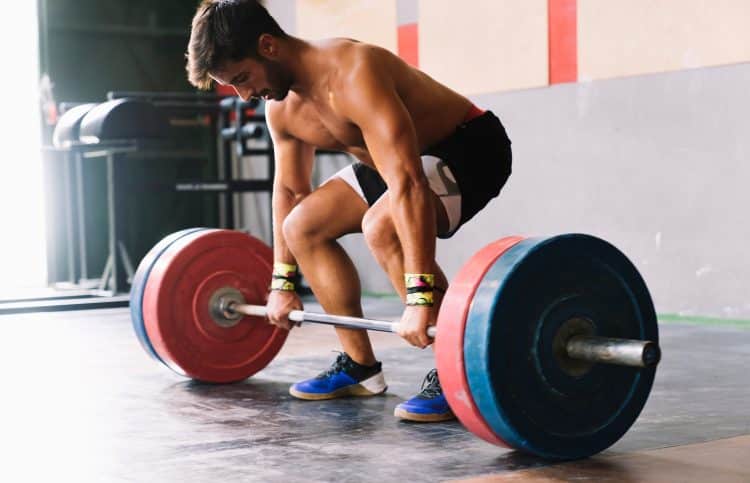
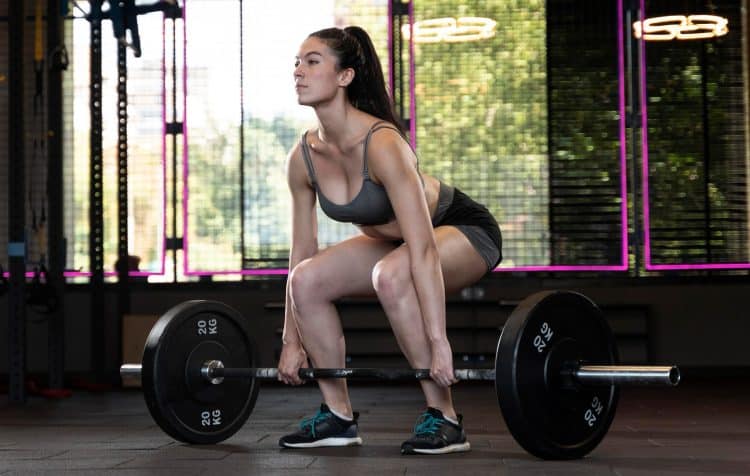
For the average person weighing 175 pounds, you can burn approximately 500 calories in an hour of deadlifting. That number can jump to 625 calories for ‘heavy’ deadlifts.
Deadlifts are not just for strength and muscle growth; they’re a significant calorie burner. Your weight, the intensity, and workout duration all play a role in how many calories you’ll burn. Ready to find out your number? Use the calculator below to estimate your calorie burn from deadlifts and learn how to maximize your workout benefits.
Calories Burned Deadlift Calculator
Calories Burned with Exercises (Weight: 175lbs)
| Exercise | MET | 15m | 30m | 45m | 60m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abs Exercises | 7.0 | 150 | 300 | 450 | 600 |
| Burpees | 8.0 | 171 | 343 | 514 | 686 |
| Jumping Rope | 8.8 | 189 | 377 | 566 | 754 |
| Squats | 5.5 | 118 | 236 | 354 | 472 |
| Jumping Jacks | 7.7 | 165 | 330 | 495 | 660 |
| Sit-Ups | 8.0 | 171 | 343 | 514 | 686 |
| Lunges | 4.0 | 86 | 171 | 257 | 343 |
| Kettlebells | 8.0 | 171 | 343 | 514 | 686 |
| Push-Ups | 3.8 | 81 | 163 | 244 | 326 |
| Rowing | 4.8 | 103 | 206 | 309 | 411 |
| Bridges | 3.0 | 64 | 129 | 193 | 257 |
| Deadlifting | 6.0 | 129 | 257 | 386 | 514 |
| Calisthenics - Vigorous | 8.0 | 171 | 343 | 514 | 686 |
How the Calculator Works
The calculator uses MET values to provide an accurate estimate of how many calories you’ll burn while doing bridges and other exercises. The higher the MET value, the more calories you can expect to burn during bridges.
Understanding the Metabolic Equivalent of Task (MET)
To calculate the number of calories burned during deadlifting, it is essential to understand the concept of the Metabolic Equivalent of Task (MET). MET is a measure of the energy expenditure during physical activity. It represents the ratio of the rate of energy expended during an activity to the rate of energy expended at rest. The MET value of an activity determines the number of calories burned per unit of time and body weight.
According to the Compendium of Physical Activities, deadlifting falls under the category of conditioning exercises and has a MET value of 6.0. This means that deadlifting consumes approximately six times the amount of energy expended at rest. Understanding the MET value of deadlifting allows us to calculate the calories burned during a deadlift workout accurately.
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating Calories Burned with Deadlifts
Calculating the calories burned during a deadlifting session involves three simple steps: determining the MET value, finding your weight in kilograms, and using the METs formula.
Step 1: Determine the MET Value of Deadlifting
As mentioned earlier, deadlifting has a MET value of 6.0, while heavy deadlifting has a value of 7.5 according to the Compendium of Physical Activities. These values indicate the intensity of the exercise and serve as reference points for estimating calorie burn.
Step 2: Find Your Weight in Kilograms
To calculate the calories burned, you need to know your weight in kilograms. To convert your weight from pounds to kilograms, divide your weight in pounds by 2.2. For example, if you weigh 175 pounds, your weight in kilograms would be approximately 79.37 kilograms.
Step 3: Use the METs Formula to Calculate Calories Burned
The METs formula for calculating calories burned during deadlifting is as follows:
Calories burned (per minute) = (body weight in kg x MET x 3.5) ÷ 200
If you engage in an hour-long deadlifting session, you can simply multiply the MET value (6.0) by your weight in kilograms and the duration of the workout. For example, if you weigh 82 kilograms and perform deadlifts for one hour, the calculation would be:
- Calories burned (per minute) = (79.37 x 6 x 3.5 ) ÷ 200
- Calories burned (per hour) = 500 calories (8.33 x 60)
If your workout is shorter, such as 30 minutes, you can adjust the formula accordingly. For a 30-minute deadlifting session, the calculation would be:
- Calories burned (30 minutes) = 250 calories (8.33 x 30)
By following these steps, you can estimate the number of calories burned during your deadlift workouts.
Factors Affecting Calorie Burn During Deadlifts
While the MET value provides a general estimate of calorie burn, several factors can influence the actual number of calories burned during deadlifting.
Body Weight
Body weight plays a significant role in determining calorie burn during any physical activity. The more you weigh, the more calories you are likely to burn. Heavier individuals require more energy to perform the same exercise compared to lighter individuals.
Exercise Intensity
The intensity of your deadlift workout also affects calorie burn. Heavier weights and higher intensity workouts generally result in more calories burned. Increasing the weight or intensity of your deadlifts can help maximize calorie burn.
Duration of the Workout
The duration of your deadlift workout directly impacts the number of calories burned. Longer workouts result in a higher calorie burn, while shorter workouts may burn fewer calories. It is important to find a balance between duration and intensity to achieve optimal calorie burn.
Rest Periods
Rest periods between sets can affect the overall calorie burn during a deadlift workout. Shorter rest periods increase the intensity of the workout and can lead to more calories burned. However, it is essential to listen to your body and allow sufficient rest to maintain proper form and prevent injury.
Muscle Mass
Having more muscle mass can increase your basal metabolic rate (BMR), which is the number of calories your body burns at rest. Deadlifting, as a compound exercise that engages multiple muscle groups, can help build muscle mass over time. Increased muscle mass can lead to a higher calorie burn even outside of your workout sessions.
Benefits of Deadlifting for Weight Loss
Deadlifting offers several benefits for weight loss in addition to calorie burn. Understanding these benefits can help you make the most of your deadlifting workouts.
High Metabolic Response
Deadlifts have a high metabolic response, meaning they continue to burn calories even after the workout is complete. This phenomenon, known as Excess Post-Exercise Oxygen Consumption (EPOC), occurs as the body works to restore energy stores, repair damaged tissues, and return to a resting state. The intense nature of deadlifting can trigger a prolonged EPOC, resulting in additional calorie burn for hours after your workout.
Muscle Growth
Deadlifting is a compound exercise that engages multiple muscle groups simultaneously. By targeting major muscle groups such as the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and core, deadlifts can stimulate muscle growth. Building muscle can increase your overall calorie burn by raising your BMR, making it easier to achieve and maintain weight loss goals. Read more muscles worked doing deadlifts here.
Full-Body Workout
One of the key advantages of deadlifting is that it provides a full-body workout. Engaging multiple muscle groups at once not only burns calories but also helps improve overall strength and body composition. Deadlifting can help tone and sculpt various muscle groups, leading to a more balanced and aesthetically pleasing physique.
Ways to Maximize Calorie Burn During Deadlift Workouts
If you want to maximize calorie burn during your deadlift workouts, there are several strategies you can incorporate:
Increase Weight or Intensity
To increase calorie burn, gradually increase the weight or intensity of your deadlifts. You can add more weight to the barbell or perform variations such as Romanian deadlifts or deficit deadlifts. Increasing the challenge of your workouts can lead to greater calorie expenditure.
Shorten Rest Periods
Reducing the rest periods between sets can increase the intensity of your deadlift workout. Shorter rest periods keep your heart rate elevated, resulting in a higher calorie burn. However, be mindful of your body’s limits and allow sufficient rest to maintain proper form and prevent overexertion.
Incorporate Circuit Training
Circuit training involves performing a series of exercises with minimal rest in between. By incorporating deadlifts into a circuit training routine, you can increase the overall calorie burn. Alternating between deadlifts and other exercises keeps your body engaged and maximizes energy expenditure.
Combine Deadlifts with Cardiovascular Exercises
To enhance calorie burn, consider combining your deadlift workouts with cardiovascular exercises such as running, cycling, or rowing. Performing cardio exercises before or after your deadlifts can create a synergistic effect, leading to greater calorie expenditure.
Prioritize Proper Form
Maintaining proper form during deadlifts is essential for both safety and optimal calorie burn. Proper form ensures that you are engaging the correct muscles and maximizing the effectiveness of the exercise. If you are unsure about proper form, consult a qualified trainer or coach for guidance.
Example of a Deadlift Workout Burning 500 Calories
Engaging in deadlifts can be a potent calorie-burning activity. For instance, deadlifting for an hour could result in burning upwards of 500 calories, although this value can fluctuate depending on one’s weight (as outlined in our calculator above).
But beyond the caloric burn, it’s pivotal to remember the muscle-building and strength-gaining advantages of this fundamental compound exercise.
Those acquainted with powerlifting can testify to the sheer intensity of a thorough deadlift workout. Let’s delve into a focused deadlift routine:
Deadlift Program:
- Kickstart with 145 lbs x 5 reps, gently easing into the exercise.
- Progress to 175 x 3 for a slightly intensified warm-up.
- Delve into the main workout phase with 195 x 8 x 2 sets.
- Grant yourself a 3 to 5-minute recovery interval between these sets. By the conclusion of this sequence, your legs and lower back might be humming with fatigue.
Remember, these routines serve as guidelines. Modify weights according to your individual strength and objectives. The primary emphasis should remain on executing deadlifts with precision and correct form, regardless of the weight being light or heavy.
Explore more deadlifting programs and workouts in our other articles you might find interesting:
- Beginner Deadlift Program
- 3 Deadlift Workout Programs
- 9 Weeks to a Bigger Deadlift Program
- Developing Your Deadlift With The Ed Coan Routine
Conclusion
Deadlifting is an effective exercise for burning calories and achieving weight loss goals. By understanding the MET value of deadlifting, calculating calories burned, and implementing strategies to maximize calorie burn, you can make the most of your deadlift workouts. Remember to prioritize proper form, gradually increase weight or intensity, and listen to your body’s needs. With consistency and dedication, deadlifting can contribute to significant calorie burn, muscle growth, and overall fitness. So, get ready to lift, burn, and transform your body with the power of deadlifts!
References:
- Jetté, M., Sidney, K., & Blümchen, G. (1990). Metabolic equivalents (METS) in exercise testing, exercise prescription, and evaluation of functional capacity. Clinical cardiology, 13(8), 555–565. https://doi.org/10.1002/clc.4960130809