Let’s get one thing straight from the outset; this is NOT an article about steroids! Most steroids are artificial forms of testosterone. Some bodybuilders and athletes take steroids to raise their testosterone levels far beyond what is possible naturally, although some are less than honest about their steroid use!
While it’s clear that “being on the juice” will have a significant impact on strength and appearance, it can also be very dangerous, especially if used in massive amounts or for long periods.
Instead, this article is about natural testosterone production and what you can do to boost your levels naturally.
What is Testosterone, Anyway?
Testosterone is a hormone or chemical messenger that tells specific cells in your body how to act. Both men and women produce testosterone, but men have around ten times more testosterone than women. Testosterone, sometimes called T, is essential for building muscle and staying lean, so it’s in your best interest to understand this crucial hormone.
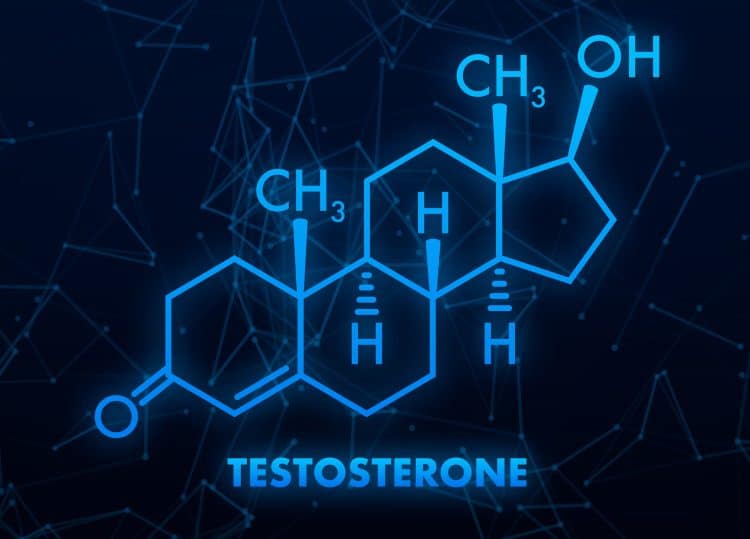
Testosterone is both anabolic and androgenic. Anabolic means it aids in muscle growth, while androgenic refers to the development of secondary male characteristics such as body hair, deep voice, and sex drive.
Your testosterone levels peak in your mid to late twenties and then start a slow and gradual decline.
Several factors can accelerate this decline, including a poor diet, excessive cardio, heavy smoking, testicular trauma, exposure to toxins, being overweight, and consuming too many estrogen-forming foods, such as soy.
If your testosterone levels fall too low, you might suffer from a condition called andropause.
Andropause leads to very low T-levels and is typically treated with hormone replacement therapy (HRT), including testosterone gel, patches, or injections – essentially doctor-prescribed steroids in therapeutic doses.
Moderately low testosterone levels often go undiagnosed and untreated. Many men live with below-average testosterone levels, feeling less formidable than they should without experiencing full-blown andropause.
If you have any of the following symptoms, you might have low testosterone levels:
- Reduced sex drive
- Fatigue
- Reduced motivation
- Difficulty building muscle
- Difficulty losing weight
- Mood swings
- Difficulty sleeping
- Difficulty concentrating
- Forgetfulness
- Decreased bone mass
- Loss of body hair/reduced need to shave
- Hot flushes/sweats
Needless to say, no man should go through life feeling like this.
If you suspect low testosterone levels, your first step should be consulting your doctor.
A simple saliva or blood test will reveal if your T-levels are normal or low. If they are very low and you are suffering from andropause, you may be a candidate for HRT.
However, it’s important to note that HRT only treats the symptom of low testosterone and not the cause. If you are not interested in having children, HRT can be a good solution, though it is not entirely risk-free. If you still want to have children, avoid HRT due to its contraceptive effect.
If HRT is not for you, several things can boost your testosterone levels naturally and get your testes working more efficiently.
10 Ways to Boost Testosterone Naturally
Boosting your testosterone levels requires a holistic approach. It’s not enough to simply eat “superfoods” or take a few supplements.
Your lifestyle, diet, and exercise regime all need to be aligned to increase your testosterone levels.
Use the following strategies to increase natural testosterone production.
1. Increase your intake of quality fats
Fat is often said to be unhealthy due to its links to heart disease, weight gain, and other health problems.

However, fat also plays a vital role in testosterone production. Fat and cholesterol are essential for synthesizing many hormones, including testosterone.
The issue with the “all fat is bad” mindset is that it overlooks the fact that there are different types of fat, some better for you than others. Trans fats are very unhealthy and linked to numerous illnesses, whereas essential fatty acids (EFAs) are very healthy and necessary for your body.
The best fats for increasing testosterone levels include:
- Olive oil
- Fish oil
- Coconut oil
- Egg yolks
- Nuts and seeds
- Avocados
Studies suggest low-fat diets might contribute to low testosterone levels (1). Consuming plenty of healthy fats can help increase your testosterone levels by providing the building blocks needed for hormone synthesis.
2. Lift heavy at the gym
To build muscle, you need to hit the gym and have adequate testosterone. If your T-levels are low, it doesn’t mean your workouts are pointless.
With a few modifications, your gym routine can help increase your testosterone levels, making your workouts more effective.
To turn your workout into a T-booster, follow these guidelines:
- Focus on large muscle groups, like your legs, chest, and back
- Use primarily compound exercises like squats and deadlifts, not leg extensions and curls
- Use heavy weights, aiming for 6-8 reps per set
- Use short rests between sets, ideally 1-2 minutes
- Train 3-4 times per week for adequate recovery
- Keep workouts to an hour or less
Golden-era bodybuilders trained like this and built incredible physiques without steroids or supplements. Research suggests these workouts helped optimize their testosterone levels naturally (2).
3. Get more sleep
Many people see sleep as a luxury, often sacrificing it for work and family commitments. However, less than the recommended eight hours of sleep per night can harm your health.
Studies on military personnel link sleep deprivation to lower testosterone levels, making sleep essential for boosting testosterone (3).
During sleep, your body recovers from daily stress, increasing testosterone and growth hormone levels. Lack of sleep reduces this anabolic hormone production window, lowering testosterone.
Too little sleep also raises cortisol levels, a stress hormone that breaks down muscle, suppresses testosterone, and increases fat storage. In short, insufficient sleep harms your T-levels.
Getting enough sleep starts with going to bed earlier. Calculate eight hours back from when you need to wake up to determine your bedtime.
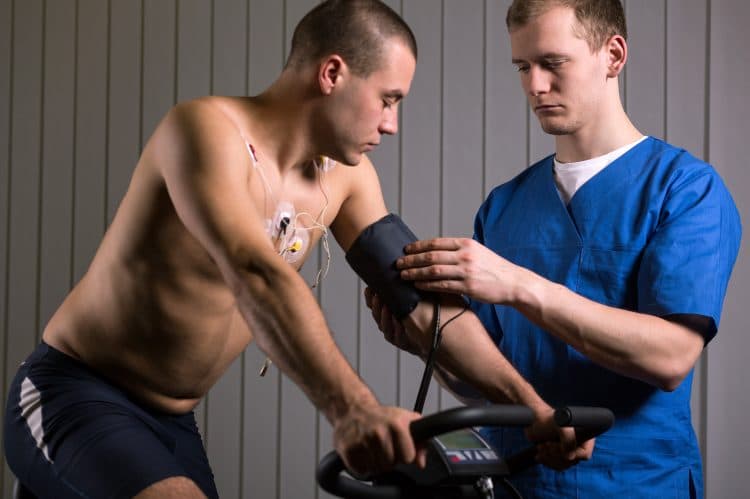
4. Watch your blood pressure
Your body functions better when fit and healthy. Being overweight, sedentary, or eating unhealthily can negatively impact all bodily functions, including testosterone production.
Scientists at the University of Tsukuba in Japan found a link between high blood pressure and low testosterone (4). High blood pressure is common among men.
Diet, stress, age, and body weight can increase blood pressure. Unfortunately, high blood pressure is often asymptomatic, so you might not know you have it. The only way to find out is to get tested.
Check your blood pressure to see if it’s affecting testosterone production. If it’s high, follow your doctor’s advice to reduce it. Lowering blood pressure will increase T-levels and potentially save your life, as high blood pressure is linked to heart disease.
Ways to lower blood pressure include:
- Eat less sodium and salty food
- Eat more potassium-rich foods like bananas, nuts, and seeds
- Eat more calcium-rich foods like low-fat dairy
- Eat more magnesium-rich foods like whole grains and legumes
- Maintain optimal weight
- Reduce caffeine intake
- Quit smoking
- Exercise more
- Drink less alcohol
- Avoid processed foods
- Reduce stress levels
- Drink more water
5. Reduce your intake of “bad” carbs
The media and some diet experts often demonize carbs, suggesting cutting them from your diet to be lean, fit, and healthy.
The problem with this advice is that you need carbs to fuel your workouts.
Muscles use glycogen for energy, which comes from carbs. To train hard and often, you need plenty of carbs.
However, not all carbs are created equal. Some are healthy, while others are not. There’s a strong link between eating too many unhealthy carbs and low testosterone levels (5).
You don’t need to adopt a low-carb diet, especially if you need energy for workouts. Instead, choose healthy carbs and avoid unhealthy ones.
“Good” sources of carbs include:
- Oats
- Rice
- Potatoes
- Pasta
- Whole meal bread
- Fruit
- Vegetables
Carbs to avoid include:
- Takeouts
- Processed meals
- Cakes and candy
- Soda
- Desserts
- Refined grains
- Anything with added sugar
Occasional sweet snacks are fine, but many people consume too many unhealthy carbs. This can lead to weight gain, low testosterone levels, and an increased risk of type two diabetes.
6. Eat more cruciferous vegetables
Vegetables are healthy, containing essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber. Not eating enough vegetables can lead to ill health.

Cruciferous vegetables have been linked to testosterone production and estrogen suppression.
Hormones are often produced in pairs. For example, insulin lowers blood glucose, while glucagon raises it. Adrenalin increases metabolism, while cortisol decreases it.
Testosterone’s opposite hormone is estrogen. Increased estrogen levels reduce testosterone levels. Environmental and dietary toxins and certain foods can increase estrogen levels, lowering T-levels.
Cruciferous vegetables like cauliflower, cabbage, and broccoli combat estrogen, helping boost testosterone.
Cruciferous vegetables can act as aromatase inhibitors, preventing estrogen production (6). Lower estrogen levels mean higher testosterone levels by default.
12 of the best estrogen-fighting (and therefore testosterone-boosting) cruciferous vegetables include:
- Arugula
- Bok choy
- Broccoli
- Brussels sprouts
- Cabbage
- Cauliflower
- Collard greens
- Kale
- Mustard greens
- Rutabaga
- Swiss chard
- Watercress
7. Try ZMA
ZMA, short for Zinc Magnesium Aspartate, is a popular supplement that contains three ingredients linked to increased testosterone production (7). ZMA is also a natural sleep aid, vital for maximizing your testosterone levels.

The three ingredients in ZMA are:
- Zinc: This trace mineral is necessary for the production of more than 300 enzymes involved in metabolism, digestion, immunity, and many other areas of your health, including testosterone production.
- Magnesium: This mineral supports hundreds of chemical reactions in your body, including energy creation and muscle and nerve function.
- Vitamin B6: This water-soluble vitamin is needed for processes such as making neurotransmitters and nutrient metabolism.
While proportions vary slightly from manufacturer to manufacturer, most ZMA products contain:
- Zinc monomethionine: 30 mg — 270% of the Reference Daily Intake (RDI)
- Magnesium aspartate: 450 mg — 110% of the RDI
- Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine): 10 mg — 650% of the RDI
Take one dose of ZMA before going to bed to boost nighttime testosterone production. You may also experience deeper sleep and very vivid dreams with ZMA. This is normal and a common side effect of this supplement.
8. Get some sun (or take Vitamin D)
Have you noticed feeling hornier on a sunny vacation? Part of the reason is less stress, but another factor is increased Vitamin D production. Sun exposure triggers your skin to produce more vitamin D, which plays a crucial role in testosterone synthesis (8).
Depending on your lifestyle and location, you might not get enough sunlight. Spending days in an artificially lit office or living in a cold, dark place limits sun exposure.
Some people avoid direct sunlight due to skin cancer and aging concerns.
20-30 minutes of sun exposure is enough for optimal vitamin D production. If you avoid the sun or stay indoors, get your daily vitamin D from a supplement. A dose of 2-3,000 IU of vitamin D3 per day should suffice.
9. Workout Smarter with High-Intensity Compound Movements
Not only does the intensity of your workouts relate to testosterone levels, but the duration and type of exercises are also crucial. You might think that more is better when it comes to exercise. However, that certainly isn’t the case. Workouts which are unnecessarily long and include excessive rest periods can lead to increased cortisol levels, which subsequently decrease testosterone levels.
It is therefore recommended to keep your workouts between 30-60 minutes and minimize rest periods to maximize your testosterone response. Cutting down rest periods from 3 minutes to 1 minute can significantly enhance this effect.
High-intensity free weight workouts, in particular, have been proven to stimulate an increase in testosterone secretion. Focus on multi-joint compound movements, such as squats, deadlifts, and bench presses. These exercises stimulate multiple muscle groups simultaneously, leading to greater testosterone production compared to machine-based exercises which involve less stabilizer activity and stimulate fewer muscles at once.
10. Try a testosterone booster
Testosterone boosters are supplements with T-boosting ingredients. These mostly natural ingredients are concentrated to produce optimal results.
Common T-boosting ingredients include:
- Ashwagandha
- Boron
- D-aspartic acid
- DHEA (Dehydroepiandrosterone)
- DIM (Diindolylmethane)
- Fenugreek
- Forskolin
- Ginger
- Horny goat weed
- Maca
- Magnesium
- Saw palmetto
- Tongkat Ali
- Tribulus Terrestris
- Vitamin D
- Zinc
Combined with a healthy diet, getting enough sleep, and hitting the weights, a testosterone booster may help increase your T-levels. However, note that T-boosters have a mild to moderate impact and are not as potent as steroids.
Wrapping Up
Whatever your training goal, testosterone (or lack of it) significantly impacts your progress. Some men naturally have higher levels, but all men eventually experience declining T-levels. This is an unavoidable part of aging, leading to increased body fat and weaker muscles.
While HRT is an option, there are many natural ways to maintain or boost testosterone levels. Dietary and lifestyle changes can significantly impact testosterone production.
However, these natural methods cannot compare to doctor-prescribed hormone replacement treatments or illicit steroids. Still, they are much safer and a good option for those who prefer a natural approach.
References:
- Hämäläinen E, Adlercreutz H, Puska P, Pietinen P. Diet and serum sex hormones in healthy men. J Steroid Biochem. 1984 Jan;20(1):459-64. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(84)90254-1. PMID: 6538617.
- Shaner, Aaron A.1; Vingren, Jakob L.1,2; Hatfield, Disa L.3; Budnar, Ronald G. Jr1; Duplanty, Anthony A.1,2; Hill, David W.1. The Acute Hormonal Response to Free Weight and Machine Weight Resistance Exercise. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research 28(4):p 1032-1040, April 2014. | DOI: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000000317
- Marcus K. Taylor, Genieleah A. Padilla, Lisa M. Hernández, Anabolic hormone profiles in elite military men: Robust associations with age, stress, and fatigue, Steroids, Volume 124, 2017, Pages 18-22, ISSN 0039-128X,
- Fogari R, Zoppi A, Preti P, Rinaldi A, Marasi G, Vanasia A, Mugellini A. Sexual activity and plasma testosterone levels in hypertensive males. Am J Hypertens. 2002 Mar;15(3):217-21. doi: 10.1016/s0895-7061(01)02280-4. PMID: 11939610.
- Morelli A, Comeglio P, Sarchielli E, Cellai I, Vignozzi L, Vannelli GB, Maggi M. Negative effects of high glucose exposure in human gonadotropin-releasing hormone neurons. Int J Endocrinol. 2013;2013:684659. doi: 10.1155/2013/684659. Epub 2013 Dec 31. PMID: 24489542; PMCID: PMC3893744.
- Balunas MJ, Su B, Brueggemeier RW, Kinghorn AD. Natural products as aromatase inhibitors. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2008 Aug;8(6):646-82. PMID: 18690828; PMCID: PMC3074486.
- Journal of The American Society of Exercise Physiologists: Effects of a Novel Zinc-Magnesium Formulation on Hormones and Strength.
- Pilz S, Frisch S, Koertke H, Kuhn J, Dreier J, Obermayer-Pietsch B, Wehr E, Zittermann A. Effect of vitamin D supplementation on testosterone levels in men. Horm Metab Res. 2011 Mar;43(3):223-5. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1269854. Epub 2010 Dec 10. PMID: 21154195.
Tip: If you're signed in to Google, tap Follow.