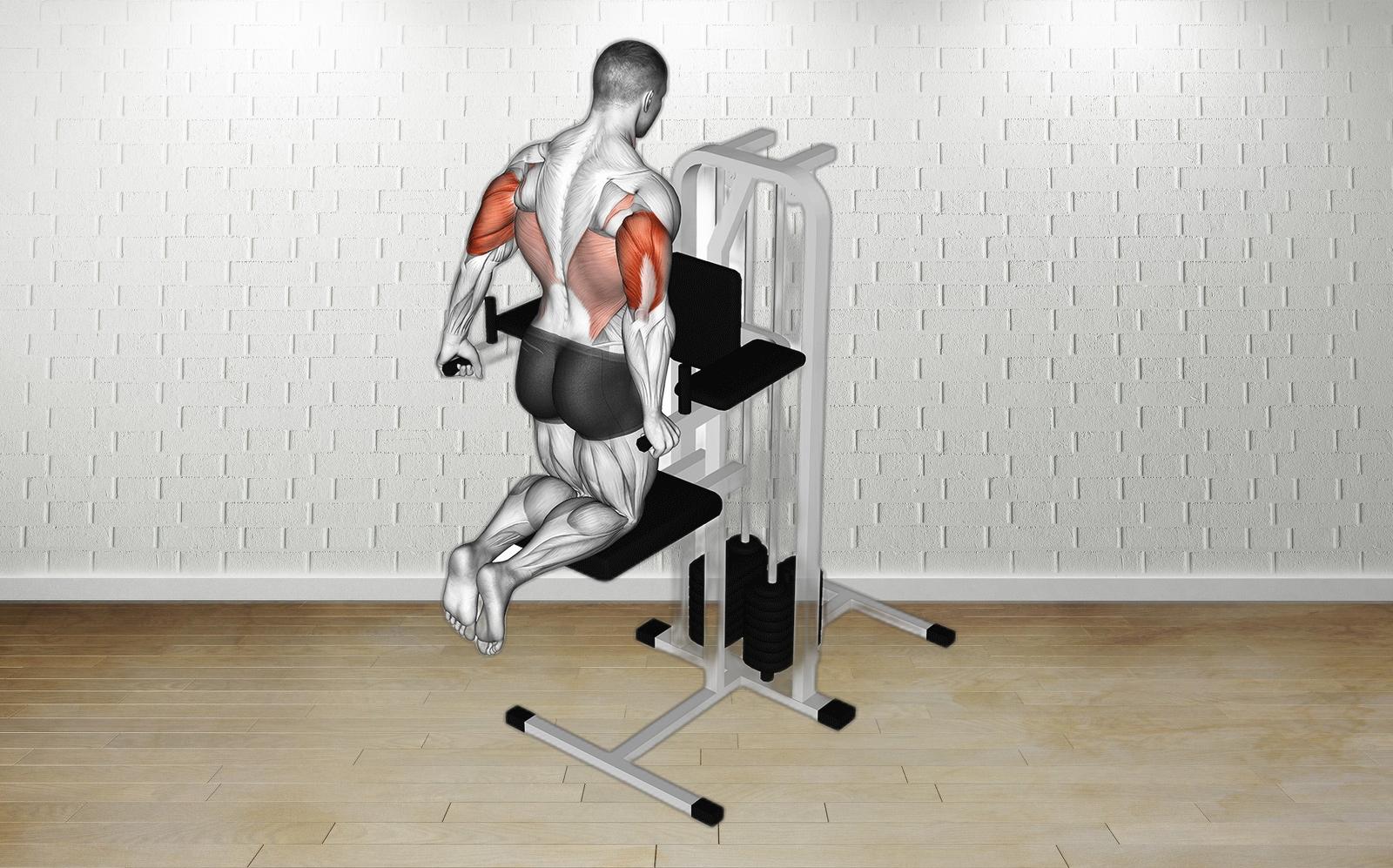
Assisted Kneeling Dips are an effective exercise for enhancing triceps strength, improving shoulder stability, and defining the upper body. This exercise specifically targets the triceps brachii, promoting muscle growth and endurance while also engaging the shoulders and chest, resulting in a comprehensive upper body workout. Incorporating this movement can significantly develop foundational strength essential for various daily activities and sports.
To achieve optimal results, it’s recommended to perform Assisted Kneeling Dips 2-3 times per week, allowing adequate recovery. Maintaining proper form is crucial; common mistakes, such as dipping too low or flaring elbows, can lead to injury or reduced effectiveness. Keep your core engaged and elbows tucked close throughout the motion for safety and better triceps engagement.
No special equipment is necessary beyond a standard leverage machine, which is available in most gyms. Modifications, such as reducing the range of motion or using resistance bands, can make the exercise more accessible for individuals with varying strength levels. This versatile exercise can also be performed at home using a bench or sturdy chair, making it easy to incorporate into any fitness regimen focused on building a stronger, more defined upper body.
How to Do a Assisted Kneeling Dips
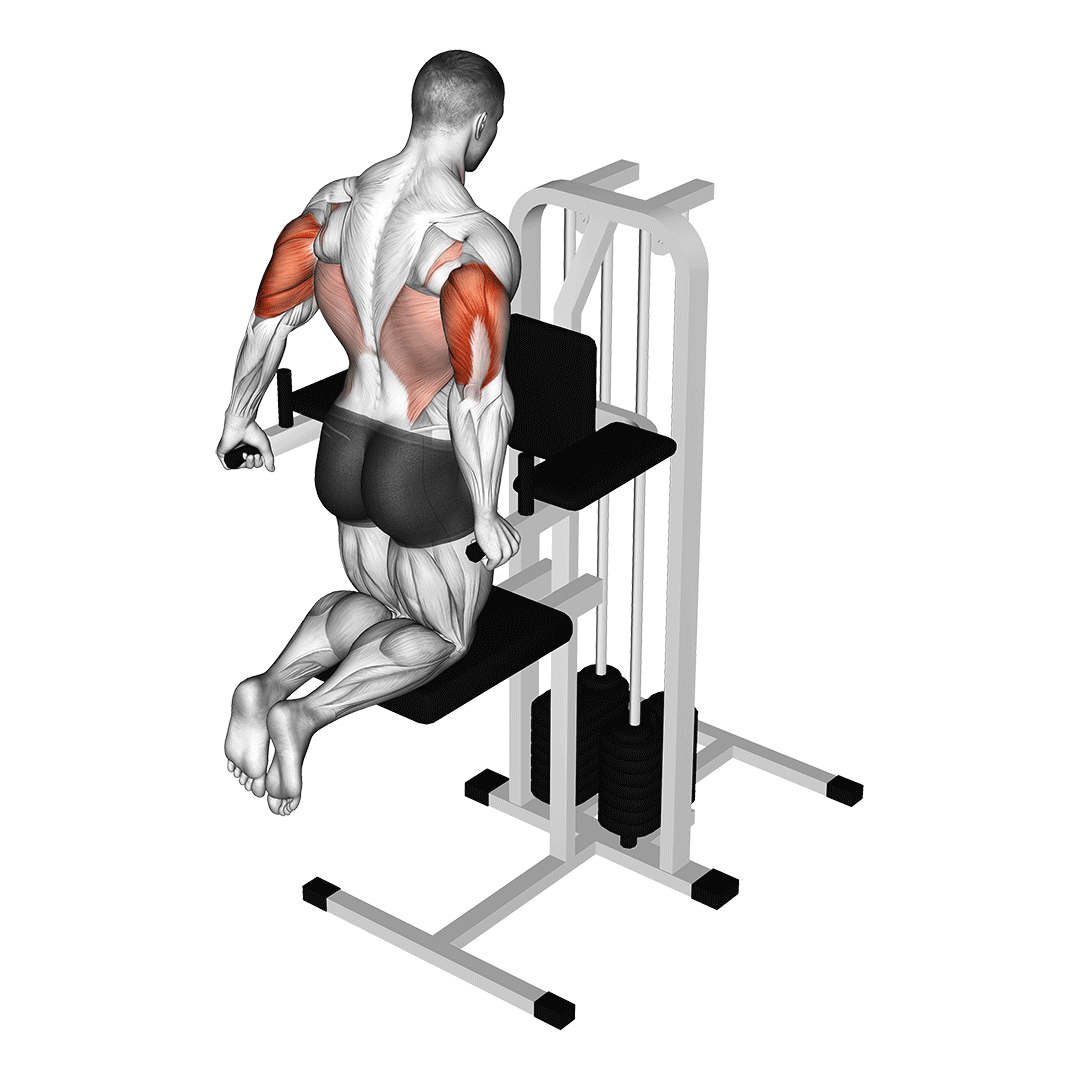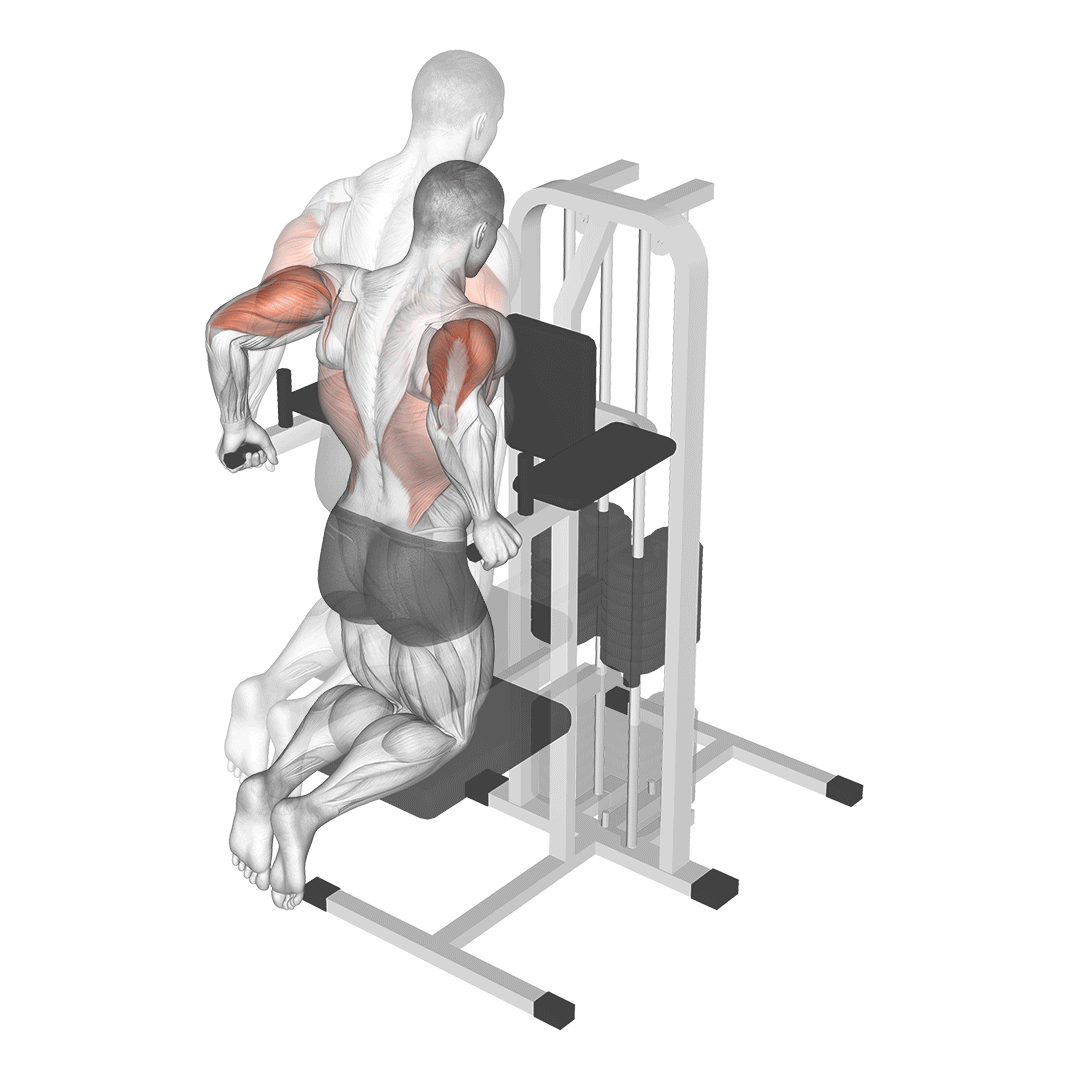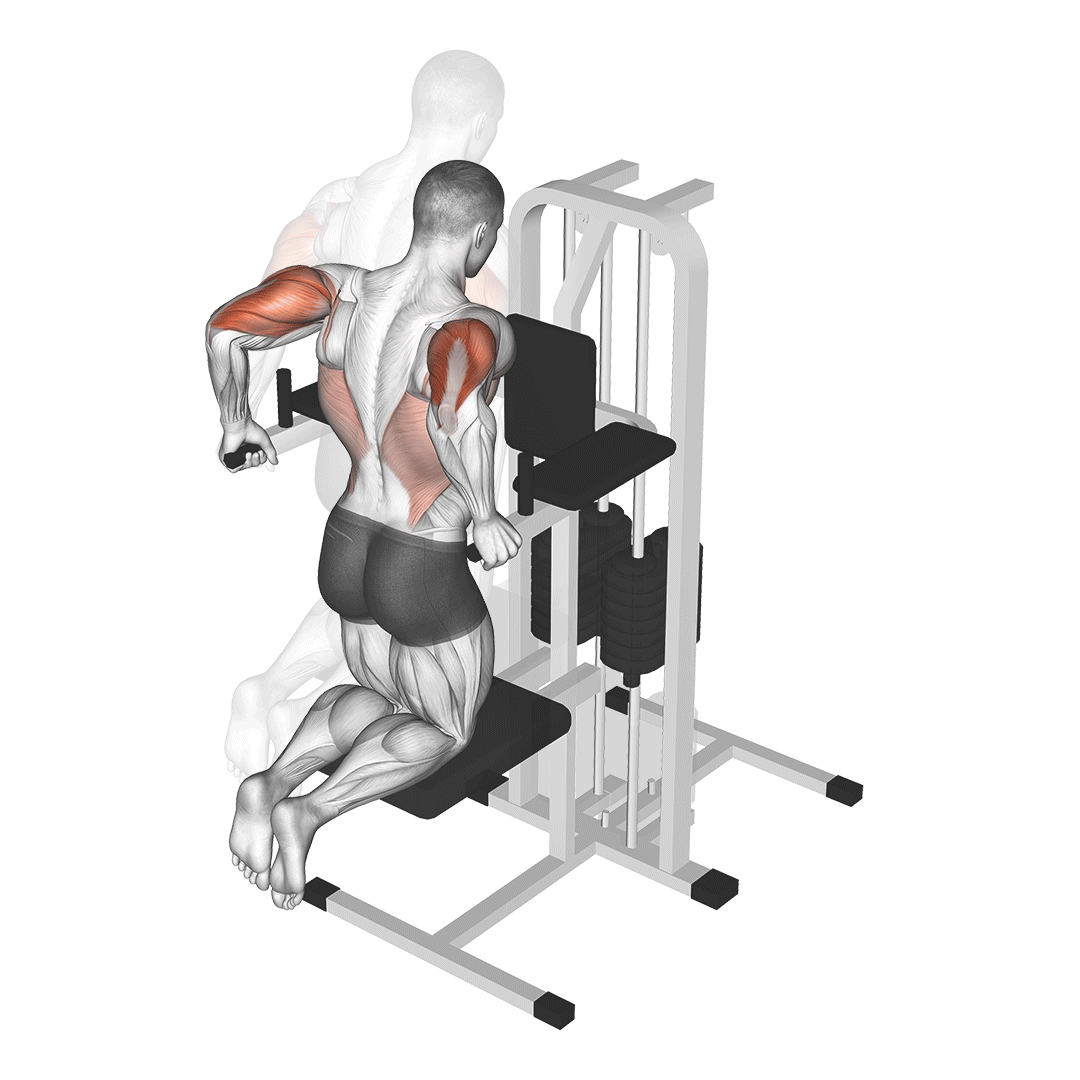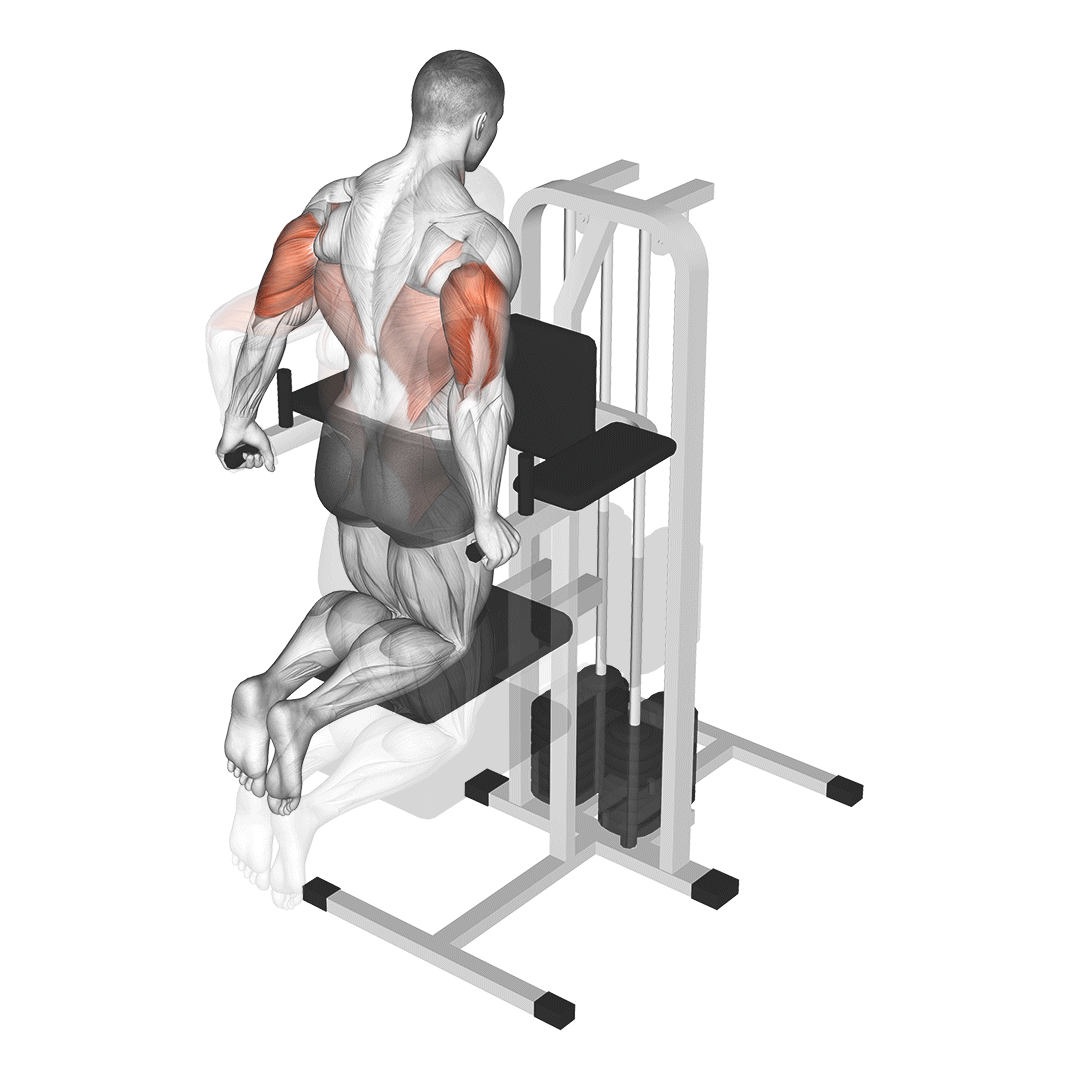
Begin by kneeling on the floor, facing the leverage machine. Adjust the machine’s arm so that it is at shoulder height and grip the handles with your palms facing down.
- Engage your core and maintain a straight posture from head to knees.
- Slowly lower your body by bending your elbows, allowing your upper arms to drop toward the floor.
- Continue lowering until your elbows are at approximately 90 degrees or your comfort level.
- Push through your palms to return to the starting position, fully extending your arms.
Inhale as you lower your body and exhale as you push back up to the starting position.
Common Mistakes in Assisted Triceps Dip (Kneeling)
- Neglecting Core Engagement: Failing to engage the core can lead to poor posture and back strain. To avoid this, actively tighten your abdominal muscles throughout the exercise.
- Dropping Heavily: Allowing the body to drop abruptly can cause excessive strain on the elbows. Instead, lower your body slowly and with control to maintain joint safety.
- Incorrect Elbow Position: Flaring the elbows too far out can lead to shoulder discomfort and reduces the effectiveness of the exercise. Keep elbows tucked close to your body as you lower and push back up.
- Insufficient Range of Motion: Stopping short of a full dip may hinder triceps development. Aim to lower to at least a 90-degree angle at the elbows for optimal engagement.
- Inconsistent Breathing: Holding your breath can increase tension and reduce performance. Remember to inhale as you lower and exhale as you push up to maintain a steady rhythm.
Benefits
- Enhanced Triceps Strength: Assisted kneeling dips effectively target the triceps, promoting muscle growth and strength in this critical upper body region.
- Improved Stability: By engaging the core and maintaining a controlled posture, this exercise helps build stability, which is essential for overall upper body strength.
- Injury Prevention: The assisted nature of the exercise allows beginners to practice proper form, reducing the risk of injury often associated with free weight exercises.
- Joint Safety: Kneeling reduces strain on the shoulder joints while still delivering a robust triceps workout, making it suitable for individuals with previous shoulder issues.
- Scalable Difficulty: The adjustable assistance allows users to tailor the challenge to their personal fitness levels, making it accessible for both beginners and advanced athletes.
Exercise Variations
Alternative Exercises
Safety Precautions
When performing assisted triceps dips, it’s crucial to ensure proper body alignment to avoid unnecessary strain. Begin by establishing a sturdy base with your knees and core engaged. Always keep your shoulders relaxed and away from your ears, preventing excessive shoulder elevation. This alignment minimizes the risk of injury and enhances your ability to effectively target the triceps.
Moreover, pay attention to the equipment settings before each session. Ensure that the machine’s arm is adjusted at the correct height for your comfort and build. Check that all components of the machine are secure and functioning properly to avoid accidents while exercising. It’s advisable to start with a lighter assist level, gradually increasing as your strength improves, allowing your body to adapt without overexertion.
Finally, listen to your body during the exercise. If you experience any sharp pain or discomfort in your shoulders, elbows, or wrists, immediately stop the movement. Adjust the depth of your dip to match your current strength level by limiting how far you lower your body. Consulting a fitness professional when trying the exercise for the first time can also provide guidance and validate your form.
Interested in measuring your progress? Check out our strength standards for Dips.
Tip: If you're signed in to Google, tap Follow.