When it comes to putting on slabs of muscle and cutting away extra body fat, a strategic bodybuilding diet will make all the difference.
But, there are three common body types (We’ll get to that in a few) we must take into account when constructing the perfect diet plan which are ectomorphs (Skinny and lanky), mesomorphs (Naturally muscular), and endomorphs (Carries more body fat).
And each body type requires a different nutritional strategy in order to reach the desired goal, in combination with a good workout plan…
Now, the word diet may sound intimidating but it’s just a word used to describe a way of eating.
So, let’s over the necessary diet rules and guidelines so you can be best prepared to take on a bodybuilding regimen…
What is a Bodybuilding Diet?
Background
When we weight train, we break down muscle tissue, and to rebuild them even bigger than previously, we need adequate protein and carbohydrates. But, to fuel our workouts and have sufficient energy for an intense session, we need sufficient carbs and fats. (1)
Now, a bodybuilding diet is going to be different than any of the popular diets like Dash, Atkins, and the South Beach because a bodybuilder needs to put on size, and these diets are not ideal.
Macronutrient ratios are especially important for putting on size and losing body weight precisely.
Back in the 60s and 70s, bodybuilders were not as meticulous about counting macronutrients like the competitors of today. Drinking lots of milk and eating more fats wasn’t as uncommon for the top bodybuilders like Reg Park, Larry Scott and even the men of Arnold Schwarzenegger’s time.
But the diets were still healthy with lean meats and vegetables; however, drinking a carton of heavy cream to bulk up wasn’t out of the ordinary.
But diet and food options have changed drastically along with supplements. So, modern bodybuilding is a more meticulous process since we have more knowledge of nutrition.
How it works
A bodybuilder is always doing either of three things (Bulking, cutting, or maintaining) but to do so effectively you must know how many calories you burn when at rest (Resting metabolic rate), your total daily energy expenditure (Calories burned per day), and, of course, you need a goal weight. (2, 3)
Bulking up
To put on serious mass you must eat an excess of energy in the form of calories which come from carbs, fat, and protein. This is called bulking, and although you will put on body fat, it’s the only way to gain muscle tissue as quickly as possible.
So, for example, if you need 2500 calories to maintain your weight, you should up that number by 250 to 500 calories in order to gain an extra pound a week.

Cutting
Losing body fat takes a caloric deficit or an increase in cardio, and this is necessary to see the cuts and striations in each muscle. So, a cutting diet is often implemented for around four months on average after a bulk.
To lose fat, you need to know your recommended daily caloric intake and decrease that number by 250 to 500 calories per day. This will ensure a slow weight loss which doesn’t wreak havoc on your health.
Maintaining
Sometimes bodybuilders eat just enough to maintain their current body weight. This is called maintaining and it’s necessary once you hit your desired goal weight.
So, stick with your daily caloric intake if you want to keep your size.
Now, to figure the approximate numbers in order to bulk, cut, or maintain; we can use the handy dandy calculators that we’re so blessed to have access too.
We can just punch in the numbers, which include age and amount of activity per day to get an estimate of required caloric and macronutrient intake.
Macro intake
Protein creates a positive nitrogen balance which is crucial for muscle growth and preventing catabolism (Breaking down or loss of muscle tissue).
But carbs also promote anabolism (Muscle building metabolic process) and it’s the only macronutrient that can burn energy efficiently enough to sustain you through intense physical activity. (4, 5)
And fats are important for energy but they help to regulate metabolism and testosterone; which equals muscle growth! (6)
How to Diet for Bodybuilding?
Determining macros will vary between individuals based on age, weight, goal, and activity levels. But there are widely accepted general guidelines regarding macronutrient ratios.
Now, the general consensus for protein intake is that 1-1.5 grams per pound of bodyweight is sufficient for protein synthesis, and creating a positive nitrogen balance for muscle growth and anabolism. But, this is only if you’re weight training.
However, protein intake can be slightly less and varies based on opinion for the most part. (7, 8)
So, people who do not weight train will need a much more conservative amount of protein.
But protein has also been shown to be beneficial for fat loss and weight control which is another reason to eat good, quality protein. (9)
Here are general macronutrient guidelines for bulking, cutting, and maintaining body weight…
Bulking/Muscle Gain
For bulking, you need more protein and carbs to put on that crucial size since more energy is required to be in an anabolic state.
- Protein: 25-35%
- Carbs: 40-60%
- Fat: 15-25%
Cutting/Fat loss
Fat loss occurs with fewer calories overall but to maintain the muscle mass you need more protein and fewer carbs to be stored as body fat.
- Protein: 40-50%
- Carbs: 10-30%
- Fat: 30-40%
Maintenance
- Protein: 25-35%
- Carbs: 30-50%
- Fat: 25-35%
The Three Body Types (Ectomorph, Mesomorph, Endomorph)
As we mentioned earlier, there are three different common body types which are ectomorph, mesomorph, and endomorph.

Ectomorphs
Ectomorphs are generally skinny with a short torso and longer limbs. These people need carbs to be on the higher to maintain a state of anabolism.
More energy = more muscle growth and weight gain.
Mesomorphs
Mesomorphs are the people who most others are usually envious of because they can put on muscle without much fat by just looking at a set of dumbbells…
Mesomorphs tend to have a solid torso with great genetics and they are very responsive to weight training and bodybuilding nutrition. There isn’t too much to say about a mesomorph regarding diet modification because they’ll be able to grow and easily tweak their macros for optimal results.
But, keeping protein high with moderate carbs and low fat can work very well.
Endomorphs
Endomorphs tend to have a pear shape with bigger bones, and a predisposition to carrying more body fat. They do put on muscle pretty easily too but have a slower metabolism and do better with lower carb and higher fat diet.
Each body type must adjust their macronutrients to fit their metabolisms and goals. But, manipulating these numbers isn’t difficult thanks to the calculators we have access to nowadays.
Best Bodybuilding foods
There are a number of foods which most bodybuilders consume because they contain high-quality nutrients, are healthy for you, and are very effective for building muscle and burning fat.
These foods include:
- Grass-fed meats
- Chicken breast
- Eggs
- Fish (Halibut, salmon, tuna)
- Cottage cheese
- Vegetables (Especially dark, leafy greens like kale and spinach)
- Fruits (Berries, bananas, apples, avocados)
- Nuts/butters (Almonds, walnuts, macadamia nuts)
- Seeds (Pumpkin, chia, flax seeds)
- Oils (Coconut, olive, macadamia, grape seed)
- Jasmine or Basmati rice
- Rice cakes
- Grains (Oats, Quinoa, buckwheat, barley)
- Roots (Sweet potatoes, potatoes, yucca, yams)
- Quality protein shakes (Whey or plant-based)
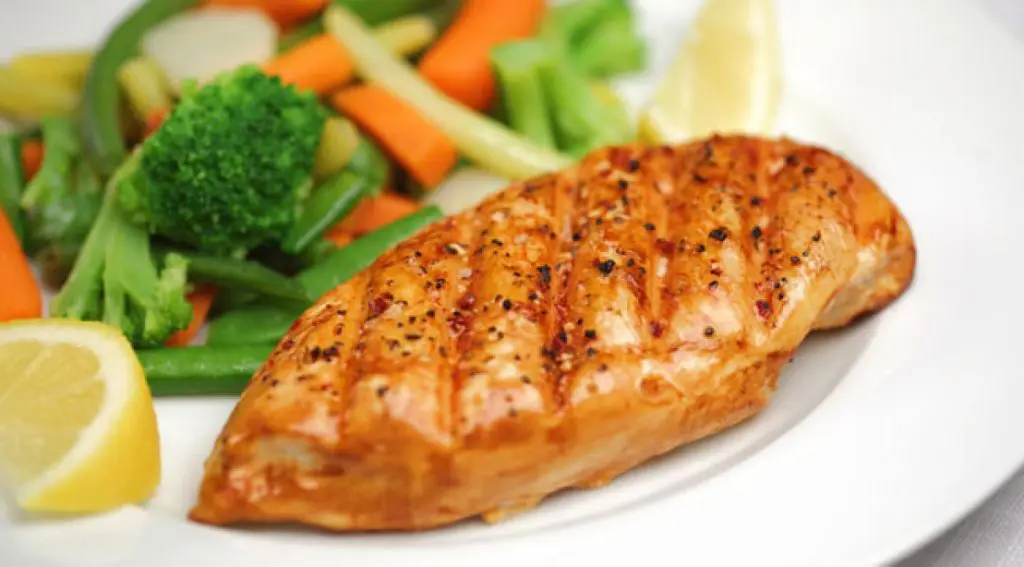

It’s very important to eat high-quality proteins to build muscle mass (Animal meats, dairy, and nuts are effective to name a few).
But complex carbs like roots and rice are great for long-lasting energy and maintaining an anabolic state (Necessary for bulking and muscle gain). (10)
Monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats are the healthy fats which we need for optimal brain function, metabolism regulation, and testosterone production. But, you want to stay away from the trans (Bad) fats by always reading nutrition labels. (11)
Now, Omega-3 fatty acids are essential for a healthy heart and they’re found in certain fish, nuts, and seeds. (12)
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) are found in fish/seafood fats. But, alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) is a plant-based fatty acid found in flaxseeds and oils.
Vitamins and minerals
A good bodybuilding diet should have all of the essential nutrients like vitamin A, C, D, B6, B12. Plus, minerals like potassium, sodium, iron, zinc, selenium, choline, etc. (13)
These vitamins and minerals work together to promote healthy cell production, health, bone, and eye health. Plus, nerve, muscle, and energy function. (14)
Pros and Cons to a Bodybuilding Diet
So, obviously a bodybuilding diet has its benefits like supplying your muscles with essential nutrients to build a muscular physique, and burning body fat to reveal your hard work. But… every blessing has its burden; however, the results are entirely worth it…
Pros of bodybuilding diet
- More muscle size
- Less body fat
- Mostly healthy food intake
Cons bodybuilding diet
- Lots of food prep
- Eating every couple hours of every day
- Can be expensive
- Increased risk of eating disorders
- There’s not much getting past the downsides of this type of dieting diet and bodybuilding is a tough job which is why it’s not a lifestyle that’s suitable for everyone.
There are risks to adopting such extreme eating habits and it’s recommended to consult a physician if you notice anything out of the ordinary.
How it compares
Bodybuilding diet vs ketogenic diet
Bodybuilding diets consist of higher carbs but if you compare it to a ketogenic diet, your body will function much differently since fat is utilized for energy. When you eat high fat, moderate protein, and low carb diet, your body goes into a state of ketosis. (15)
This allows your body to use fat for fuel and protein for pure muscle building.
Now, some bodybuilders do implement a keto diet before a contest, however, this may not be a sustainable way to achieve optimal performance and results.
Bodybuilding diet vs Paleo diet
Paleo involves eating whole, natural foods that were available during the Stone Age. But with all of the processed foods we have nowadays, it’s hard to eat in a similar fashion.
But, some people do Paleo for health reasons as the benefits for staving off chronic illness and health conditions are evident. Eating a clean diet free of processed foods will improve heart health, blood sugar, and type-2 diabetes. (16)
The typical bodybuilding isn’t as strict as the Paleo diet (Especially in the offseason) as it tends to be difficult to get huge by just eating foods from the Earth as the calories aren’t always enough.
So, many bodybuilders will let loose a little and hit up a burger joint when not in contest prep and be a little more lenient with their diets.

Vegan bodybuilding diet
If you’re not familiar with the vegan type diets then no worries.
Vegans avoid any meat, dairy or animal by-products. So, whey protein and eggs are completely off limits too. But the same macro numbers need to be met (If you’re the type to keep track).
Now, it’s very important for vegan bodybuilders to get B12 through supplementation or fortified foods. The vegan lifestyle often gets a bad rap since many people who implement this diet experience illness and deficiencies. (17)
But a lot of people starting a vegan diet don’t do so properly and they neglect the importance of adequate nutrition. And sometimes, it just takes a little getting used too but it’s always a good idea to get blood work done (No different from a meat eater).
Non-vegans get their B12 from meat and eggs, so this isn’t usually an issue for these bodybuilders.
A typical vegan bodybuilding diet includes lots of the following foods…
- Nuts/nut butter/seeds (Almonds, walnuts, peanuts, etc)
- Legumes (Garbanzo beans, Edamame, etc)
- Lentils
- Grains (Quinoa, barley, millet, etc)
- Oils (Coconut, macadamia, olive, etc)
- Vegetables
- Fruit
- Rice
- Plant-based protein powder (Pea protein, brown rice protein, etc).
- Tofu
- Tempeh
- Potatoes
- Soy
Bodybuilding diet for women
Women can benefit from more protein and fats rather than having to consume such a high number of carbs when bulking.
Carbs should be on the lower end because women tend to carry more body fat on average when compared to men and any excess carbs can be stored as fat. And since women have less testosterone than men it’s best to not over bulk because less testosterone means slower fat burning potential. (18)
But, women should train just as hard as men to build lean muscle mass, and diet should only be tweaked slightly with carbs on the lower end, fat on the higher end, and protein should be around 1 gram per pound of bodyweight each day.
Bodybuilding diet on a budget
You can still look incredible and get the job done on a budget.
There are several ways to go about getting food for cheap and all you need is a little strategy to do this effectively. Buying food in bulk is a great way to spend less money on food and it helps to have access to wholesale clubs with many options.
Another way to bulk on the cheap is to choose only nutrient dense bodybuilding foods without too much variety.
Some great cheap foods include:
- Tuna
- Chicken breast
- Spinach
- Mixed vegetables
- Rice cakes
- Nut butter
- Rice
- Avocadoes
- Sweet potatoes
- Potatoes
- Bananas
- Protein powders (Substitute for a few meals)
So, combining a few of each food listed for each meal is a great budget way to save and still get results. But, of course, these are only a few of many options as each individual should experiment for different ways to eat on the cheap.
What to Eat On a Low Carb Diet?
Low carb diets don’t have to be complicated. You just have to be careful to check the food labels and fit the carb contents into your macro requirements. But, when doing low carb make sure to keep protein intake at moderate amounts (One gram per pound bodyweight) and fat slightly higher to allow for ketosis.
Now, some people just feel better overall and experience a more desirable body composition by consuming lower carbs. But, this is purely based on each individual’s genetics and health.
Here are some great low carb foods…
Low carb foods:
- Meat
- Eggs
- Legumes
- Green leafy vegetables
- Oils (Coconut, Macadamia, Olive, etc)
- Berries
- Rice cakes
- Protein shakes
- Nuts and seeds

Foods to avoid:
- Pasta
- Bread
- High sugar fruits (Mangoes, grapes, figs, bananas)
- Cereals
- Potatoes
- Rice
- Refined sugar
Simple carbs and too many carbohydrates, in general, may be dangerous for many people who suffer from high blood sugar levels, which can result in diabetes. The body breaks down carbs into sugar and this enters the bloodstream, therefore creating higher insulin resistance. (19)
So, check with a doctor if you feel any strange feelings after consuming higher amounts of carbs because your health is nothing to take lightly.
Meal Timing
It’s best spread your meals out so that you’re eating 4-6 times per day to maintain healthy blood sugar levels and provide a constant supply of nutrients to the muscles. (20)
Pre-workout
Eating complex carbs and protein before a workout is a good idea because it will maximize glycogen stores (Sustained energy), and help to preserve muscle mass. But eating lots of fat is not recommended as it slows digestion, therefore preventing you from having optimal training sessions. (21)
But studies also show amino acid consumption before a workout to beneficial for promoting protein synthesis. So, supplementing with EAA’s is a good idea. (21)
The best foods for pre-workout will give you sufficient energy stores to sustain you, and these include oatmeal, rice, sweet potatoes, chicken breast, protein shakes, etc.
Post workout
After a workout our glycogen stores are low and our muscle tissue has been broken down. But there’s a certain window of time we can maximize post-workout nutrition, called the “anabolic window”.
This anabolic window is around 3-5 hours (And maybe slightly longer) after a workout and you can maximally replenish your lost nutrients in this time frame. But, if you do have a protein shake go with fast-digesting whey. (21, 22)
Carbs should be simple (Bananas, maltodextrin, etc) to replenish lost glycogen quickly. This way you’re body continued to burn carbs and use protein to repair muscle tissue.
Eating before bed
There’s a myth that’s been around for a long time and that is to stop eating before bed as this will cause body fat accumulation. Well, your body needs slow digesting foods like oatmeal, cottage cheese, etc to build muscle throughout the night.
Or, you can opt for milk or a slow-digesting casein protein supplement. (23)
We fast when we sleep but we could be building muscle instead (We prefer the latter option). And this doesn’t mean you have to load up on bad carbs and fried foods.
Bodybuilding Diet Tips
- Experiment with different macro ratios if you’re not getting the desired results.
- Aim to gain no more than one pound per week to bulk and lose no more than 1-2 pounds per week for fat loss.
- Consume protein and amino acids before a workout for optimal protein synthesis.
- Have protein and .5 grams/per pound of bodyweight of simple carbs after a workout to maximize protein synthesis, and replenish glycogen.
- Limit processed (junk) foods as much as possible for optimal health and quality gains.
- Always read nutrition labels to make sure you’re not eating unhealthy amounts of processed ingredients like refined sugars, trans fats, white flours, palm oil, artificial sweeteners, etc.
- Get blood work done once in a while to ensure you’re not deficient in any vitamins and minerals.
- Use supplements to fill in what your diet cannot.
- Drink lots of water!
- Train hard to get the benefits of a strict bodybuilding diet!
Final Thoughts
An effective bodybuilding diet will make all the difference when it comes to making gains. In fact, many believe diet is even more important than training (They’re likely equal).
But, whether or not this is true, choosing the right foods to get the job done is imperative for muscle growth and effective fat loss.
So, this information on bodybuilding diets for beginners should give you enough information to start your bodybuilding journey and be well equipped to achieve your best physique yet.
But, remember, there’s no one size fits all formula as every bodybuilder is different and therefore will require a different strategy. Macros will vary as well as the type of foods consumed. So, be creative and don’t be afraid to experiment in order to find your ideal bodybuilding diet.
References
- How Do Muscles Grow? by Young sub Kwon, M.S. and Len Kravitz, Ph.D. unm.edu
- Resting Metabolic Rate: Basal Metabolic Rate Calculation from ACE. ACE Fitness.
- Controversies in Metabolism by Paige Kinucan and Len Kravitz, Ph.D. unm.edu
- Chemistry for Biologists. RSB.
- Energy and Metabolism. auburn.edu
- Helms, Eric R.; Aragon, Alan A.; Fitschen, Peter J. (2014-05-12). Evidence-based recommendations for natural bodybuilding contest preparation: nutrition and supplementation. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition.
- Nelse, Miriam E.; PhD. Will Eating More Protein Help Your Body Gain Muscle Faster?. WebMD.
- Phillips, Stuart M.; Van Loon, Luc J. C. (2011). Dietary protein for athletes: from requirements to optimum adaptation. Journal of Sports Sciences. 29 Suppl 1: S29–38.
- Pesta, Dominik H; Samuel, Varman T (2014-11-19). A high-protein diet for reducing body fat: mechanisms and possible caveats. Nutrition & Metabolism.
- The Carbohydrate Advantage. Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine.
- Publishing, Harvard Health. The truth about fats: the good, the bad, and the in-between. Harvard Health.
- Publishing, Harvard Health. The truth about fats: the good, the bad, and the in-between. Harvard Health.
- Vitamins. medlineplus.gov.
- Minerals. medlineplus.gov.
- Ketosis. WebM
- Paleo diet: Eat like a cave man and lose weight?. Mayo Clinic.
- Office of Dietary Supplements – Vitamin B12. ods.od.nih.gov.
- Blaak, E. (2001-11). Gender differences in fat metabolism. Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition and Metabolic Care. 4 (6): 499–502.
- Boston, 677 Huntington Avenue; Ma 02115 +1495‑1000 (2013-08-05). Carbohydrates and Blood Sugar. The Nutrition Source.
- Helms, Eric R; Aragon, Alan A; Fitschen, Peter J (2014-05-12). Evidence-based recommendations for natural bodybuilding contest preparation: nutrition and supplementation. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition. 11: 20
- Stark, Matthew; Lukaszuk, Judith; Prawitz, Aimee; Salacinski, Amanda (2012-12-14). Protein timing and its effects on muscular hypertrophy and strength in individuals engaged in weight-training. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition. 9: 54.
- Meal Timing: What and When to Eat for Performance and Recovery. www.acefitness.org
- Kinsey, Amber W.; Cappadona, Stacy R.; Panton, Lynn B.; Allman, Brittany R.; Contreras, Robert J.; Hickner, Robert C.; Ormsbee, Michael J. (2016-07-27). The Effect of Casein Protein Prior to Sleep on Fat Metabolism in Obese Men. Nutrients. 8 (8).