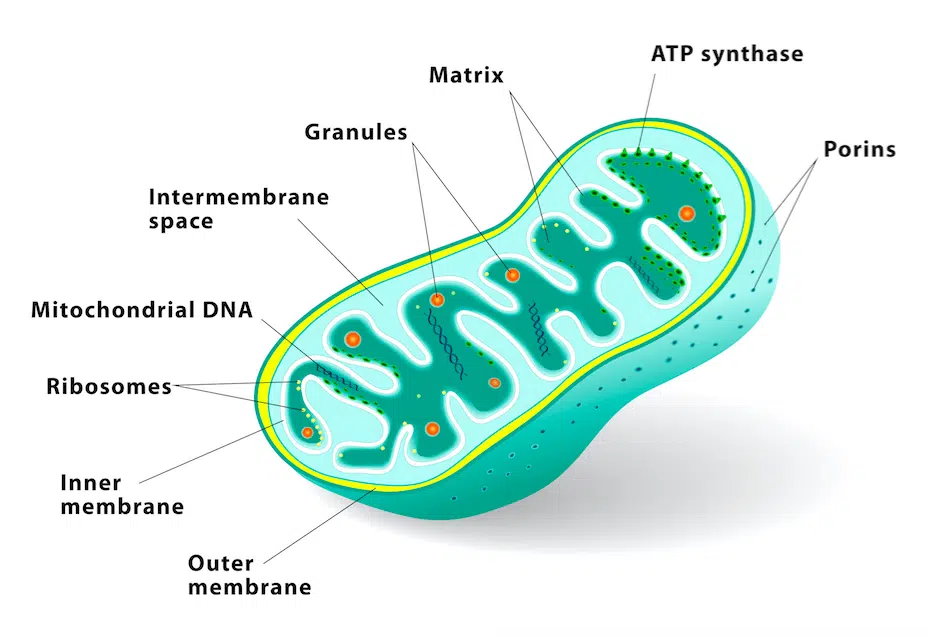
Mitochondria are the energy powerhouses within our cells that convert nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which fuels all cellular functions. Optimizing mitochondrial health and density is essential for building muscle, enhancing strength and endurance, boosting fat loss, and improving overall health.
What Are Mitochondria and Why Are They So Important?
Mitochondria are tiny oval-shaped organelles found in large numbers within almost every cell of the body. Ranging in size from 0.5 to 10 micrometers, a single human cell can contain well over 100,000 mitochondria, comprising up to 35% of the cell’s volume in high energy tissues like heart and skeletal muscle [1].
The primary role of mitochondria is to produce ATP through a process called cellular respiration or oxidative phosphorylation. This ATP provides immediate energy to power all metabolic processes in the body.
Without healthy functional mitochondria, we simply wouldn’t have the energy to move, think, breathe, or even live. That’s why optimizing mitochondrial health is absolutely essential.
Research shows that increasing mitochondrial density directly enhances muscular endurance, power output, strength, and growth [2]. More mitochondria allow your muscles to more efficiently take up nutrients, utilize oxygen, and generate ATP to sustain repeated contractions. This leads to significant gains in strength and endurance.
Beyond energy production, mitochondria play integral roles in:
- Metabolic regulation – They help control the metabolism of fats, carbohydrates, proteins, and micronutrients.
- Hormone and neurotransmitter synthesis – Mitochondria regulate the biosynthesis of thyroid hormone, estrogen, testosterone, serotonin, dopamine, and melatonin [3].
- Detoxification – They neutralize toxic byproducts of cellular metabolism like ammonia and destructive reactive oxygen species [4].
- Apoptosis – Mitochondria control the intrinsic pathway of programmed cell death.
- Genetic inheritance – Mitochondria have their own DNA distinct from nuclear DNA that is solely passed down maternally [5].
- Immune function – Mitochondria produce signaling molecules that activate immune cells and trigger defense pathways [6].
- Heart function – Up to 35% of cardiac cell volume is occupied by mitochondria, underscoring their importance for heart health [7].
It’s clear that optimizing mitochondrial health provides immense whole-body benefits beyond just building muscle and burning fat. Supporting mitochondrial function should be a priority for overall health, longevity, and disease prevention.
How To Increase Mitochondrial Biogenesis Naturally
Exercise and specific dietary factors powerfully stimulate mitochondrial biogenesis – the growth of new mitochondria [9].
This occurs by activating gene expression and cell signaling pathways that trigger mitochondrial formation, differentiation, and growth.
Applying science-backed strategies to enhance mitochondrial density and function leads to direct improvements in body composition, athletic performance, cognition, and work capacity.
Exercise That Maximizes Mitochondrial Adaptations
- High-intensity interval training (HIIT) – Alternating short bursts of intense activity with rest periods potently activates PGC-1α and downstream pathways to increase mitochondrial biogenesis [10]. Sprinting is an ideal form of HIIT to drive mitochondrial growth.
- Resistance training – Lifting heavier weights (~60-80% 1RM) in lower rep ranges helps recruit fast-twitch muscle fibers which have 5-10X higher mitochondrial density than slow-twitch fibers [11]. This provides a strong mitochondrial stimulus.
- Low-moderate intensity training – Longer duration aerobic activity like jogging or cycling done for 30-90 minutes 3-5 days per week stimulates mitochondrial adaptation and promotes fat burning [12].
Dietary Strategies To Increase Mitochondrial Biogenesis
- Caloric restriction – Reducing calorie intake 15-30% below maintenance powerfully activates SIRT1, PGC-1α, and other signaling molecules that trigger mitochondrial biogenesis [13].
- Ketogenic dieting – Consuming very low carb, high fat ketogenic diets provides an alternative fat-based fuel source for mitochondria while enhancing their efficiency [14].
- Intermittent fasting – Periodic fasting for 16+ hours stimulates gene expression and cell signaling pathways that activate mitochondrial biogenesis [15].
- Polyphenols – Abundant in tea, coffee, red wine, blueberries, broccoli sprouts and other plants. Polyphenols directly activate SIRT1 and PGC-1α which increase mitochondrial biogenesis [16].
Key Supplements To Enhance Mitochondrial Function
- Coenzyme Q10 – Shuttles electrons in the electron transport chain to facilitate ATP synthesis. Levels decline with age [17].
- PQQ – Stimulates mitochondrial biogenesis by activating PGC-1α, the master regulator of mitochondrial function [18].
- Alpha-lipoic acid – Powerful antioxidant that also serves as a mitochondrial cofactor in energy production [19].
- D-Ribose – Provides raw material for the rapid regeneration of ATP to restore cellular energy [20].
- L-Carnitine – Transports long-chain fatty acids into the mitochondrial matrix to be burned for energy [21].
- B vitamins – Including niacin (B3), pyridoxine (B6), methylcobalamin (B12). Essential cofactors in mitochondrial energy metabolism [22].
Optimize Mitochondria for Maximum Performance and Health
Focusing on mitochondrial health provides a direct pathway to achieving your body composition, performance, and longevity goals.
Implementing science-backed strategies to increase mitochondrial biogenesis will allow you to:
- ✅ Lose fat by upregulating mitochondrial fat oxidation and energy expenditure
- ✅ Build muscle by enhancing cellular energy capacity for growth
- ✅ Increase strength through improved neuromuscular function
- ✅ Improve endurance via greater ATP generation and resistance to fatigue
- ✅ Enhance work capacity by reducing lactate accumulation and accelerating recovery
- ✅ Boost cognition by increasing brain energy metabolism [23]
- ✅ Combat aging by enhancing mitochondrial function and biogenesis [24]
Optimizing mitochondria also supports cardiovascular and metabolic health, immune function, and overall wellbeing.
Make mitochondrial support a top priority by incorporating targeted exercise, nutrition, and supplementation. Dramatically boost your energy levels, torch fat, build muscle, enhance cognitive performance, and optimize health by harnessing the power of your cellular power plants!
FAQs
How long does it take to increase mitochondrial density through training?
Research shows that just 6 sessions of high-intensity interval training over 2 weeks significantly increased mitochondrial protein synthesis and mitochondrial enzyme activity [26]. Consistent training continues to augment mitochondrial density and function over months.
What is the best type of exercise to increase mitochondria?
High-intensity interval training (HIIT) and heavy resistance training provide the strongest signals for mitochondrial biogenesis. But all exercise stimulates mitochondrial growth to some degree.
What foods boost mitochondrial function?
Key mitochondria-supporting foods include fatty fish, dark leafy greens, avocados, olive oil, berries, cruciferous vegetables, dairy, tea/coffee, dark chocolate, and citrus fruits.
How can I test my mitochondrial function?
VO2 max testing analyzes respiratory capacity during graded exercise to assess mitochondrial fitness. Blood lactate levels also provide insight on mitochondrial function. Genetic tests like 23andMe map mitochondrial DNA markers.
Learn more about Creatine:
- The 5 Supplements Worth Taking (And Another Five That Aren't)
- Creatine Before and After: How Creatine Supplement Affects Your Body
- I’m a Supplement Researcher — These 3 Creatine Forms Will Supercharge Your Gains (and One’s a Total Rip-Off)
- Creatine and Acne: Are You Making This Common Mistake?
- STOP Wasting Your Creatine! The Ultimate Guide to Proper Usage
- How Long Does Creatine Stay in Your System? A Doctor Explains
- What Happens To Your Body When You Take Creatine Every Day For Muscle Gain?
- Creatine + Whey Synergy: The Science Behind This Power Duo's Muscle-Building Magic
Conclusion
Mitochondria are microscopic organelles that generate energy within our cells to power all metabolic functions. Supporting mitochondrial health and biogenesis through exercise, diet, and supplementation provides immense whole-body benefits.
Increasing mitochondrial density enhances muscular strength, endurance, power output, and growth. It accelerates fat loss, boosts cognition, improves heart health, and combats aging.
By applying science-backed strategies to optimize mitochondria, you can achieve your body composition goals while also supporting overall health, performance, and longevity.
Happy Lifting!
References:
[1] Netzer WJ, Powell C, Nong Y, Blundell J, Wong L, Duff K, Flajolet M, Greengard P. Lowering beta-amyloid levels rescues learning and memory in a Down syndrome mouse model. PLoS One. 2010 Jun 3;5(6):e10943. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010943. PMID: 20532168; PMCID: PMC2880593. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2880593/
[2] Turchinovich, A., Baranova, A., Drapkina, O., & Tonevitsky, A. (2018, August 20). Cell-Free Circulating Nucleic Acids as Early Biomarkers for NAFLD and NAFLD-Associated Disorders. Frontiers. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.01256
[3] Fraser AJ, Webster TF, Watkins DJ, Strynar MJ, Kato K, Calafat AM, Vieira VM, McClean MD. Polyfluorinated compounds in dust from homes, offices, and vehicles as predictors of concentrations in office workers’ serum. Environ Int. 2013 Oct;60:128-36. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2013.08.012. Epub 2013 Sep 14. PMID: 24041736; PMCID: PMC3904429. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3904429/
[4] Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, Fan W, Georges GE, Schwartz JL, Kepler CM, Lee H, Suchanek AL, Cronk MR, Brumbaugh A, Engel JH, Yukawa M, Zhao LP, Heimfeld S, Stirewalt DL. Identification of radiation-induced expression changes in nonimmortalized human T cells. Radiat Res. 2011 Feb;175(2):172-84. doi: 10.1667/rr1977.1. Epub 2010 Nov 17. PMID: 21268710; PMCID: PMC3136539. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3136539/
[5] Goodyear RJ, Legan PK, Christiansen JR, Xia B, Korchagina J, Gale JE, Warchol ME, Corwin JT, Richardson GP. Identification of the hair cell soma-1 antigen, HCS-1, as otoferlin. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2010 Dec;11(4):573-86. doi: 10.1007/s10162-010-0231-6. Epub 2010 Aug 31. PMID: 20809368; PMCID: PMC2975885. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2975885/
[6] Netzer WJ, Powell C, Nong Y, Blundell J, Wong L, Duff K, Flajolet M, Greengard P. Lowering beta-amyloid levels rescues learning and memory in a Down syndrome mouse model. PLoS One. 2010 Jun 3;5(6):e10943. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010943. PMID: 20532168; PMCID: PMC2880593. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2880593/
[7] Netzer WJ, Powell C, Nong Y, Blundell J, Wong L, Duff K, Flajolet M, Greengard P. Lowering beta-amyloid levels rescues learning and memory in a Down syndrome mouse model. PLoS One. 2010 Jun 3;5(6):e10943. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010943. PMID: 20532168; PMCID: PMC2880593. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2880593/
[8] Netzer WJ, Powell C, Nong Y, Blundell J, Wong L, Duff K, Flajolet M, Greengard P. Lowering beta-amyloid levels rescues learning and memory in a Down syndrome mouse model. PLoS One. 2010 Jun 3;5(6):e10943. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010943. PMID: 20532168; PMCID: PMC2880593. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2880593/
[11] Early Time-Restricted Feeding Improves Insulin Sensitivity, Blood Pressure, and Oxidative Stress Even without Weight Loss in Men with Prediabetes. (2018, May 10). Early Time-Restricted Feeding Improves Insulin Sensitivity, Blood Pressure, and Oxidative Stress Even Without Weight Loss in Men With Prediabetes – ScienceDirect. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2018.04.010 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1550413118302535
[12] Bond, S. T., Kim, J., Calkin, A. C., & Drew, B. G. (2019, April 17). The Antioxidant Moiety of MitoQ Imparts Minimal Metabolic Effects in Adipose Tissue of High Fat Fed Mice. Frontiers. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2019.00543 https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphys.2019.00543/full
[13] Li L, Wang Z, Zuo Z. Chronic intermittent fasting improves cognitive functions and brain structures in mice. PLoS One. 2013 Jun 3;8(6):e66069. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066069. PMID: 23755298; PMCID: PMC3670843. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3670843/
[14] Alencar CM, Pedrinha VF, Araújo JLN, Esteves RA, Silva da Silveira AD, Silva CM. Effect of 10% Strontium Chloride and 5% Potassium Nitrate with Fluoride on Bleached Bovine Enamel. Open Dent J. 2017 Aug 31;11:476-484. doi: 10.2174/1874210601711010476. PMID: 28979576; PMCID: PMC5611777. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5611777/
[15] Koppe SW, Elias M, Moseley RH, Green RM. Trans fat feeding results in higher serum alanine aminotransferase and increased insulin resistance compared with a standard murine high-fat diet. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2009 Aug;297(2):G378-84. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.90543.2008. Epub 2009 Jun 18. PMID: 19541924; PMCID: PMC2724085. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2724085/
[18] Coenzyme Q10. (2014, April 28). Linus Pauling Institute. https://lpi.oregonstate.edu/mic/dietary-factors/coenzyme-Q10#function
[19] Bazar G, Kovacs Z, Tsenkova R. Evaluating Spectral Signals to Identify Spectral Error. PLoS One. 2016 Jan 5;11(1):e0146249. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146249. PMID: 26731541; PMCID: PMC4701180. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4701180/
[20] Shomstein S, Behrmann M. Object-based attention: strength of object representation and attentional guidance. Percept Psychophys. 2008 Jan;70(1):132-44. doi: 10.3758/pp.70.1.132. PMID: 18306967; PMCID: PMC2739629. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2739629/
[21] Toprani VM, Sahni N, Hickey JM, Robertson GA, Middaugh CR, Joshi SB, Volkin DB. Development of a candidate stabilizing formulation for bulk storage of a double mutant heat labile toxin (dmLT) protein based adjuvant. Vaccine. 2017 Oct 4;35(41):5471-5480. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2017.03.101. Epub 2017 May 24. PMID: 28551040; PMCID: PMC5628956. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5628956/
[22] Sahlin K. Boosting fat burning with carnitine: an old friend comes out from the shadow. J Physiol. 2011 Apr 1;589(Pt 7):1509-10. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2011.205815. PMID: 21486835; PMCID: PMC3099008. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3099008/
[24] Mueller JW, Gilligan LC, Idkowiak J, Arlt W, Foster PA. The Regulation of Steroid Action by Sulfation and Desulfation. Endocr Rev. 2015 Oct;36(5):526-63. doi: 10.1210/er.2015-1036. Epub 2015 Jul 27. PMID: 26213785; PMCID: PMC4591525. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4591525/
[25] Glick D, Barth S, Macleod KF. Autophagy: cellular and molecular mechanisms. J Pathol. 2010 May;221(1):3-12. doi: 10.1002/path.2697. PMID: 20225336; PMCID: PMC2990190. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2990190/
Tip: If you're signed in to Google, tap Follow.