It’s not clear who first uttered the words “you are what you eat,” but they were definitely on to something.
Some people attribute this expression to Hippocrates, the Greek philosopher and the father of medicine, while others believe it was Jean Anthelme Brillat-Savarin, a French lawyer, politician, and famous gastronome.
Regardless of who it was, they spoke the truth!
Modern science has shown us that you really are what you eat. The food in your diet affects you at a cellular level and becomes part of your body, either structurally or as a fuel source.
So, if you eat plenty of healthy, nutritious food, your body will itself become healthy. Needless to say, functions such as building muscle and burning fat are more efficient when your body is working correctly.
In contrast, if you eat a lot of fatty, processed, unhealthy junk food, it should be no surprise that you gain weight and your health suffers.
This means that, regardless of your training goal, you need to pay as much attention to your diet as you do your workout program. In fact, you could end up sabotaging your progress by eating the wrong foods, even if you train with adequate intensity and consistency.
It’s beyond the scope of this article to provide you with a diet to follow. After all, we all have different food preferences, grocery budgets, and culinary skills, so what works for one person may not work for another.
That said, there are several foods that most bodybuilders should try and eat regularly. Start adding these foods to your existing diet while cutting back on junk food to get more from your training and achieve your body composition goals sooner.
Nine Foods That Every Bodybuilder Should Eat
Build muscle, burn fat, look better naked, and improve your health with the nine best foods for bodybuilders!
1. Broccoli
If you only eat one vegetable, broccoli should probably be it. Broccoli is a cruciferous vegetable, which means it has a cross-like structure. As well as being a valuable source of vitamins, minerals, and fiber, broccoli is high in anti-estrogenic compounds.
Bodybuilders need an abundance of testosterone to build muscle and burn fat. Elevated estrogen levels drive down testosterone, undermining your muscle-building and fat-burning efforts. So, it makes sense to try and keep a firm lid on your estrogen levels.
Eating broccoli can help lower estrogen (1), so testosterone levels are free to rise naturally.
In addition, broccoli is very low in calories, filling, and high in health-boosting antioxidants. It’s a bonafide superfood!
2. Oatmeal
Good old-fashioned oatmeal is the real breakfast of champions. High in slow-releasing carbs and fiber, oatmeal keeps you feeling fuller for longer, making it easier to stick to your healthy eating diet.
The fiber in oatmeal is good for all aspects of your health, including lowering your risk of bowel cancer, diverticulitis, and keeping your blood glucose levels low and stable, which is important for fat burning (2).
Also, oatmeal has been shown to be very heart-friendly and can help lower your cholesterol and triglycerides. Given how many bodybuilders are dying of heart disease and other cardiac problems, any additional protection has got to be worth pursuing.
However, not all oatmeal was created equal, and packets of instant oats are often loaded with sugar and powdered milk. So, instead, buy plain oats and prepare it yourself to enjoy all the benefits that oatmeal has to offer. Mix one part oats with two parts water or milk for the perfect bowl of oatmeal.
3. Salmon
Tuna is part of most bodybuilding diets. After all, it’s readily available, a good source of protein, and you can eat it straight from the can or pouch for a high-protein snack on the go. But, while tuna is undoubtedly a bodybuilding staple, salmon may be a better choice.
Salmon contains more omega-3 fatty acids than tuna, which is something every bodybuilder needs more of. Omega-3s can help reduce inflammation and lessen joint pain, which is something every bodybuilder knows all about.
In addition, salmon is very heart-healthy, and regular consumption is linked to a reduced risk of coronary heart disease.
Salmon is loaded with protein, and that protein is more biologically available than chicken, pork, or beef, making this oily fish the bodybuilder’s friend. Buy it in cans or pouches, try salmon jerky, or buy fresh salmon fillets, which are perfect for steaming, baking, grilling, and barbequing.
4. Spinach
There isn’t a bodybuilder alive who doesn’t train for the pump. This is when blood is forced into your muscles to make them swell. As well as making your muscles temporarily bigger, a pump is a factor in long-term muscle growth, as it floods your muscles with anabolic nutrients.
Getting a pump is partly dependent on vasodilation, where the blood vessels open up to facilitate increased blood flow. Nitric oxide, a chemical often included in pre-workouts, boosts vasodilation for a better pump.
However, spinach is also high in nitric acid and can help improve blood flow. This is not only good for getting a muscle pump but also enhances circulation all around your body, including your heart and reproductive organs (4). Yes – that’s right – spinach is natural Viagra!
In addition, spinach is high in iron, and iron plays a critical role in the formation and function of hemoglobin, which is the oxygen-carrying part of your blood cells. More hemoglobin means more oxygen for your muscles, allowing you to train harder and longer.
Eaten raw or lightly cooked, spinach is a green superfood that lives up to its promises, and it turns out that Popeye the Sailor was right!
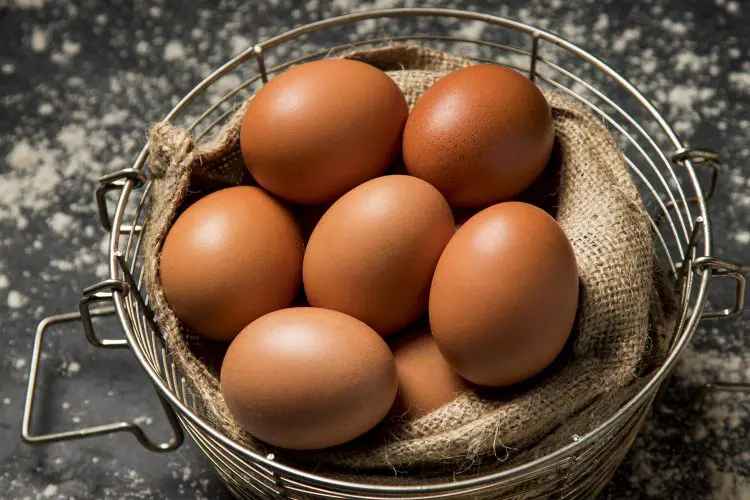
5. Eggs
Eggs are another food that most bodybuilders should eat in abundance. Eggs are a cheap and readily available source of muscle-building protein. They also contain fats and cholesterol, which are the building blocks of anabolic hormones.
And don’t worry – the cholesterol in eggs won’t have much of an impact on your serum cholesterol levels. When you eat high-cholesterol foods like eggs, your body responds by producing less.
While you can save some fat calories by eating just the whites and discarding the yolks, it’s worth mentioning that most of an egg’s nutrients are in the yellow part. Some studies even suggest that whole eggs are better for muscle building than eating just the whites (5). It seems that protein is absorbed and utilized more easily in the presence of fat.
There are lots of different ways to prepare eggs, and they’re all pretty quick and easy. But, regardless of how you cook them, eggs should be part of your bodybuilding diet.
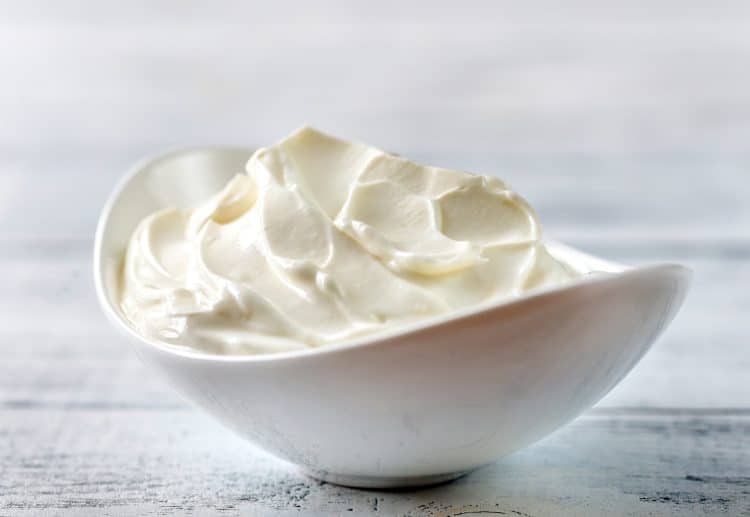
6. Greek Yogurt
While the taste can take some getting used to, plain Greek yogurt is another bodybuilding superfood.
Packed with protein (far more than standard yogurt), Greek yogurt is the perfect base for smoothies, can be used in place of cream to reduce calories, and is also high in probiotics. Probiotics are friendly bacteria found in your gut that have several important functions, including gut health, boosting immunity, and controlling cholesterol levels.
Greek yogurt contains several essential vitamins and minerals, including testosterone, immunity-boosting zinc, and fat-burning calcium.
Don’t be fooled into buying flavored Greek yogurt as, invariably, it’ll contain added sugar. Instead, stick to the plain, certified live stuff and then flavor it yourself with berries, sugar-free syrup, or even a scoop of whey protein.
Lactose intolerant? Good news! Greek yogurt is lower in lactose than most other dairy products, and the probiotics it contains actually help to digest lactose.
Read more about Greek yogurt here.
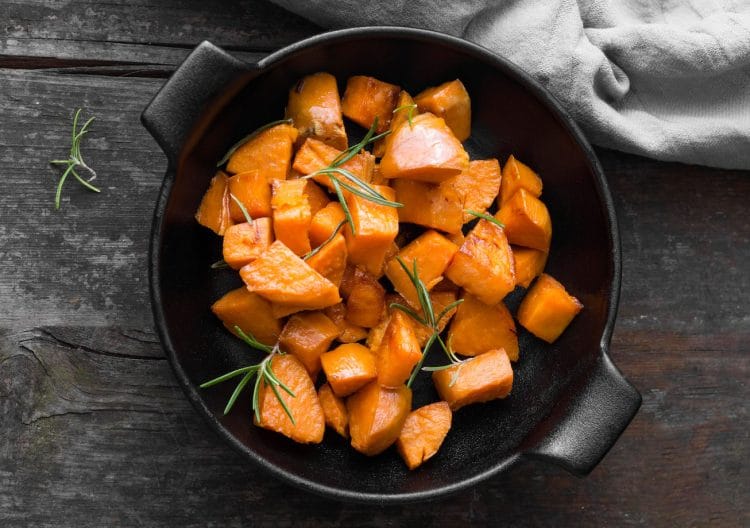
7. Sweet Potatoes
Muscle is not built with protein alone. You also need to eat carbohydrates. Carbs are your body’s primary source of energy during high-intensity training. They’re also your main source of vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
So, while you can go full keto and all but eliminate carbs from your diet, most people do better when they eat moderate amounts of carbohydrates.
That said, there are definitely “good” carbs and “bad” carbs. Bad carbs include refined wheat products, processed grains, sugar, trans fats, and other sources of empty calories and antinutrients.
Sweet potatoes are an excellent source of starchy (slow releasing) carbs, fiber, vitamins, and minerals, and they taste delicious, too. You can prepare sweet potatoes in several different ways, including mashed, baked, and made into savory wedges.
All in all, sweet potatoes are one of the best sources of carbs for bodybuilders – period!
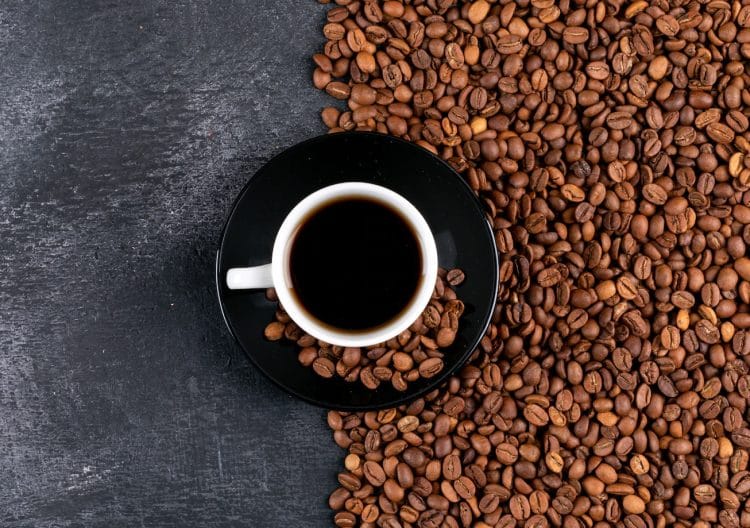
8. Coffee
Coffee is the world’s favorite beverage, and millions of people start their day with an energizing cup or two.
Coffee contains caffeine, which is a central nervous system stimulant that affects both your body and mind. In fact, up until the 1960s, caffeine was on the International Olympic Committee’s list of banned substances.
But coffee is more than a convenient source of energy – it’s also very good for you. It’s packed with antioxidants, has liver, colon, and lung health benefits, and can even lower your risk of heart disease and depression (6).
That said, not all coffees were created equal. For example, there is a massive difference between a cup of freshly brewed coffee and coffee-based beverages made with cream, sugar, syrup, and sprinkles. When it comes to getting benefits from coffee, it pays to be picky and consume the purest type you can.
Of course, if you are chugging coffee by the gallon to overcome a sleep deficit, you may be doing your body more harm than good. But, if you’re consuming 2-4 cups per day and still getting plenty of sleep, you’ll be glad to hear that there are no significant side effects to regular coffee use.
You can use coffee as a pre-workout energizer, too. Caffeine helps slow the onset of fatigue and also reduces exercise muscle pain, so you’ll be able to train harder and longer. That’s why so many pre-workout supplements contain big hits of caffeine.
However, those same pre-workouts may contain as much as 400mg of caffeine (about four cups’ worth), so they may be unnecessarily strong. Also, a cup of coffee is cheaper, contains more nutrients, and won’t leave you feeling anxious or nervous like some pre-workouts can.
Note: If you prefer to avoid caffeine, rest assured that decaffeinated coffee is also beneficial. It still contains an abundance of antioxidants, but no caffeine means no energizing effect.
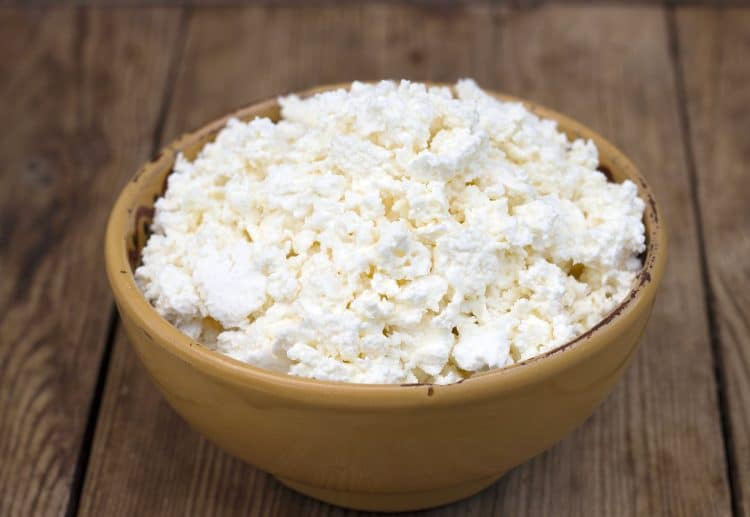
9. Cottage Cheese
Cottage cheese is another of those foods that some people love while others hate it. For sure, it does have an unusual taste and texture! But, if you can tolerate it, cottage cheese is an excellent source of slow-releasing protein caseinate, calcium, and various vitamins and minerals.
Like yogurt, you can eat cottage cheese straight from the tub, making it an ideal snack when you are on the go. Try adding a spoonful of fruit preserve to sweeten it and make it more enjoyable to eat. Alternatively, cottage cheese makes an excellent topping for baked potatoes.
So, whether you want to get lean or build muscle, low-fat, high-protein cottage cheese can help!
Wrapping Up
Whether you are cutting or bulking, your diet plays a big part in your success. After all, if you don’t supply your body with the nutrients it needs, it won’t have the building blocks necessary for muscle growth. Conversely, if your diet contains an excess number of calories, fat gain is all but inevitable.
So, while you are what you eat, you are also what you DON’T eat.
Consuming fewer refined carbs, less sugar, and minimal junk food means you’ll have more space in your diet for the foods that’ll do you good.
Start adding these nine foods to your diet to build muscle, burn fat, and look good naked!
References:
1 – PubMed: Altered estrogen metabolism and excretion in humans following consumption of indole-3-carbinol https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1656396/
2 – PubMed: Nutritional Advantages of Oats and Opportunities for Its Processing as Value Added Foods https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4325078/
3 – PubMed: The Effect of Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Patients with Active Rheumatoid Arthritis Receiving DMARDs Therapy: Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4965662/
4 – PubMed: Effects of a Short-Term High-Nitrate Diet on Exercise Performance https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5037521/
5 – PubMed: Consumption of Whole Eggs Promotes Greater Stimulation of Post-Exercise Muscle Protein Synthesis Than Consumption of Isonitrogenous Amounts of Egg Whites in Young Men https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28978542/
6 – British Medical Journal: Coffee Consumption and Health Meta-Analysis https://www.bmj.com/content/359/bmj.j5024