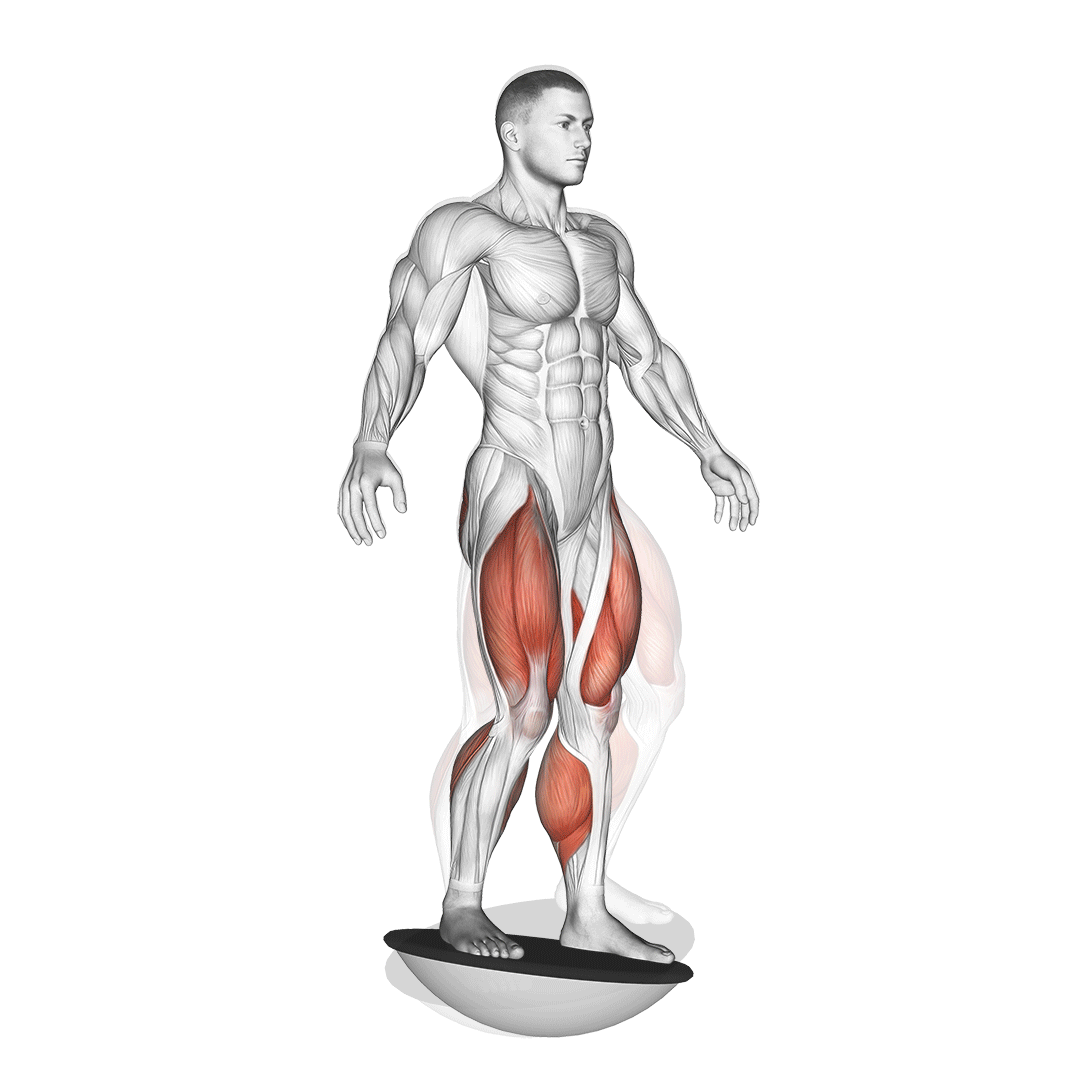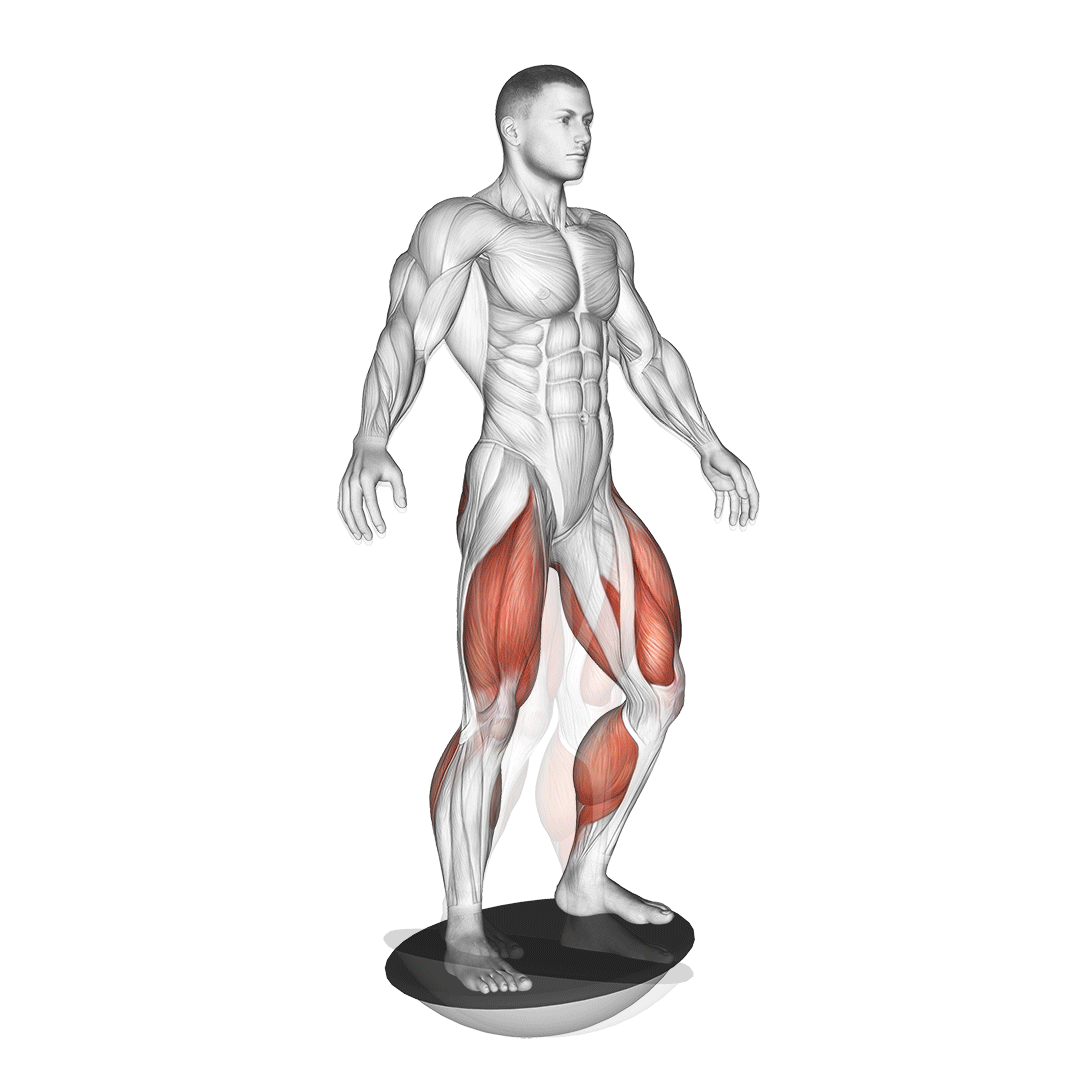
Begin by standing upright on a balance board with your feet shoulder-width apart, ensuring your weight is evenly distributed. Engage your core and maintain a straight posture.
- Slowly bend your knees and lower your body into a squat position, keeping your chest lifted and back straight.
- Ensure your knees are aligned over your toes as you descend.
- Hold the squat position momentarily, focusing on balance and stability.
- Gradually push through your heels to rise back to the starting position, maintaining control throughout the movement.
- Repeat for the desired number of repetitions, keeping your movements smooth and controlled.
Inhale as you lower into the squat and exhale as you rise back up. Aim to perform these workouts 2-3 times a week for optimal results.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Incorrect Foot Placement: Placing your feet too close or too wide can lead to instability. Always ensure your feet are shoulder-width apart and balanced on the board.
- Neglecting Core Engagement: Failing to activate your core muscles compromises balance. Tighten your abdominal muscles to maintain stability throughout the exercise.
- Knees Caving Inward: Allowing your knees to fall inward puts unnecessary stress on your joints. Keep your knees aligned with your toes to promote proper form and reduce injury risk.
- Leaning Forward: Excessive forward lean can throw off your balance. Maintain an upright posture with your chest up and hips back to distribute weight evenly.
- Rushing the Movement: Performing the exercise too quickly can compromise form and effectiveness. Focus on slow, controlled movements to maximize strengthening benefits.
Benefits
- Enhances Quad Strength: Effectively targets and builds the quadriceps, essential for overall leg strength.
- Improves Balance and Stability: Challenges your stability, leading to improved coordination and proprioception.
- Engages Core Muscles: Promotes a stronger core by requiring constant engagement for balance.
- Reduces Injury Risk: Strengthening the quads and improving balance help minimize the risk of knee and lower-body injuries.
- Boosts Athletic Performance: Enhanced quad strength and balance contribute to better performance in sports and physical activities.
Exercise Variations
Alternative Exercises
Safety Precautions
When engaging in balance board workouts, safety is paramount:
- Use a Stable Surface: Ensure the balance board is on a flat, non-slip surface to prevent falls.
- Clear Your Space: Remove any obstacles around you to avoid accidents.
- Warm Up Properly: Perform dynamic stretches and light cardio to prepare your muscles.
- Listen to Your Body: If you feel discomfort or struggle to maintain balance, take a break.
- Start with Support: Beginners should consider standing near a wall or sturdy object for added stability.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can beginners use a balance board for quad workouts?
Absolutely! Beginners can start by standing on the balance board near a wall or support to build confidence and stability before progressing to more challenging movements.
How often should I do balance board workouts?
Aiming for 2-3 sessions per week allows adequate time for muscle recovery while providing consistent benefits to quad strength and balance.
What type of balance board is best for these exercises?
A wobble board or rocker board works well for quad-focused exercises. Choose one that matches your fitness level and offers the right amount of challenge.
Can balance board workouts help with knee pain?
Strengthening the quadriceps can support knee health. However, if you have existing knee pain, consult a healthcare professional before starting new exercises.
Final Thoughts
Balance board workouts offer an engaging way to boost quad strength, enhance stability, and elevate your overall fitness journey. By incorporating these exercises into your routine, you’ll not only sculpt stronger thighs but also improve coordination and reduce injury risk. Remember to prioritize proper form and safety as you challenge yourself and progress.
Looking for more ways to enhance your lower body strength? Check out our guide on best leg exercises for comprehensive workouts.
Interested in measuring your progress? Check out our strength standards for Squat.
Tip: If you're signed in to Google, tap Follow.









