Building muscle is a process called hypertrophy. When you train, you cause microscopic damage to your muscles and deplete your glycogen stores. These events are the triggers that makes your muscles grow back bigger and stronger. That way, when you next train, your body is better prepared for the demands of your workout.
Of course, the next time you hit the gym, you do your best to pump out an extra rep or two or lift a little more weight. This causes yet more trauma, and so your muscles grow again. That’s why progressive resistance is so important; if you don’t make your workouts gradually more challenging, there is no stimulus for change.
Needless to say, this process is very slow. But, by training consistently, eating well, and getting enough rest and sleep, your muscles will grow.
Unfortunately, your body operates on the principle of use it or lose it. If you stop training, your muscles will gradually return to their pre-trained state, and you’ll lose size and strength. That’s why your workouts need to be consistent; you can’t store fitness!
In this article, we discuss the opposite of hypertrophy – atrophy – so you can understand what it is, how to avoid it, and how to bounce back after enforced layoffs.
What is Atrophy?
Your body is constantly breaking down and rebuilding itself. Breaking down is a catabolic process while building up is an anabolic process. For example, old cells are replaced with new ones, which is called autophagy.
Level Up Your Fitness: Join our 💪 strong community in Fitness Volt Newsletter. Get daily inspiration, expert-backed workouts, nutrition tips, the latest in strength sports, and the support you need to reach your goals. Subscribe for free!
Ideally, and especially if you are a bodybuilder, anabolism should exceed catabolism. Your workouts cause muscle breakdown, and your body responds by not just repairing that damage but super-compensating and making your muscles bigger and stronger.
This is a sort-of immunological response. Your body increases muscle size and strength to protect itself from further stress. It’s a form of self-preservation, like building calluses if you do a lot of manual labor, or a suntan to protect your skin from ultraviolet light damage (aka sunburn).
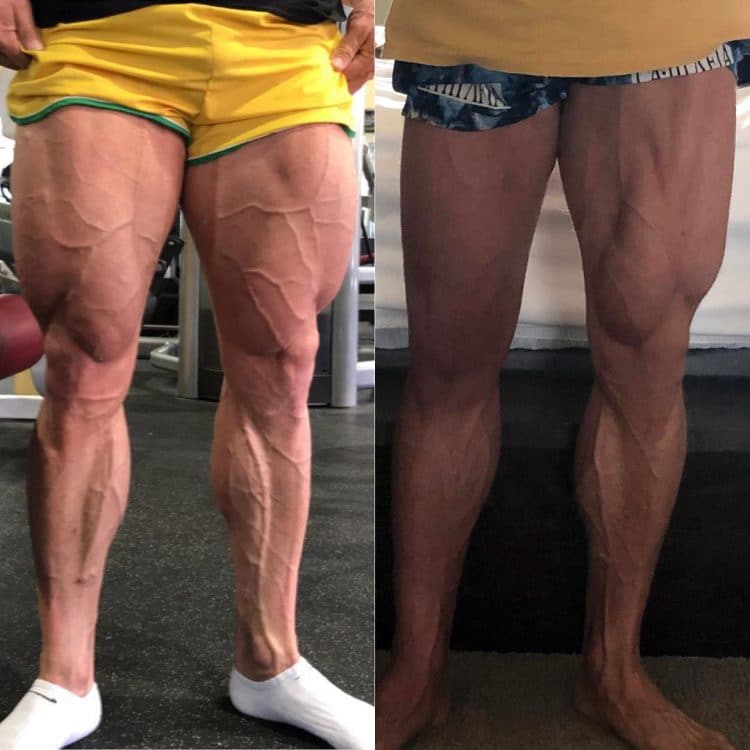
However, if you take a break from training, you remove the trigger for muscle growth, and your muscles will start to shrink. This is called atrophy.
Atrophy doesn’t happen immediately and can take several weeks to become noticeable. However, your muscles will get smaller and weaker over time until, eventually, they return to their pre-trained state.
Causes of Atrophy
Atrophy is caused mainly by disuse. Not just missing a couple of workouts or even taking a one-week vacation from training, but several weeks or months of inactivity.
Causes of atrophy include:
Lengthy breaks from training
When you train, your body sends signals to your muscles to get bigger and stronger. When you take a break from training, those signals are no longer sent, and your muscles respond by shrinking and getting weaker. Muscle atrophy caused by breaks from training is usually noticeable after 3-4 weeks, although it may be apparent sooner if you are forced into inactivity.
However, it’s worth noting that training just once a week may be enough to prevent muscle atrophy (1).
Illness
While it’s possible to train through minor illnesses, like a mild cold, more serious medical conditions may necessitate a more extended break from training. The less active you are, the more atrophy you will experience. For example, if you are confined to bed, you will lose muscle faster than someone who can still remain moderately active, even if they cannot train (2).
Injury
Most bodybuilders train around injuries. An elbow injury might mean you can’t do upper body workouts, but you can still train your legs. However, the muscles not being trained will experience some atrophy.
However, if an injury is so severe that the limb needs to be immobilized, e.g., put in a cast or sling, the affected muscles will atrophy much faster.
Muscle-wasting conditions
There are several conditions and diseases that cause muscle atrophy. Muscles wasting diseases include:
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
- Muscular dystrophy
- Multiple sclerosis (MS)
- Spinal muscular atrophy
- Peripheral neuropathy
- Stroke
If you experience unexplained muscle atrophy or weakness, especially if you are training consistently, consult your doctor to determine if there are any underlying medical reasons for muscle atrophy.
Aging

The aging process is usually accompanied by muscle atrophy. After the third decade, anabolic hormone production decreases, and catabolic metabolism starts to catch up and then exceed anabolism.
Continuing to train as you get older will help minimize atrophy, but like death and taxes, losing muscle is an inevitable part of the aging process (3). Age-related muscle atrophy is called sarcopenia.
How to Prevent Atrophy
It takes a lot of time, effort, and dedication to build muscle. Given a choice, your body would prefer to be soft and weak! So, if you are faced with a lengthy layoff from training, you’ll probably want to minimize atrophy and preserve your hard-won gains.
Depending on your circumstances, some atrophy may be inevitable. For example, you are confined to bed for two weeks because of illness.
However, in some cases, you may be able to reduce atrophy or prevent it entirely.
Assuming it is safe for you to do so, here are a few anti-atrophy strategies you can use to help preserve muscle mass:
Isometric contractions
While you might not be able to train, that doesn’t mean you can’t challenge your muscles with isometric contractions. During an isometric contraction, your muscles generate force but do not change in length, e.g., a wall squat.
If you are able, contracting your major muscles isometrically may help reduce the rate of atrophy and loss of strength (4).
Level Up Your Fitness: Join our 💪 strong community in Fitness Volt Newsletter. Get daily inspiration, expert-backed workouts, nutrition tips, the latest in strength sports, and the support you need to reach your goals. Subscribe for free!
Electro Myo-stimulation
Known as EMS for short, this is a type of treatment used by therapists to stimulate weak, flaccid muscles. Studies also suggest that EMS can be used to reduce atrophy (5).
EMS involves passing a mild electrical current through a muscle to trigger an involuntary contraction. TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation) works on a similar principle. There are EMS and TENS machines available for home use.
Try yoga

While serious lifters may balk at the idea of swapping barbells for Bikram, studies show that while yoga is not an effective muscle builder, it does trigger an increase in protein synthesis and could help preserve existing muscle mass (6).
If injury means you need to take a break from heavy strength training, doing yoga may help decrease atrophy. It’ll certainly improve your flexibility, mobility, and balance.
Related: The 7 Best Yoga Poses for Bodybuilders
Do just one workout a week
Most bodybuilders train anywhere from 3-6 times a week. That’s a big commitment of time and energy. But, if you don’t have time to train that frequently, it’s good to know that a single workout per week is all you need to preserve your existing muscle mass and avoid atrophy (1).
If you know you won’t have time to train more, just commit to hitting the gym once a week and doing a basic, full-body workout like this one:
| No. | Exercise | Sets | Reps |
| 1 | Squat | 3-5 | 6-8 |
| 2 | Bench press | 3-5 | 6-8 |
| 3 | Pull-up/chin-up | 3-5 | Max |
| 4 | Romanian deadlift | 3-5 | 8-12 |
| 5 | Overhead press | 3-5 | 8-12 |
While not the most perfectly balanced program, this short workout hits all your major muscle groups and should provide enough stimulation to prevent atrophy, even if you only have one hour a week to train.
Related: For more on time-pressed training, check out our Weekend Warrior Workout.
Train the non-injured side of your body
If you are unable to train one limb, evidence suggests that training the opposite side of your body could help preserve muscle mass on the side you cannot use (8). For example, if you break your left arm, doing curls, pushdowns, and presses with your right arm could help maintain some muscle mass and strength on the injured side.
Read more about unilateral exercises here.
Take creatine

Creatine is the most popular, well-researched supplement in the world. Among its many benefits, studies reveal that creatine can help reduce sarcopenia in the elderly. As such, it may help minimize atrophy in younger people. As creatine is a naturally-occurring substance, cheap and safe for most people to use, it’s worth taking it to try and reduce atrophy during a break from training.
Related: Best Creatine Supplements of Reviewed & Ranked
Remain active
Even if you can’t train, staying active could help reduce muscle atrophy. For example, walking is a viable way to preserve lower body muscle mass and strength even if you can’t lift weights. Swimming would do much the same for your upper body. Atrophy is always quicker during inactivity.
Muscle Atrophy – Wrapping Up
Muscle atrophy is often unavoidable. Enforced layoffs from training due to illness and injury are just a part of life. Use the strategies in this article to minimize atrophy and preserve your existing muscle mass.
While atrophy can be disheartening, it’s also important to remember that, because of a phenomenon called muscle memory, you’ll soon bounce back and regain lost muscle when you return to training (9).
However, after any lengthy layoff, it’s important to remember that you are no longer as fit or strong as you were, and your workouts should reflect this. Don’t jump back into the same training program you were using before your break; that’s a recipe for injury.
Instead, adopt a beginner mindset and return to training gradually. Increase workout volume and intensity over several weeks to avoid crippling delayed onset muscle soreness or reinjury.
References:
1. PubMed: Exercise dosing to retain resistance training adaptations in young and older adults https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21131862/
2. PubMed: The impact of extended bed rest on the musculoskeletal system in the critical care environment https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4600281/
3. PubMed: Strength and muscle mass loss with the aging process. Age and strength loss https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3940510/
4. PubMed: Muscle damage produced by isometric contractions in human elbow flexors https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29074710/
5. PubMed: Electromyo-stimulation to fight atrophy and to build muscle: facts and numbers https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6104107/
6. PubMed: Routine yoga practice impacts whole-body protein utilization in healthy women https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28422542/
7. PubMed: Muscular Atrophy and Sarcopenia in the Elderly: Is There a Role for Creatine Supplementation? https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31652853/
8. American Physiological Society: Unilateral strength training leads to muscle-specific sparing effects during opposite homologous limb immobilization https://journals.physiology.org/doi/full/10.1152/japplphysiol.00971.2017
9. PubMed: Myonuclei acquired by overload exercise precede hypertrophy and are not lost on detraining https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2930527/